Abstract
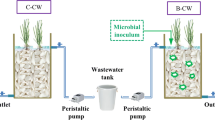
Constructed wetland is typically occupied on the urban area, which emulates the function of natural wetland. It is necessary to supply nutrients that vegetation can absorb for its growth thus sustaining the nature system where represents as vegetation. Phosphorus is one of the essential nutrients for the growth of vegetation, whereas in natural wetlands the amount of phosphorus available for the growth of vegetation is insufficient. In this study, Phosphate Solubilization Microbe (PSM) was used for changing the phosphate’s chemical structure in wetland by its metabolism. Therefore, if PSM is added in wetlands, it is expected that the phosphorus removal mechanism by vegetation can be microbially boosted by the PSM. The PSM activity was measured from the soil sampled in advance, and then the experiment was conducted by culturing PSM in string media, excluding vegetation in the wetland module, and varying the concentration of phosphorus and the numbers of media. It was found that the concentration of the available phosphorus was proportional to the number of media by showing the more than half of conversation ratio orthophosphate into the available phosphorus. This study was conducted for verifying hypothesis that PSM might be help to activate a wetland environment without vegetation and PSM can be very useful to environmentally activating a wetland at the beginning of its formation and establishment in nature or after the winter season when the environment of wetland is relatively dormant.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abd-Alla MH (1994) Use of organic phosphorus by rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viceae phosphatases. Biol Fertil Soils 18:216–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00647669
Adnane B, Karlm L, Mohamed C, Youssef Z, Driss D (2018) Soil Microbial resources for improving fertilizers efficiency in an integrated plant nutrient management system. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.01606
Andrea BV, Lina MRG, Natalia SC, Rafael GJ, Lucas DPC, Raúl APP, Claudia MRH, Lucía ADA, Aura MPR (2020) Phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas sp., and Serratia sp., co-culture for Allium cepa L. growth promotion. Heliyon. 6:10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05218
Ashworth J, Mrazek K (1995) Modified kelwnatest for available phosphorus and potassium in soil. Commun Soil Sci Plan Anal 26:731–739. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103629509369331
Kang C, Gil K (2023) Constructing an internet of things wetland monitoring device and a real-time wetland monitoring system. Membrane Water Treat. https://doi.org/10.12989/mwt.2023.14.4.155
Chitkala DT, Bharathalakshmi M, Kumari MBGS, Naidu NV (2012) Effect of sources and levels of phosphorus with zinc on yield and quality of sugarcane. Sugar Tech 14:195–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-012-0144-2
Colby JM, Michean JV, Jeffrey GW, Daniel DR (2023) Phosphorus fluxes in restored Carolina Bay Wetland following eight years of restoration. Wetlands 43:73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s1317-023-0172-z
Djuuna IAF, Prabawardani S, Massora M (2022) Population distribution of phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms in agricultural soil. Microbes Environ 37. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME21041
Edi-Premono M, Moawad AM, Vlek PLG (1996) Effect of phosphate-solubilizing pseudomonas putida on the growth of maize and its survival in the rhizosphere. Indonesian J Crop Sci 11:13
Eissa MA (2019) Efficiency of P fertigation for drip-irrigated potato grown on calcareous sandy soils. Potato Res 62:97–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11540-018-9399-7
Preveen S, Altaf W, Vohra N, Bautista ML, Harper RG, Wapnir RA (2002) Effect of gestational age on cord blood plasma copper, zinc, magenesium and albumin. Early Hum Dev. 69:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-3782(02)00024-5
Gilroy S, Jones DL (2000) Through form to function: root hair development and nutrient uptake. Trends Plant Sci 5(2):56–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(99)01551-4
Li GX, Wu XQ, Ye JR, Yang HC (2018) Characteristics of organic acid secretion associated with the interaction between Burkholderia multivorans WS-FJ9 and poplar root system. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9619724
Jain R, Saxena J, Sharma V (2010) The evaluation of free and encapsulated aspergillus awamori for phosphate solubilisation in fermentation and soil plant system. Application Soil Ecol 46:90–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2010.06.008
Im J, Gil K (2023) Characteristics of micro-plastics in stormwater sediment basin: case study of J wetland. Membrane Water Treat 14(4):147. https://doi.org/10.12989/mwt.2023.14.4.147
Katznelson H, Peterson EA, Rouatt JW (1962) Phosphate-dissolving microorganisms on seed and in the root zone of plants. Can J Bot 40(9):1181–1186. https://doi.org/10.1139/b62-108
Koopmans GF, Chardon WJ, Dolfing J, Oenema O, van der Meer P, van Riemsdijk WH (2003) Wet chemical and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of phosphorus speciation in a sandy soil receiving long-term fertilizer or animal manure applications. J Environ Qual 32:287–295. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2003.2870
Yue L, Jiao L, Tao M, Xu L, Cao X, Chen F, Wang C, Cheng B, Wang Z (2023) Dynamic of organic acid exudation and rhizobacteria in maize rhizosphere respond to N-CDs. Sci Total Environ 901:25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166500
