Abstract
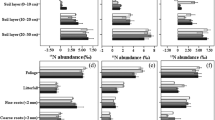
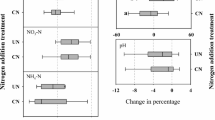
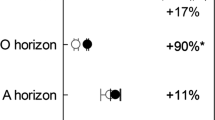
Chronic atmospheric nitrogen deposition affects the cycling of carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) in forest ecosystems, and thereby alters the stable C isotopic abundance of plant and soil. Three successional stages, disturbed, rehabilitated and mature forests were studied for their responses to different nitrogen input levels. N-addition manipulative experiments were conducted at low, medium and high N levels. To study the responses of C cycling to N addition, the C concentration and 13C natural abundances for leaf, litter and soil were measured. Labile organic carbon fractions in mineral soils were measured to quantify the dynamics of soil organic C (SOC). Results showed that three-year continuous N addition did not significantly increase foliar C and N concentration, but decreased C/N ratio and enriched 13C in N-rich forests. In addition, N addition significantly decreased microbial biomass C, and increased water soluble organic C in surface soils of N-rich forests. This study suggests that N addition enhances the water consumption per unit C assimilation of dominant plant species, restricts SOC turnover in N-poor forests at early and medium successional stages (thus favored SOC sequestration), and vice versa for N-rich mature forests.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aber JD, Nadelhoffer KJ, Steudler P, Melillo JM (1989) Nitrogen saturation in northern forest ecosystems. Bioscience 39:378–386 doi:10.2307/1311067
Aber JD, McDowell W, Nadelhoffer K, Magill A, Berntson G, Kamakea M, McNulty S, Currie W, Rustad L, Fernandez I (1998) Nitrogen saturation in temperate forest ecosystems. Bioscience 8:921–934 doi:10.2307/1313296
Albaugh TJ, Allen HL, Dougherty PM, Johnsen KH (2004) Long-term growth responses of loblolly pine to optimal nutrient and water resource availability. For Ecol Manage 192:3–19
Amundson R, Baisden WT (2000) Stable isotope tracers and mathematical models in soil organic matter studies. In: Sala OE, Jackson RB, Mooney HA, Howarth RW (eds) Methods in Ecosystem Science. Springer, New York, pp 117–137
Berger TW, Neubauer C, Glatzel G (2002) Factors controlling soil carbon and nitrogen stores in pure stands of Norway spruce (Picea abies)and mixed species stands in Austria. For Ecol Manage 159:3–14
Bowden RD, Davidson E, Savage K, Arabia C, Steudler P (2004) Chronic nitrogen additions reduce total soil respiration and microbial respiration in temperate forest soils at the Harvard Forest. For Ecol Manage 196:43–56
Brown KR, Thompson WA, Camm EL, Hawkins BJ, Guy RD (1996) Effects of N addition rates on the productivity of Picea Sitchensis, Thuja plicata, and Tsuga heterophylla seedlings II. Photosynthesis, 13C discrimination and N partitioning in foliage. Trees (Berl) 10:198–205
Cadisch G, Imhof H, Urquiaga S, Boddey RM, Giller KE (1996) Carbon turnover (δ13C) and nitrogen mineralization potential of particulate light soil organic matter after rainforest clearing. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1555–1567 doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(96)00264-7
Carter MR, Angers DA, Gregorich EG, Bolinder MA (2003) Characterizing organic matter retention for surface soils in eastern Canada using density and particle size fractions. Can J Soil Sci 83:11–23
Chantigny MH, Angers DA, Prévost D (1999) Dynamics of soluble organic C and C mineralization in cultivated soils with varying N fertilization. Soil Biol Biochem 31:543–550 doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00139-4
Choi W, Chang SX, Allen HL, Kelting DL, Ro H (2005) Irrigation and fertilization effects on foliar and soil carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios in a loblolly pine stand. For Ecol Manage 213:90–101
De Forest JL, Zak DR, Pregitzer KS, Burton AJ (2004) Nitrate deposition and the microbial degradation of cellulose and lignin in a northern hardwood forest. Soil Biol Biochem 36:965–971 doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.02.011
De Forest JL, Zak DR, Pregitzer KS, Burton AJ (2005) Atmospheric nitrate deposition and enhanced dissolved organic carbon leaching: test of a potential mechanism. Soil Sci Soc Am J 69:1233–1237 doi:10.2136/sssaj2004.0283
Fang YT, Zhu WX, Mo JM, Zhou GY, Gundersen P (2006) Dynamics of soil inorganic nitrogen and their responses to nitrogen additions in three subtropical forests, South China. J Environ Sci (China) 18:752–759
