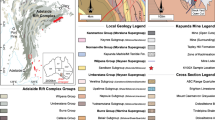
Abstract
Sedimentary rocks of the Upper Cretaceous, Middle Miocene, Plio-Pleistocene, and Quaternary periods are present in the Red Sea coastal plain from south of El Quseir to Marsa Alam, and they are dispersed over Late Proterozoic basement rocks. The zinc and lead ores intercalated with celestite in Wadi Essel are dispersed throughout the adjacent rocks and intense in Middle Miocene sedimentary strata in clastic rocks. This work studied the fluid inclusions hosted in the celestite, which is in close to the lead–zinc mineralization, to measure the microthermometric parameters giving knowledge about the nature, composition and the condition of formation of celestite as well as lead- zinc mineralization. The fluid inclusions study for the celestite revealed that this celestite deposited from saline water (up to 9.054 wt% NaCl eq.) with density up to 1.045 g/cm3 and the deposition of the celestite probably took place at temperatures between 50 and 75 °C for Wadi Essel celestite as well as accompanying lead–zinc sulphide, which considered as Mississippi valley type (MVT) Pb–Zn deposits.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw data of the present study is available upon request from the corresponding author (hodaragab@hotmail.com).
References
Amin MS (1955) Geological features of some mineral deposits in Egypt. Bull Inst Desert Egypt 1(1):209–239
Angus S, Armstrong B, Dereuck K, Altumin V, Gadesku O, Chapela G, Rowlinson J (1976) International thermodynamic tables of the fluid state, carbon dioxide, vol 3. Oxford Pergaman Press, London
Assal EM (2009) Sedimentology and sequence stratigraphy of a mixed siliclastic-carbonate syb-rift Miocene platform of Wadi Essel-Wadi Sharm El Qibli area, Red Sea coast, Egypt. Ph.D. thesis, Mansoura University
Bayer HL, Hotzl H, Jado AR, Roscher B, Voggenreiter W (1988) Sedimentary and structural evolution of the northwest Arabian Red Sea margin. Tectonophysics 153:137–152
Beandnall HJ (1924) Report on the geology of the Red Sea Coast between Qusseir and Wadi Ranga: Pete. Research Series, Min. Finance, Cairo, Bull., 13:37
Beetz H, Bauer G, Trabandt H, Zimmermann J (1962) Geological and mineralogical investigations and mining plans for the mines, Um Gheig, Gebel El-Rusas of the associated Mines Co., Cairo: Report of Stobberger Zink AG. Fure Bergbau u. Huttenbetrieb, Aachen
Beurlen H, da Silva MRR, de Castro C (2001) Fluid inclusion microthermometry in Be-Ta-(Li-Sn)-bearing pegmatites from the Borborema Province, Northeast Brazil. Chem Geol 173:107–123
Bodnar RJ (1993) Revised equation and table for determining the freezing point depresion of H2O-NaCl solutions. Geochmica et Cosmochimica Acta 57:683–684.
