Abstract
The shallow habitats of coastal lagoons play an invaluable role for fish communities as nursery areas and provide essential habitats for threatened fish species. Shoreline modification is an anthropogenic coastal stressor that can negatively affect aquatic communities through the modification of nearshore habitats. The aim of the present study was to quantify the effects of two types of shoreline conditions on habitat structure and fish community of littoral habitats. Unmodified shorelines adjacent to saltmarshes and recreational beaches in urbanised areas of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon were compared. The results showed that there were significant differences in habitat structure, fish community structure and fish species abundance by shoreline type. Recreational beaches were characterised by higher water depth and homogeneous substrata, while unmodified shorelines showed high substrata heterogeneity and supported well developed meadows of submerged vegetation. The latter shoreline type provided an important nursery habitat for marine species such as Sparus aurata and Liza saliens, and represented critical habitats for species of conservation concern such as Aphanius iberus and Syngnathus abaster. Littoral areas adjacent to modified shorelines were dominated by Pomatoschistus marmoratus. We suggest that urbanisation has impacted fish assemblages through degradation of habitat structure (loss of complexity and refuge areas).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreu-Soler A, Oliva-Paterna FJ, Torralva M (2006) Seasonal variations in somatic condition, hepatic and gonad activity of sand smelt Atherina boyeri (Teleostei Atherinidae) in the Mar Menor coastal lagoon (SE Iberian Peninsula). Folia Zoologica 55:151–161
Attrill MJ, Power M (2004) Partitioning of temperature resources amongst an estuarine fish assemblage. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 61:725–738
Bain MB (1999) Substrate. In: Bain MB, Stevenson NJ (eds) Aquatic habitat assesment: common methods. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, pp 95–100
Baldó F, Drake P (2002) A multivariate approach to the feeding habits of small fishes in the Guadalquivir Estuary. Journal of Fish Biology 61:21–32
Bilkovic DM, Roggero MM (2008) Effects of coastal development on nearshore estuarine nekton communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 358:27–39
Carreño MF, Esteve MA, Martínez J, Palazón JA, Pardo MT (2008) Habitat changes in coastal wetlands associated to hydrological changes in the watershed. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 77:475–483
Clarke KR, Warwick RM (2001) Change in marine communities: an approach to statistical analysis and interpretation, 2nd edn. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Courrat A, Lobry J, Nicolas D, Amara R, Lepage M, Girardin M, Le Pape O (2009) Anthropogenic disturbances on nursery function of estuarine areas for marine fish species. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 81:179–190
DeLuca WV, Studds CE, King RS, Marra PP (2008) Coastal urbanization and the integrity of estuarine waterbird communities: threshold responses and the importance of the scale. Biological Conservation 141:2669–2678
Elliott M, Whitfield AK, Potter IC, Blaber SJM, Cyrus DP, Nordlie FG, Harrison TD (2007) The guild approach to categorize estuarine fish assemblages: a global review. Fish and Fisheries 8:241–268
Fernández-Delgado C, Drake P, Arias AM, García D (2000) Peces de Doñana y su entorno. Organismo Autónomo de Parques Nacionales. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid
França S, Costa MJ, Cabral HN (2009) Assesing habitat specific fish assemblages in estuaries along the Portuguese coast. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 83:1–12
França S, Vasconcelos RP, Tanner S, Máguas C, Costa MJ, Cabral HN (2011) Assesing food web dynamics and relative importance of organic matter sources for fish species in two Portuguese estuaries: a stable isotope approach. Marine Environmental Research 72:204–215
Franco A, Franzoi P, Malavasi S, Riccato F, Torricelli P, Mainardi D (2006) Use of shallow habitats by fish assemblages in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 66:67–83
Franco A, Elliott M, Franzoi P, Torricelli P (2008) Life strategies of fishes in European estuaries: the functional guild approach. Marine Ecology Progress Series 354:219–228
Koutrakis ET, Tsikliras AC, Sinis AI (2005) Temporal variability of the ichthyofauna in a Northern Aegean coastal lagoon (Greece). Influence of environmental factors. Hydrobiologia 543:245–257
Lloret J, Marín A, Marín-Guirao L, Velasco J (2005) Changes in macrophytes distribution in a hypersaline coastal lagoon associated with the development of intensively irrigated agriculture. Ocean & Coastal Management 48:828–842
Martínez J, Esteve-Selma MA, Robledano-Aymerich F, Pardo-Sáez MT, Carreño-Fructuoso MF (2005) Aquatic birds as bioindicators of trophic changes and ecosystem deterioration in the Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain). Hydrobiologia 550:221–235