Fang H, Mo JM, Peng SL, Li ZA, Wang H (2007) Cumulative effects of nitrogen additions on litter decomposition in three tropical forests in southern China. Plant Soil 297:233–242 doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9339-9
Findlay SEG (2005) Increased carbon transport in the Hudson River: unexpected consequence of nitrogen deposition? Front Ecol Environ 3:133–137
Frey SD, Knorr M, Parrent JL, Simpson RT (2004) Chronic nitrogen enrichment affects the structure and function of the soil microbial community in temperate hardwood and pine forests. For Ecol Manage 196:159–171
Galloway JN, Dentener FJ, Capone DG, Boyer EW, Howarth RW, Seitzinger SP, Asner GP, Cleveland C, Green P, Holland E, Karl DM, Michaels AF, Porter JH, Townsend A, Vörösmarty C (2004) Nitrogen cycles: past, present and future. Biogeochemistry 70:153–226 doi:10.1007/s10533-004-0370-0
Garten CT Jr, Post WM III, Hanson PJ, Cooper LW (1999) Forest soil carbon inventories and dynamics along an elevation gradient in the southern Appalachian Mountains. Biogeochemistry 45:115–145 doi:10.1007/BF01106778
Garten CT Jr, Cooper LW, Post WM III, Hanson PJ (2000) Climate controls on forest soil C isotope ratios in the southern Appalachian Mountains. Ecology 81:1108–1119
He C, Chen S, Liang Y (1982) The soils of Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve. Trop Subtropical For Ecosyst 1:25–38 in Chinese with English abstract
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007 – the physical science basis. In: Solomon S Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Millar HL (eds) Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p 996
Jobbágy EG, Jackson RB (2000) The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol Appl 10:423–436 doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2000)010[0423:TVDOSO]2.0.CO;2
Kalbitz K, Solinger S, Park JH, Michalzik B, Matzner E (2000) Controls on the dynamics of dissolved organic matter in soils: a review. Soil Sci 165:277–304 doi:10.1097/00010694-200004000-00001
Kong GH, Liang C, Wu HM (1993) Dinghushan Biosphere Reserve: Ecological Research History and Perspective. Science Press, Beijing, China, p 38
Li DJ, Mo JM, Fang YT, Cai XA, Xue JH, Xu GL (2004) Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on growth and photosynthesis of Schima superba, Castanopsis chinensis and Cryptocarya concinna seedlings. Acta Ecol Sin 24(5):876–882 in Chinese with English abstract
Lynch DH, Voroney RP, Warman PR (2006) Use of 13C and 15N natural abundance techniques to characterize carbon and nitrogen dynamics in composting and in compost-amended soils. Soil Biol Biochem 38:103–114 doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.04.022
Maier CA, Johnsen KH, Butnor J, Kress LW, Anderson PH (2002) Branch growth and gas exchange in 13-year-old loblolly pine (Pinus taeda) trees in response to elevated carbon dioxide concentration and fertilization. Tree Physiol 22:1093–1106
Mäkipää R, Karjalainen T, Pussinen A, Kellomäki S (1999) Effects of climate change and nitrogen deposition on the carbon sequestration of a forest ecosystem in the boreal zone. Can J Res 29:1490–1501 doi:10.1139/cjfr-29-10-1490
McDowell WH, Magill AH, Aitkenhead-Peterson JA, Aber JD, Merriam JL, Kaushal SS (2004) Effects of chronic nitrogen amendment on dissolved organic matter and inorganic nitrogen in soil solution. For Ecol Manage 196:29–41
Micks P, Aber JD, Boone RD, Davidson EA (2004) Short-term soil respiration and nitrogen immobilization response to nitrogen applications in control and nitrogen-enriched temperate forests. For Ecol Manage 196:57–70
Mo JM, Brown S, Xue JH, Fang YT, Li ZA (2006) Response of litter decomposition to simulated N deposition in disturbed, rehabilitated and mature forests in subtropical China. Plant Soil 282:135–151 doi:10.1007/s11104-005-5446-7
Mo JM, Zhang W, Zhu WX, Fang YT, Li DJ, Zhao P (2007) Response of soil respiration to simulated N deposition in a disturbed and a rehabilitated tropical forest in southern China. Plant Soil 296:125–135 doi:10.1007/s11104-007-9303-8
Mo JM, Zhang W, Zhu WX, Gundersen P, Fang YT, Li DJ, Wang H (2008) Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in a mature tropical forest in southern China. Glob Change Biol 14:403–412
Murthy R, Dougherty PM, Zarnoch SJ, Allen HL (1996) Effects of carbon dioxide, fertilization, and irrigation on photosynthetic capacity of loblolly pine trees. Tree Physiol 16:537–546
Nadelhoffer KJ, Emmett BA, Gundersen P, Kjnaas OJ, Koopmans CJ, Schleppi P, Tietemal A, Wright RF (1999) Nitrogen deposition makes a minor contribution to carbon sequestration in temperate forests. Nature 398:145–148 doi:10.1038/18205