Bodnar RJ, Vityk MO (1994) Interpretation of microthennometric data for H2O-NaCl. In: De Vivo B, Frezzotti ML (eds) Fluid inclusions in minerals: methods and application, shon course on the working group (!MA) “inclusions in minerals.” Virgina Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg, pp 117–130
Bowers TS, Helgson HC (1983) Calculation of the thermodynamic and geochemical consequences of non-ideal mixing in the system H2O-CO2-NaCl on phase relations in geologic system: equation of state H2O-CO2-NaCl fluids at high pressures and temperatures. Geochhim Cosmochim Acta 47:1247–1275
Brown PE (1989) Flincor, A microcomputer program for the reduction and investigation of fluid inclusion data. Am Mineral 74:1390–1393
Chi G-X, Savard MM (1995) Fluid evolution and mining in the Gays River carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit and its surrounding barren areas, Nova Scotia. Atlantic Geol 31:141–152
Chi G-X, Savard M, Heroux Y (1995) Constraints from fluid-inclusion data on the origin of the Jubilee carbonate-hosted Zn-Pb deposit, Cape Breton, Nova Scotia. Can Mineral 33:709–722
Crawford ML, Kraus DW, Hollister LS (1979) Petrologic and fluid inclusion study of czic-silicate rocks, Prince Rupert, British Columbia. Am J Sci 279:1135–1159
El Aref MM (1981) Lead-zinc deposits along the Red Sea coast of Egypt. New observations and genetic models on the occurrences of Um Gheig, Wizr, Essel and Zug El Bohar. Ph.D. Thesis, Heidelberg Univ
El Aref MM (1984) Strata-bound and stratiform iron sulphides, sulfar and galena in the Miocene evaporites, Ranga, Red Sea (with special emphasis on their diagenetic crystallization rhythmites). In: Wauschkuhn et al (eds) Syngenesis and epigenesis in the formation of mineral deposits. Springer, Berlin, pp 457–467
El Aref MM (1993) Paleokarast surfaces in the Neogene succession of Wadi Essel-Wadi Sharm El Bahari area, Egyptian Red Sea Coast as an indication of uplifting and exposure. Geodynamics and sedintation of the Red Sea–Gulf of Aden Rift System. The geological Society of Egypt. Geol. Soc. Egypt., Spec. Puhl. No. 1, pp 205–231
El Aref MM, Ahmed S (1986) Diagenetic crystallization rhythmites (DCRs) of dolomite-barite-calcite in karst environment, Gabal Abu Ghorban, Red Sea coastal zone, Egypt. In: Rodriguez-Clemente R, Tardy Y (eds) Geochemistry and mineral formation in the surface. CEP de la Biblioteca, Madrid, pp 609–622
El Aref MM, Amstutz GC (1983) Lead-zinc deposits along the Red Sea coast of Egypt, new observations and genetic modefs on the occurrences of Um Gheig, Wizr, Essel and Zug El Bobar. Monogr. Ser. on Mineral Deposits, Borntraeger Stuttgart, 21
El Aref MM, Abdel Wahab S, Ahmed S (1985) Surficial calcareous crust of caliche type along the Red Sea coast, Egypt. Geol Rundsch 74:155–163
El Aref MM, Awadalah F, Ahmed S (1986) Karst landform development and related sediments. in the Miocene rocks. of the Red Sea coastal zone, Egypt. Geol Runsch 75:781–790
El Haddad AA (1984) Sedimentological and geological studies on the Neogene sediments of the Egyptian part of the Red Sea. Ph.D. Thesis, Assiut Univ., Egypt
El-Shazly EM, Barakat N (1956) Spectrographic distribution of chemical elements in Egyptian minerals from lead zinc, copper and gold deposiys. Bull Inst Egypt Tome XXXVII 2:31–46
El-Shazley EM, Mansour A, Afia MS, Ghobrial MG (1959) Miocene lead and zinc deposits in Egypt. XX International. Geol. Congress, Mixico, Section XIII, Applied Geology, pp 119–134.