Nordstrom KF (2005) Beach nourishment and coastal habitats: research needs to improve compatibility. Restoration Ecology 13:215–222
Oliva-Paterna FJ, Andreu-Soler A, Miñano PA, Verdiell-Cubedo D et al (2006) YOY fish species richness in the littoral shallows of the mesosaline coastal lagoon (Mar Menor, Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula). Journal of Applied Ichthyology 22:235–237
Oliva-Paterna FJ, Ruiz-Navarro A, Torralva M, Fernández-Delgado C (2009) Biology of the endangered cyprinodontid Aphanius iberus in a saline wetland (SE Iberian Peninsula). Italian Journal of Zoology 76:316–329
Pérez-Ruzafa A, Marcos C, Gilabert J (2005) The ecology of the Mar Menor coastal lagoon: a fast changing ecosystem under human pressure. In: Gönenç IE, Wolflin JP (eds) Coastal lagoons. Ecosystem processes and modelling for sustainable use and development. CRC Press, Boca Ratón, pp 392–422
Pérez-Ruzafa A, García-Charton JA, Barcala E, Marcos C (2006) Changes in benthic fish assemblages as a consequence of coastal works in a coastal lagoon: the Mar Menor (Spain, Western Mediterranean). Marine Pollution Bulletin 53:107–120
Peterson MS, Comyns BH, Hendon JR, Bond PJ, Duff GA (2000) Habitat use by early life-history stages of fishes and crustaceans along a changing estuarine landscape: differences between natural and altered shoreline sites. Wetlands Ecology and Management 8:209–219
Pombo L, Elliot M, Rebelo JE (2005) Environmental influences on fish assemblage distribution of an estuarine coastal lagoon, Ria de Aveiro (Portugal). Scientia Marina 69(1):143–159
Quinn G, Keough M (2002) Experimental design and data analysis for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rountree RA, Able KW (2007) Spatial and temporal habitat use patterns for salt marsh nekton: implications for ecological functions. Aquatic Ecology 41:25–45
Sanger DM, Holland AF, Hernandez DL (2004) Evaluation of the impacts of dock structures and land use on tidal creek ecosystems in South Carolina estuarine environments. Environmental Management 33(3):385–400
Seitz RD, Lipcius RN, Olmstead NH, Seebo MS, Lambert DM (2006) Influence of shallow-water habitats and shoreline development on abundance, biomass and diversity of benthic prey and predators in Chesapeake Bay. Marine Ecology Progress Series 326:11–27
Silliman BR, Bertness MD (2003) Shoreline development drives invasion of Phragmites australis and the loss of plant diversity on New England salt marshes. Conservation Biology 18(5):1424–1434
Underwood AJ (1997) Experiments in Ecology. The Logical Design and Interpretation Using Analysis of Variance. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Vasconcelos RP, Resi-Santos P, Fonseca V, Maia A, Ruano M, França S, Vinagre C, Costa MJ, Cabral H (2007) Assessing anthropogenic pressures on estuarine fish nurseries along the Portuguese coast: A multi-metric index and conceptual approach. Science of the Total Environment 374:199–215
Velasco J, Lloret J, Millán A, Marín A, Barahona J, Abellán P, Sánchez-Fernández D (2006) Nutrient and particulate inputs into the Mar Menor lagoon (SE Spain) from an intensive agricultural watershed. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 176:37–56
Verdiell-Cubedo D, Oliva-Paterna FJ, Andreu A, Torralva M (2007a) Characterisation of the nursery areas for YOY Sparidae fish species in a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (SE Iberian Peninsula). Anales de Biologia 29:3–11
Verdiell-Cubedo D, Egea-Serrano A, Oliva-Paterna FJ, Torralva M (2007b) Biología trófica de los juveniles del género Liza (Pisces: Mugilidae) en la laguna costera del Mar Menor (SE Península Ibérica). Limnetica 26:67–74
Verdiell-Cubedo D, Oliva-Paterna FJ, Egea-Serrano A, Torralva M (2008) Population biology and habitat associations of benthic fish species in the shallow areas of a Mediterranean coastal lagoon (SE Iberian Peninsula). Scientia Marina 72:319–328
Verdiell-Cubedo D (2009) Ictiofauna de las zonas someras litorales del Mar Menor (SE, Península Ibérica): parámetros de su biología y relaciones con el hábitat. University of Murcia, Spain
Acknowledgements
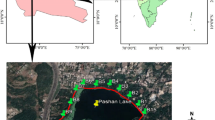
We are grateful to Pedro A. Miñano, Andrés Egea and Ana Ruiz for help in field sampling and laboratory processing, and to Melissa Crim and Javier Lloret for their English revision and expert commentaries, respectively. Many thanks to María Francisca Carreño for her help in Fig. 1. We also acknowledge the comments of two anonymous reviewers which have greatly improved the manuscript. Part of this research was supported by the Environmental Service of the Autonomous Government of Murcia, Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verdiell-Cubedo, D., Torralva, M., Andreu-Soler, A. et al. Effects of Shoreline Urban Modification on Habitat Structure and Fish Community in Littoral Areas of a Mediterranean Coastal Lagoon (Mar Menor, Spain). Wetlands 32, 631–641 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-012-0296-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-012-0296-6