Abstract
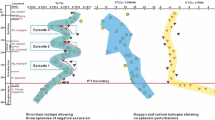
The Early-Middle Permian δ13Ccarb variations are recorded by the marine carbonates of the Luduba section in the northern margin of the South China Block. The investigated interval (~ 300 m) spans the Chihsia and Maokou formations. Preservation of the investigated micritic carbonates was evaluated by multiple petrographic and geochemical screening tools. The δ13Ccarb and δ18O values of near-primary micrites range from 2.3 to 5.0‰ (VPDB) and from − 6.4 to − 3.4‰ (VPDB), respectively, showing insignificant correlation (R2 = 0.13). Similarly, the Mn/Sr ratios show insignificant correlation with δ13Ccarb or δ18O ratios. In addition, the Al and Sr concentrations exhibit insignificant correlation, which suggests preservation of at least near-primary δ13Ccarb signatures that can be utilized to construct a reliable C-isotope profile of the equatorial eastern Paleo-Tethys for global correlations. The C-isotope profile exhibits distinct short-time negative shifts superimposed on the general long-term trend of increase in δ13Ccarb values. The long-term trend likely reflects a consistent global sea-level rise during the Early Guadalupian, which was associated with one of the largest Permian transgressions. The general sea-level rise was disrupted by few minor short-term sea-level low-stands associated with negative δ13Ccarb shifts (~ 1–2 ‰) on the C-isotope profile, which are associated with similar minor positive 87Sr/86Sr shifts (~ 0.0005 each) on the Sr isotope profile and with Al enrichment, possibly caused by the combination of global eustasy and regional tectonics in South China. Two negative δ13Ccarb shifts have been recorded in the lower and upper Chihsia Formation that can be correlated with the Early Kungurian and the Kungurian/Roadian boundary, respectively. Also, the Maokou Formation records a middle negative shift that inferred correlates with the Early Wordian. These three negative δ13Ccarb shifts are globally comparable with those documented by both the eastern Paleo-Tethys and western Panthalassa Early-Middle Permian sedimentary records and can be utilized as chemostratigraphic markers. The general increase in the δ13Ccarb values peaks at ~ 5 ‰ near the top of the Maokou Formation that resembles the Kamura event recorded in Tethy but there are issues with the origin and timing of this positive δ13Ccarb excursion. The petrological characteristics of the Luduba section carbonates support the suggested scenario of the general long-term trend of sea-level rise.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Arthur MA, Schlanger SO, Jenkyns HC (1987) The Cenomanian—Turonian oceanic anoxic event, II. Palaeoceanographic controls on organic-matter production and preservation. Geol Soc 26(1):401–420. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1987.026.01.25 (Special Publications)
Azmy K (2019a) Carbon-isotope stratigraphy of the uppermost Cambrian in eastern Laurentia: implications for global correlation. Geol Mag 156(5):759–771. https://doi.org/10.1017/s001675681800002x
Azmy K (2019b) Carbon-isotope stratigraphy of the SPICE event (Upper Cambrian) in eastern Laurentia: implications for global correlation and a potential reference section. Geol Mag 156(8):1311–1322. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0016756818000638
Azmy K, Lavoie D (2009) High-resolution isotope stratigraphy of the Lower Ordovician St. George group of western Newfoundland, Canada: implications for global correlation. Can J Earth Sci 46(6):403–423. https://doi.org/10.1139/e09-032
Azmy K, Stouge S, Christiansen JL, Harper DA, Knight I, Boyce D (2010) Carbon-isotope stratigraphy of the lower Ordovician succession in Northeast Greenland: implications for correlations with St. George group in western Newfoundland (Canada) and beyond. Sediment Geol 225(1–2):67–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.01.007
Azmy K, Stouge S, Brand U, Bagnoli G, Ripperdan R (2014) High-resolution chemostratigraphy of the Cambrian-Ordovician GSSP: enhanced global correlation tool. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 409:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.05.010
Azmy K, Kendall B, Brand U, Stouge S, Gordon GW (2015) Redox conditions across the Cambrian-Ordovician boundary: elemental and isotopic signatures retained in the GSSP carbonates. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 440:440–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.09.014