Fourtau R (1912) Le Gebel Rusas et ses environs:Bull. Inst. D’Egypt, Le Caire, Ser. V., VI, fasc. 1, pp 110–113
Goldstein RH, Reynolds TJ (1994) Systematics of fluid inclusions in diagenetic minerals; Society for Sedimentary Geology Short Course 31
Guilhaumou N (1982) Analyse ponetuelle des inclusions fluids par microsonde moleculaire a laser (Mole) et microthermometrie
Hassan MM (1990) Studies on lead–zinc sulphide mineralization in the Red Sea coastal zone, Egypt. In: Proceeding of the eighth quadrennial AGOD symposium Ottawa, Canada, pp 835–847
Hume WF (1937) Geology of Egypt: survey of Egypt. Cairo, II 3:689–990
Hussein AAA (1990) Mineral deposits of Egypt. In: Said R (ed) Geology of Egypt. Balkema/Rotterdam/Brookfield. Chapter. 26, pp 511–566
Jarrige JJ, Ott d’Estevou P, Burollet PF, Kart JC, Montenant C, Prat P, Richert JR, Sehans P, Thiriet JP (1986) Inherited discontinuities and Neogene structures; the Gulf of Suez and the northwestern edge of the Red Sea. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 317:129–139
Kontak DJ (1998) A study of fluid inclusions in sulfide and non-sulphide mineral phases from a carbonatehosted Zn-Pb deposit, Gays River, Nova Scotia. Econ Geol 93:793–817
Kontak DJ, Macdonald AS (1995) Initial results of a fluid inclusion study of fluorite from Lake Ainslie barite-fluorite deposits, Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia. In: MacDonald DR (eds) Mines and minerals branch report of activities 1994; Nova Scotia Department of Natural Resources, Report 95-1, pp 99–106
Kontak DJ, Sangster DF (1998) Aqueous and liquid petroleum inclusions in barite from the Walton deposit, Nova Scotia, Canada: a carboniferous carbonate-hosted Ba-Pb-Zn-Cu-Ag deposit. Econ Geol 93:845–868
Leach LD, Sangester DF, Kelley KD, Large RR, Graven G, Cameron R, Allen CR, Guttzmer J, Walters S (2005) Sediment hosted lead-zinc deposits: a global perspective
Mira HI (2011) Behavior of REE and some isovalent elements in Um Gheig Miocene sedimentary rocks, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Sediment Soc Egypt 19(23–40):548
Montenat C, Ott d’Estevou PO, Purser BH (1988) Tectonic and sedimentary evolution of the Gulf of Suez and the Northwestern Red Sea: a review. Doc. Trav IGAL, Pans 10:7–18
Morsy MA (2000) Application of multivariate statistics to study stream sediment data from the vicinity of lead–zinc occurrences at Gabal Rusas area, Eastern Desert, Egypt. International archives of 551 photogeommetry and remote sensing, XXXIII part 87 Amesterdam
Oakes CS, Bodnar RJ, Simonson JM (1990) The system NaCl-CaCl2-H2O. I. The vapor-saturated ice liquids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:603–610
Orgeval JJ (1994) Peridiapiric Metal concentration: example of the Bou Grine Deposit (Tunisian Atlas). In: Fontbote L, Boni M (eds) Sediment-hosted Zn-Pb ores. Special publication of the society for geology applied to mineral deposits, vol 10. Springer, Berlin, pp 354–389
Perthuisot V (1978) Dynamique et petrogenese des extrusions triasiques en Tunisie septentrionale. These es Sciences Ecole Normale Superieure, Paris, p 312p
Perthuisot V, Saliot P (1979) Neoformations silicates dans le Trias des diapris tunisiwens: Role des solusions hydrothermals. Sci Terre Nancy 23:75–83
Philobbos ER, El Haddad AA (1983) Tectonic control of Neogene edimentation along the Egyptian part of the Red Sea coastal area. In: 5th international conference of basement tectonics, Cairo, abstract. pp 5
Philobbos ER, El Haddad AA (1984) Regional tectonic control of Neogene sedimentation along the Egyptian coast of the Red Sea. In: 5th Congr. Eur. Sedirnentol., Marseilles, abstract
Philobbos ER, El Haddad AA, Mahran TM (1988) Comparison between Miocene and Pliocene facies distribution related to syn-rift tectonics along the Egyptian Red Sea Coastal area. In: E.G.P.C. 9th petroleum exploration and production conference, vol 1, pp 246–254
Philobbos ER, El Haddad AA, Mahran TM (1989) Sedimentology of syn-rift Upper Miocene (?)-Pliocene sediments of the Red Sea area: a model from the environs o (Mersa Alam, Egypt). Egypt J Geo 33:201–226