Nakaji T, Fukami M, Dokiya Y, Izuta T (2001) Effects of high nitrogen load on growth, photosynthesis and nutrient status of Cryptomeria japonica and Pinus densiflora seedlings. Trees (Berl) 15:453–461
Nakaji T, Takenaga S, Kuroha M, Izuta T (2002) Photosynthetic response of Pinus densiflora seedlings to high nitrogen load. Environ Sci 9:269–282
Neff JC, Townsend AR, Gleixner G, Lehman SJ, Turnbull J, Bowman WD (2002) Variable effects of nitrogen additions on the stability and turnover of organic carbon. Nature 419:915–917 doi:10.1038/nature01136
Peng SL, Wang BS (1995) Forest succession at Dinghushan, Guangdong, China. Chin J Bot 7:75–80 in Chinese with English abstract
Powers JS, Schlesinger WH (2002) Geographic and vertical patterns of stable carbon isotopes in tropical rain forest soils of Costa Rica. Geoderma 109:141–160 doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00148-9
Prescott CE, Kabzems R, Zabek LM (1999) Effects of fertilization on decomposition rate of Populus tremuloides foliar litter in a boreal forest. Can J Res 29:393–397 doi:10.1139/cjfr-29-3-393
Ripullone F, Lauteri M, Grassi G, Amato M, Borghetti M (2004) Variation in nitrogen supply changes water-use efficiency of Pseudotsuga menziesii and Populus xeuroamericana; a comparison of three approaches to determine water-use efficiency. Tree Physiol 24:671–679
Roscoe R, Buurman P, Velthorst EJ, Vasconcellos CA (2001) Soil organic matter dynamics in density and particle size fractions as revealed by the 13C/12C isotopic ratio in a Cerrado’s oxisol. Geoderma 104:185–202 doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(01)00080-5
Sparks JP, Ehleringer JR (1997) Leaf carbon isotope discrimination and nitrogen content for riparian trees along elevational transects. Oecologia 109:362–367 doi:10.1007/s004420050094
Stevens CJ, Dise NB, Owen MJ, Gowing DJ (2004) Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science 303:1876–1879 doi:10.1126/science.1094678
Tang XL, Liu SG, Zhou GY, Zhang DQ, Zhou CY (2006) Soil atmoshpheric exchange of CO2, CH4, and N2O in three subtropical forest ecosystems in southern China. Glob Change Biol 12:546–560 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01109.x
Tessier JT, Raynal DJ (2003) Use of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios in plant tissue as an indicator of nutrient limitation and nitrogen saturation. J Appl Ecol 40:523–534 doi:10.1046/j.1365-2664.2003.00820.x
Turunen J, Roulet NT, Moore TR, Richard PJH (2004) Nitrogen deposition and increased carbon accumulation in ombrotrophic peatlands in eastern Canada. Global Biogeochem Cycles 18:1–12 doi:10.1029/2003GB002154
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707 doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6
Waldrop MP, Zak DR (2006) Response of oxidative enzyme activities to nitrogen deposition affects soil concentrations of dissolved organic carbon. Ecosystems (N Y, Print) 9:921–933 doi:10.1007/s10021-004-0149-0
Wallenstein MD, McNulty S, Fernandez IJ, Boggs J, Schlesinger WH (2006) Nitrogen fertilization decreases forest soil fungal and bacterial biomass in three long-term experiments. For Ecol Manage 222:459–468
Wynn JG, Harden JW, Fries TL (2006) Stable carbon isotope depth profiles and soil organic carbon dynamics in the lower Mississippi Basin. Geoderma 131:89–109 doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.03.005
Xue JH, Mo JM, Li J, Li DJ (2007) The short-term response of soil microorganism number to simulated nitrogen deposition. Guihaia 27(2):174–179 in Chinese with English abstract
Zhou GY, Liu SG, Li Z, Zhang DQ, Tang XL, Zhou CY, Yan JH, Mo JM (2006) Old-growth forests can accumulate carbon in soils. Science 314:1417 doi:10.1126/science.1130168
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (40601097, 30590381, 30600071), Knowledge Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-YW-432,O7V70080SZ),the President Fund of GUCAS(O85101PM03) and “Hundred Talents” Program (CXTD-Z2005-1). We gratefully acknowledge Dr. Yang Xueming and Dr. Zhuang Jie for revising the English writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ute Skiba.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, HJ., Yu, GR., Cheng, SL. et al. 13C abundance, water-soluble and microbial biomass carbon as potential indicators of soil organic carbon dynamics in subtropical forests at different successional stages and subject to different nitrogen loads. Plant Soil 320, 243–254 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9890-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9890-7