Azomani E, Azmy K, Blamey N, Brand U, Al-Aasm I (2013) Origin of Lower Ordovician dolomites in eastern Laurentia: controls on porosity and implications from geochemistry. Mar Pet Geol 40:99–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2012.10.007
Bagherpour B, Bucher H, Yuan DX, Leu M, Zhang C, Shen SZ (2018) Early Wuchiapingian (Lopingian, late Permian) drowning event in the South China block suggests a late eruptive phase of Emeishan large Igneous Province. Global Planet Change 169:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2018.07.013
Bond DPG, Hilton J, Wignall PB, Ali JR, Stevens LG, Sun YD, Lai XL (2010a) The Middle Permian (Capitanian) mass extinction on land and in the oceans. Earth Sci Rev 102(1–2):100–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.07.004
Bond DPG, Wignall PB, Wang W, Izon G, Jiang HS, Lai XL, Sun YD, Newton RJ, Shao LY, Védrine S, Cope H (2010b) The mid-Capitanian (Middle Permian) mass extinction and carbon isotope record of South China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 292(1–2):282–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.03.056
Buggisch W, Wang X, Alekseev AS, Joachimski MM (2011) Carboniferous-Permian carbon isotope stratigraphy of successions from China (Yangtze platform), USA (Kansas) and Russia (Moscow Basin and Urals). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 301(1–4):18–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.12.015
Buggisch W, Krainer K, Schaffhauser M, Joachimski M, Korte C (2015) Late Carboniferous to late Permian carbon isotope stratigraphy: a new record from post-Variscan carbonates from the Southern Alps (Austria and Italy). Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 433:174–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.05.012
Cao CQ, Cui C, Chen J, Summons RE, Shen SZ, Zhang H (2018) A positive C-isotope excursion induced by sea-level fall in the middle Capitanian of South China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 505:305–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.06.010
Cao J, Xia LW, Wang TT, Zhi DM, Tang Y, Li WW (2020) An alkaline lake in the Late Paleozoic Ice Age (LPIA): a review and new insights into paleoenvironment and petroleum geology. Earth Sci Rev 202:103091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103091
Chen ZQ, Jin YG, Shi GR (1998) Permian transgression-regression sequences and sea-level changes of South China. Proc R Soc Victoria 110(1/2):345–367
Chen ZQ, George AD, Yang WR (2009) Effects of Middle-Late Permian sea-level changes and mass extinction on the formation of the Tieqiao skeletal mound in the Laibin area, South China. Aust J Earth Sci 56(6):745–763. https://doi.org/10.1080/08120090903002581
Chen B, Joachimski MM, Sun YD, Shen SZ, Lai XL (2011) Carbon and conodont apatite oxygen isotope records of Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary sections: climatic or sea-level signal? Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 311(3–4):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2011.08.016
Chen B, Joachimski MM, Shen SZ, Lambert LL, Lai XL, Wang XD, Chen J, Yuan DX (2013) Permian ice volume and palaeoclimate history: Oxygen isotope proxies revisited. Gondwana Res 24:77–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2012.07.007
Cheng C, Li SY, Xie XY, Cao TL, Manger WL, Busbey AB (2019) Permian carbon isotope and clay mineral records from the Xikou section, Zhen’an, Shaanxi Province, central China: climatological implications for the easternmost Paleo-Tethys. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 514:407–422
Deng, X. L. (2020) The boundary of the middle upper Permian and the paleogeographic pattern of the late Maokou formation in northwest Sichuan. Master Dissertation, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, 1–74
Dickson JAD (1966) Carbonate identification and genesis as revealed by staining. J Sediment Petrol 36:491–505
Fang Q, Jing XC, Deng SH, Wang XL (2012) Roadian-Wuchiapingian conodont biostratigraphy at the Shangsi section, northern Sichuan. J Stratigr 36:692–699 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Friedman I, O’Neil JR (1977) Compilation of stable isotope fractionation factors of geochemical interest. In: Fleisher M (ed) Data of Chemistry. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 440-KK:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3133/pp440kk