Pirajno F (2009) Hydrothermal process and mineral systems. Springer, Netherlands, p 1250
Plaziat JC, Purser RH, Philobbos ER (1988) Diversity of Neogene seismites of the NW Red Sea (Egypt): a characteristic sedimentary expression of rifting. Tectonophysics 153:295
Plaziat JC, Purser BH, Philobbos E (1990) Seismic deformation structure (seismites) in the syn-rift sediments of the NW Red Sea (Egypt), Bull. Soc. Geo. France, t. VI, vol 3, pp 419–434
Purser BH, Hotzl H (1988) The sedimentary evolution of the Red Sea rift: a comparison of the northwest (Egyptian) and northeast (Saudi Arabian) margins. Tectonophysics 153:193–203
Purser BH, Philobbos ER, Plaziat J-C (1990) Miocene seismite deformation breccias and their reservoir potential, examples from the Egyptian Red Sea coast. In: 10th petroleum exploration & production conference, cairo, 7 p
Ramboz C, Pichavant M, Weisbrod A (1982) Fluid immiscibility in natural processes: use and misuse of fluid inclusion data. II. Interpretation of fluid inclusion data in terms of immiscibility. Chem Geol 37:29–48
Ravenhurst CE, Reynolds PH, Zentilli M, Krueger HW, Blenkinsop J (1989) Formation of Carboniferous Pb-Zn and barite mineralization from basin-derived fluids, Nova Scotia, Canada. Econ Geol 84:1471–1488
Robb L (2005) Introduction to ore-forming processes. Blackwell Science Ltd, Hoboken, p 373
Roedder E (1984) Fluid inclusions. Reviews in mineralogy. Mineral Soc Am 12:644
Roedder E, Bodnar RJ (1997) Geologic pressure determinations from fluid inclusion studies. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 8(1):263–301
Roussel N, Purser BH, Orszag-Sperber F, Plaziat J-C, Soliman M, El Haddad AA (1986) Geologie de la region- de Quseir (Egypte). Doc. et Trav. IGAL, Paris, vol 10, pp 129–144
Sabet AH, Tsogoev VB, Bordonosov VP, Beloshitsky VA, Kuznetosov DN, Hakim HA (1976) On some geological and structural peculations of locatization of the polymental, minewralization in the Middle Miocene sediments along the Red Sea Goast, Annals Geol. Surv. Egypt, VI, pp 223–236
Said R (1990) The geology of Egypt. A. A. Bulke ma, Rotterdam, 732 Scrivenor JB (1937) Note on Buchanan, s laterites. Geol Mag 47:356–362
Soliman M, Hassan M (1969) Contribution to the geology and geochemistry of lead, zinc and sulfur deposits of Gebel El-Rousas, Anz and Ranga localities, Eastern Desert, Egypt. 6th Arab Sci. Cong. Damuscus, (4: B), pp 591–660
Sterner M, Hall D, Bodner R (1988) Synthetic fluid inclusions. V. Solubility relationships in the system NaC-KCl-H2O under vapor-saturated conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:989–1005
Tischendorh W (1957) Report for the visit to the lead-zinc mines of the Associated Mines Company, Cairo, (Internal Report). Econ. Geol., 100th Anniversary volume, pp 561–607
Zaid SM (2017) Petrography and geochemistry of the Middle Miocene Gebel El Rusas sandstones, Eastern Desert, Egypt: implications for provenance and tectonic setting. J Earth Syst Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-17-0873-4
Zhang YG, Frantz JD (1987) Determination of thehomogenization temperatures and dacites of supercritical fluids in the system NaCl KCl CaCl2 H2O using synthetic fluid inclusions. Chem Geol 64(3–4):335–350
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my gratitude to Prof. Dr. Osama Attia, Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Cairo University, for the fluid inclusion study facilities and Prof. Dr Mohamed Abdel Moneam, Geology Department, Faculty of Science, Assiut University and also, Dr. Ehab Assal, and Dr. Haytham Sehsah, Faculty of science, Damietta university, for their kind help and revising the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HRS wrote the manuscript text and prepared figures and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Saad, H.R. The Mississippi valley type Zn-Pb-celestite deposits at Wadi Essel, the Eastern Desert of Egypt: fluid inclusions and microthermometry evidences. Carbonates Evaporites 38, 64 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00887-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-023-00887-5