Pan L, Cai B (2023) Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: advances in their physiology, molecular mechansims and microbial community effects. Microorganisms 11:12. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122904
Machado CTT, Furlani AMC (2004) Root phosphate activity, plant growth and phosphorus accumulation of maize genotypes. Soils Plant Nutr 61:2. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-90162004000200015
Mažylyte˙ R, Kaziuniene J, Orola L, Valkovska V, Lastauskiene E, Gegeckas A (2022) Phosphate solubilizing microorganism Bacillus sp. MVY-004 and its significance for biomineral fertilizers’ development in agrobiotechnology. Biology 11(2):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/Biology11020254
McLaughlin MJ, McBeath TM, Smernik R, Stacey SP, Ajiaboye B, Guppy C (2011) The chemical nature of P accumulation in agricultural soils-implications for fertiliser management and design: an Australian perspective. Plant Soil 349:69–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0907-7
Micheal SC (2001) The Lancaster soil test method A an alternative to the Mehilich 3 soil test method1. Soil Sci 166(7):484–489. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-200107000-00006]
Nautiyal CS (1999) An efficient microbiological growth medium for screening phosphate solubilizing microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Lett 170(1):265–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb13383.x]
OECD (2007) 2007 annual report on sustainable development work in the OECD
Pande A, Pandey P, Mehra S, Singh M, Kaushik S (2017) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their efficiency on the growth of maize. J Genetic Eng Biotechnol 15(2):379–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2017.06.005
Pedro JZT, Daniela OC, Héctor EM, Elizabeth HA, Gilberto AG, Eduardo C (2024) Hydrogeochemical influence on the nitrogen and phosphorus concentration and stocks in Herbaceous Karst wetlands. Wetlands 44(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s1317-023-01764-6
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with the vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 17:362–370
Queensland Government (2013) Environment, land and water. The State of Queensland https://www.qld.gov.au/legal/copyright
Rodriguez H, Fraga R, Gonzalez T, Bashan Y (2006) Genetics of phosphate solubilization and its potential applications for improving plant growth-promoting bacteria. Plant Soil 287:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-006-9056-9
Sheel B, Irena FC, Brian AT, Scott DB, Ankur RD, Ken WK, Scott CN, Gregory BN, Donald OR, Carl T, Kimberly PW, Scott TA, Ariane AO, Anna RA, Dennis B, Kakoli B, David B, Peter B, Matthew JB, Alex TC, William HC, Christopher C, Courtney C, Tonya D, Jamie AD, Megan E, Fennessy MS, Sarah AF, Mathias G, Sabine G, Meghan H, Ellen H, Mohammad MRJ, Olivia FJ, Miriam CJ, Jerrrey JK, Sara K, Kevin DK, Kevin AK, David L, Amanda LL, Shizhou M, Damien TM, Gavin M, Jacob M, Beth AM, Christopher M, Purbasha M, Abhijit M, Courtney M, Amanda MN, Sue N, Jessica LOC, Patty O, Max PB, Charles AS, Changchun S, Camille LS, Jessica T, Rodrigo V, MarkPW, Marcus BW, Zhaouhui AW, Eric JW, Debra AW, Stephanie Y, Xiaoyan Z (2023) Practical guide to measuring wetland carbon pools and fluxes. Wetlands 43(105). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-023-01722-2
Singh AV, Prasad B, Shah S (2011) Influence of phosphate solubilizing bacteria for enhancement of plant growth and seed yield in lentil. J Crop Weed 7(1):1–4
Suleman M, Sumera Y, Rasul M, Yahya M, Atta M, Mirza MS (2018) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria with glucose dehydrogenase gene for phosphorus uptake and beneficial effects on wheat. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204408
United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) (2021) Sixth assesment report. Korea
Vassilev N, Vassileva M, Fenice M, Fedrici F (2001) Immobilized cell technology applied in solubilisation insoluble inorganic(rock) phosphates and P plant acquisition. Bioresour Technol 79:263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00017-7
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2007) Co-inoculation of nitrogen-fixing and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria to promote growth, yield and nutrient uptake in chickpea. Acta Agron Hugarica 55(3):315–323. https://doi.org/10.1556/AAgr.55.2007.3.7
Wang Y, Luo D, Xiong Z, Wang Z, Gao M (2023) Changes in rhizosphere phosphorus fractions and phosphate-mineralizing microbial populations in acid soil as influenced by organic acid exudation. Soil Tillage Res 225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2022.105543
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Program funded by the Seoul National University of Science and Technology (Grant numbers 2023 − 1280). Author Kyungik Gil has received research support from Seoul National University of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The corresponding author Kyungik Gil contributed to the research conception, design and revisions for the final manuscript. The first author Sungryul Kim contributed to experiment for this research and the first draft of manuscript were performed.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Gil, K. Evaluation of Phosphate Solubilization Microbe(PSM) Activity During Initial Operation of Constructed Wetland. Wetlands 44, 40 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-024-01795-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-024-01795-7