Garbelli C, Shen SZ, Immenhauser A, Brand U, Buhl D, Wang WQ, Zhang H, Shi GR (2019) Timing of early and middle Permian deglaciation of the southern hemisphere: brachiopod-based 87Sr/86Sr calibration. Earth Planetary Sci Lett 516:122–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2019.03.039
Grossman EL, Yancey TE, Jones TE, Bruckschen P, Chuvashov B, Mazzullo SJ, Mii HS (2008) Glaciation, aridification, and carbon sequestration in the Permo-Carboniferous: the isotopic record from low latitudes. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 268(3–4):222–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.03.053
Halverson GP, Hoffman PF, Schrag DP, Maloof AC, Rice AHN (2005) Toward a Neoproterozoic composite carbon-isotope record. GSA Bull 117(9–10):1181–1207. https://doi.org/10.1130/b25630.1
Haq BU, Schutter SR (2008) A chronology of Paleozoic sea-level changes. Science 322(5898):64–68. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1161648
He B, Xu YG, Wang YM, Xiao L (2005) Nature of the Dongwu movement and its temporal and spatial evolution. Earth Sci 30(1):89–96 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He B, Xu YG, Guan JP, Zhong YT (2010) Paleokarst on the top of the Maokou formation: further evidence for domal crustal uplift prior to the Emeishan flood volcanism. Lithos 119(1–2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-y
Huang SJ (1997) A study on carbon and strontium isotopes of Late Paleozoic carbonate rocks in the Upper Yangtze platform. Acta Geol Sin 71:45–53 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang H, Cawood PA, Hou MC, Ni SJ, Yang JH, Du YS, Wen HG (2018) Provenance of Late Permian volcanic ash beds in South China: implications for the age of Emeishan volcanism and its linkage to climate cooling. Lithos 314:293–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2018.06.009
Huang YG, Chen ZQ, Wignall PB, Grasby SE, Zhao LS, Wang XD, Kaiho K (2019a) Biotic responses to volatile volcanism and environmental stresses over the Guadalupian-Lopingian (Permian) transition. Geology 47(2):175–178. https://doi.org/10.1130/G45283.1
Huang YG, Chen ZQ, Zhao LS, Stanley GD, Yan JX, Pei Y, Yang WR, Huang JH (2019b) Restoration of reef ecosystems following the Guadalupian-Lopingian boundary mass extinction: evidence from the Laibin area, south China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 519:8–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.08.027
Isozaki Y (2009) Illawarra reversal: the fingerprint of a superplume that triggered Pangean breakup and the end-Guadalupian (Permian) mass extinction. Gondwana Res 15:421–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2008.12.007
Isozaki Y, Kawahata H, Minoshima K (2007) The Capitanian (Permian) Kamura cooling event: the beginning of the Paleozoic-Mesozoic transition. Palaeoworld 16(1–3):16–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palwor.2007.05.011
Isozaki Y, Aljinović D, Kawahata H (2011) The Guadalupian (Permian) Kamura event in European Tethys. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 308(1–2):12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.09.034
Jarvis I, Mabrouk A, Moody RT, de Cabrera S (2002) Late Cretaceous (Campanian) carbon isotope events, sea-level change and correlation of the Tethyan and Boreal realms. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 188(3–4):215–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-0182(02)00578-3
Jost AB, Mundil R, He B, Brown ST, Altiner D, Sun YD, DePaolo DJ, Payne JL (2014) Constraining the cause of the end-Guadalupian extinction with coupled records of carbon and calcium isotopes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 396:201–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2014.04.014
Kaufman AJ, Knoll AH (1995) Neoproterozoic variations in the C-isotopic composition of seawater: stratigraphic and biogeochemical implications. Precambr Res 73(1–4):27–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-9268(94)00070-8
Koch JT, Frank TD (2012) Imprint of the Late Palaeozoic Ice Age on stratigraphic and carbon isotopic patterns in marine carbonates of the Orogrande Basin, New Mexico, USA. Sedimentology 59(1):291–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.2011.01258.x
Korte C, Jasper T, Kozur HW, Veizer J (2005) δ18O and δ13C of Permian brachiopods: a record of seawater evolution and continental glaciation. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 224(4):333–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.03.015
