Abstract
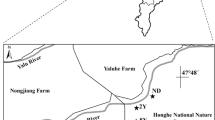
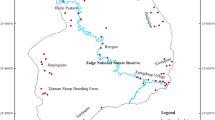
Through restoration, degraded wetlands are thought to recover their carbon storage function over time. However, little is known about the dynamics of soil organic carbon (SOC) and its fractions after restoration of degraded wetlands. In this study, we selected four wetlands, two degraded (one grazed and one graze-released site), one restored for 6 years and one natural site from the Zoigê wetlands on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China to investigate the dynamics of SOC following restoration. The concentrations of SOC, dissolved organic carbon (DOC), light fraction organic carbon (LFOC), and heavy fraction organic carbon (HFOC) in the degraded sites were significantly lower than those in the natural wetland. In contrast, soil δ13C (i.e. 13C/12C ratio) in the degraded sites was significantly higher than that in the natural site. After 8 years of restoration, the restored and the natural wetland sites did not differ significantly in SOC, DOC, LFOC, HFOC or δ13C. Therefore, restored wetlands regained some of their role in carbon storage over time. SOC turnover was slower in the natural wetland than in the degraded and restored sites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badiou P, McDougal R, Pennock D, Clark B (2011) Greenhouse gas emissions and carbon sequestration potential in restored wetlands of the Canadian prairie pothole region. Wetlands Ecology and Management 19:237–256
Chai X, Lang HQ, Jin SR, Zu WC, Ma XH, Zhang ZY (1965) Marshes on Zoige plateau. Science Press, Beijing
Chimner RA, Cooper DJ (2003) Influence of water table levels on CO2 emissions in a Colorado subalpine fen: an in situ microcosm study. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 35:345–351
Daulat W, Clymo R (1998) Effects of temperature and watertable on the efflux of methane from peatland surface cores. Atmospheric Environment 32:3207–3218
Ding W, Cai Z, Wang D (2004) Preliminary budget of methane emissions from natural wetlands in China. Atmospheric Environment 38:751–759
Euliss NH, Gleason RA, Olness A, McDougal RL, Murkin HR, Robarts RD, Bourbonniere RA, Warner BG (2006) North American prairie wetlands are important nonforested land-based carbon storage sites. Science of the Total Environment 361:179–188
Fang HJ, Yu GR, Cheng SL, Mo JM, Yan JH, Li SG (2009) 13C abundance, water-soluble and microbial biomass carbon as potential indicators of soil organic carbon dynamics in subtropical forests at different successional stages and subject to different nitrogen loads. Plant and Soil 320:243–254
Freixo AA, Machado PLOA, Dos Santos HP, Silva CA, Fadigas FS (2002) Soil organic carbon and fractions of a Rhodic Ferralsol under the influence of tillage and crop rotation systems in southern Brazil. Soil and Tillage Research 64:221–230
Ghani A, Dexter M, Perrott K (2003) Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: a sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilisation, grazing and cultivation. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 35:1231–1243
Gregorich E, Monreal C, Carter M, Angers D, Ellert BH (1994) Towards a minimum data set to assess soil organic matter quality in agricultural soils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 74:367–385
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and human well-being: wetlands and water synthesis. Island Press, Washington
Mitsch WJ, Gosselink JG (2007) Wetlands. Wiley, Hoboken
National Dynamic Atlas (2012) http://www.webmap.cn/index.php?&embeded=&map=chinaadmin
Povin C, Lechowicz MJ, Tardif S (1990) The statistical analysis of ecophysiological response curves obtained from experiments involving repeated measures. Ecology 71:1389–1400
Roscoe R, Buurman P (2003) Tillage effects on soil organic matter in density fractions of a Cerrado Oxisol. Soil and Tillage Research 70:107–119
Silvola J, Alm J, Ahlholm U, Nykanen H, Martikainen PJ (1996) CO2 fluxes from peat in boreal mires under varying temperature and moisture conditions. Journal of Ecology: 219–228
Stuefer JF, Huber H (1998) Differential effects of light quantity and spectral light quality on growth, morphology and development of two stoloniferous Potentilla species. Oecologia 117:1–8
Sun G, Zhang W, Zhang J (1998) The mire and peatland of the Hengduan Mountainous region. Science Press, Beijing
Swanston CW, Caldwell BA, Homann PS, Ganio L, Sollins P (2002) Carbon dynamics during a long-term incubation of separate and recombined density fractions from seven forest soils. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 34:1121–1130
Tuittila ES, Komulainen VM, Vasander H, Laine J (1999) Restored cut-away peatland as a sink for atmospheric CO2. Oecologia 120:563–574
Turetsky MR (2004) Decomposition and organic matter quality in continental peatlands: the ghost of permafrost past. Ecosystems 7:740–750
Waddington J, McNeil P (2002) Peat oxidation in an abandoned cutover peatland. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 82:279–286
Waddington J, Price J (2000) Effect of peatland drainage, harvesting, and restoration on atmospheric water and carbon exchange. Physical Geography 21:433–451
Wang XW, Li XZ, Hu YM, Lv JJ, Sun J, Li ZM, Wu ZF (2010) Effect of temperature and moisture on soil organic carbon mineralization of predominantly permafrost peatland in the Great Hing’an Mountains, Northeastern China. Journal of Environmental Sciences 22:1057–1066
Wang H, Wang RQ, Yu Y, Mitchell MJ, Zhang LJ (2011) Soil organic carbon of degraded wetlands treated with freshwater in the Yellow River Delta, China. Journal of Environmental Management 92:2628–2633
Werth M, Kuzyakov Y (2010) 13C fractionation at the root-microorganisms-soil interface: a review and outlook for partitioning studies. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 42:1372–1384
Yli-petäys M, Laine J, Vasander H, Tuittila ES (2007) Carbon gas exchange of a re-vegetated cut-away peatland five decades after abandonment. Boreal Environment Research 12:177–190
Yu FH, Dong M (2003) Effect of light intensity and nutrient availability on clonal growth and clonal morphology of the stoloniferous herb Halerpestes ruthenica. Acta Botanica Sinica 45:408–416
Zhang J, Song C, Wang S (2007) Dynamics of soil organic carbon and its fractions after abandonment of cultivated wetlands in northeast China. Soil and Tillage Research 96:350–360
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank two anonymous reviewers for their critical and constructive comments. We also thank Dr. Fei-Hai Yu and Dr. Fang-Li Luo for their help on improving the manuscript. This research is supported by the Forestry Commonweal Program (200804005) and NSFC (41071329, 30700108).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Zhang, X., Lei, G. et al. Soil Organic Carbon and its Fractions in Relation to Degradation and Restoration of Wetlands on the Zoigê Plateau, China. Wetlands 34, 235–241 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-013-0487-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-013-0487-9