Laya JC, Tucker ME, Gröcke DR, Perez-Huerta A (2013) Carbon, oxygen and strontium isotopic composition of low-latitude Permian carbonates (Venezuelan Andes): climate proxies of tropical Pangea. Geol Soc 376(1):367–385. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp376.10 (Special Publications)
Li Q, Xu SL, Chen HD, Lin LB, Yu Y, Sun FR, Dong YX, Deng X (2018) Geochemical characteristics and palaeo-environmental implication of Middle Permian Maokou formation in Wangcang region, Sichuan Basin, China. J Chengdu Univ Technol (sci Technol Edn) 45(3):268–281 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Q, Yang S, Azmy K, Chen HD, Hou MC, Wang ZJ, Xu SL, Yang D, Zhang XH, Chen AQ (2021a) Strontium isotope evolution of Middle Permian seawater in the Sichuan Basin, South China: possible causes and implications. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 56(3–4):110188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.110188
Li Q, Azmy K, Yang S, Xu SL, Yang D, Zhang XH, Chen AQ, Chen HD (2021b) Early-Middle Permian strontium-isotope stratigraphy of marine carbonates from the northern marginal areas of South China: controlling factors and implications. Geol J 56(3):1658–1672. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.4010
Liu C, Jarochowska E, Du YS, Vachard D, Munnecke A (2017) Stratigraphical and δ13C records of Permo-Carboniferous platform carbonates, south China: responses to late Paleozoic icehouse climate and icehouse-greenhouse transition. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 474:113–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.07.038
Lucas SG, Shen SZ (2018) The Permian timescale: an introduction. Geol Soc 450(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp450.15 (Special Publications)
Metcalfe I (2013) Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys. J Asian Earth Sci 66:1–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020
Mii HS, Shi GR, Cheng CJ, Chen YY (2012) Permian Gondwanaland paleoenvironment inferred from carbon and oxygen isotope records of brachiopod fossils from Sydney Basin, southeast Australia. Chem Geol 291:87–103
Mii HS, Shi GR, Wang CA (2013) Late Paleozoic middle-latitude Gondwana environment-stable isotope records from Western Australia. Gondwana Res 24(1):125–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2012.10.013
Miller JF, Repetski JE, Nicoll RS, Nowlan G, Ethington RL (2014) The conodont Iapetognathus and its value for defining the base of the Ordovician System. GFF 136(1):185–188. https://doi.org/10.1080/11035897.2013.862851
Qie WK, Algeo TJ, Luo GM, Herrmann A (2019) Global events of the late Paleozoic (early Devonian to Middle Permian): a review. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 531:109259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109259
Qiu Z, Wang QC, Zou CN, Yan DT, Wei HY (2014) Transgressive-regressive sequences on the slope of an isolated carbonate platform (Middle-Late Permian, Laibin, South China). Facies 60(1):327–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-012-0359-4
Rampino MR, Shen SZ (2019) The end-Guadalupian (259.8 Ma) biodiversity crisis: the sixth major mass extinction? Historical Biol. https://doi.org/10.1080/08912963.2019.1658096
Rees PM, Ziegler AM, Gibbs MT, Kutzbach JE, Behling PJ, Rowley DB (2002) Permian phytogeographic patterns and climate data/model comparisons. J Geol 110(1):1–31. https://doi.org/10.1086/324203
Saitoh M, Isozaki Y, Ueno Y, Yoshida N, Yao J, Ji Z (2013) Middle-Upper Permian carbon isotope stratigraphy at Chaotian, South China: pre-extinction multiple upwelling of oxygen-depleted water onto continental shelf. J Asian Earth Sci 67:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.02.009
Scholle PA, Arthur MA (1980) Carbon isotope fluctuations in Cretaceous pelagic limestones: potential stratigraphic and petroleum exploration tool. Am Asso Petrol Geol Bull 64(1):67–87. https://doi.org/10.1306/2f91892d-16ce-11d7-8645000102c1865d
Scorrer S, Azmy K, Stouge S (2019) Carbon-isotope stratigraphy of the Furongian Berry Head formation (Port au Port Group) and Tremadocian Watts Bight Formation (St. George Group), western Newfoundland, and the correlative significance. Can J Earth Sci 56(3):223–234. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjes-2018-0059
Shellnutt JG (2014) The Emeishan large igneous province: a synthesis. Geosci Front 5:369–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2013.07.003
Shen SZ, Shi GR (2002) Paleobiogeographical extinction patterns of Permian brachiopods in the Asian-western Pacific region. Paleobiology 28:449–463. https://doi.org/10.1666/0094-8373(2002)028%3c0449:pepopb%3e2.0.co;2
Shen SZ, Shi GR (2009) Latest Guadalupian brachiopods from the Guadalupian/Lopingian boundary GSSP section at Penglaitan in Laibin, Guangxi, South China and implications for the timing of the pre-Lopingian crisis. Palaeoworld 18(2–3):152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palwor.2009.04.010
Shen SZ, Zhang YC (2008) Earliest Wuchiapingian (Lopingian, late Permian) brachiopods in southern Hunan, South China: implications for the pre-Lopingian crisis and onset of Lopingian recovery/radiation. J Paleontol 82(5):924–937. https://doi.org/10.1666/07-118.1
Shen SZ, Cao CQ, Zhang H, Bowring SA, Henderson CM, Payne JL, Davydov VI, Chen B, Yuan DX, Zhang YC, Wang W, Zheng QF (2013) High-resolution δ13Ccarb chemostratigraphy from latest Guadalupian through earliest Triassic in South China and Iran. Earth Planet Sci Lett 375:156–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.05.020
Shen SZ, Zhang H, Zhang YC, Yuan DX, Chen B, He WH, Mu L, Lin W, Wang WQ, Chen J, Wu Q, Cao CQ, Wang Y, Wang XD (2019) Permian integrative stratigraphy and timescale of China. Sci China Earth Sci 62(1):154–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-017-9228-4
Shen SZ, Yuan DX, Henderson CM, Wu Q, Zhang YC, Zhang H, Mu L, Ramezani J, Wang XD, Lambert LL, Erwin DH, Hearst JM, Xiang L, Chen B, Fan JX, Wang Y, Wang WQ, Qi YP, Chen J, Qie WK, Wang TT (2020) Progress, problems and prospects: an overview of the Guadalupian series of south China and North America. Earth Sci Rev 221:103412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103412
Shi L, Feng QL, Shen J, Ito T, Chen ZQ (2016) Proliferation of shallow-water radiolarians coinciding with enhanced oceanic productivity in reducing conditions during the Middle Permian, South China: evidence from the Gufeng Formation of western Hubei Province. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 444:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.11.031
Shi ZJ, Li WJ, Luo QC, Zhang J, Wang Y, Tian YM, Yin G (2020) Emeishan mantle plume activity and carbon isotope responses in the Middle Permian, South China. J Asian Earth Sci 189(1–8):104145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104145
Shields GA, Mills BJW (2017) Tectonic controls on the long-term carbon isotope mass balance. Proc of Natl Acad Sci 114(17):4318–4323. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1614506114
Stampfli G, Borel G (2002) A plate tectonic model for the Paleozoic and Mesozoic constrained by dynamic plate boundaries and restored synthetic oceanic isochrons. Earth Planet Sci Lett 196:17–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(01)00588-x
Veizer J (1983) Chemical diagenesis of carbonates: theory and application. Stable Isot Sediment Geol 10:3–100. https://doi.org/10.1306/212f7df6-2b24-11d7-8648000102c1865d
Veizer J, Ala D, Azmy K, Bruckschen P, Buhl D, Bruhn F, Carden GAF, Diener A, Ebneth S, Godderis Y, Jasper T, Korte C, Pawellek F, Podlaha OG, Strauss H (1999) 87Sr/86Sr, δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater. Chem Geol 161(1–3):59–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(99)00081-9
Wang Y, Jin YG (2000) Permian palaeogeographic evolution of the Jiangnan basin, South China. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 160(1–2):35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-0182(00)00043-2
Wang LL, Azmy K (2020) Palaeoenvironmental changes in slope carbonates across the late Cambrian-early Ordovician in western Newfoundland. Geol J 55(5):3451–3463. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3602
Wang CS, Li XH, Chen HD, Tian JX (1999) Permian sea-level changes and rising-falling events in South China. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica 17(4):536-541 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang W, Cao CQ, Wang Y (2004) The carbon isotope excursion on GSSP candidate section of Lopingian-Guadalupian boundary. Earth Planet Sci Lett 220(1–2):57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(04)00033-0
Wang WQ, Garbelli C, Zhang FF, Zheng QF, Zhang YC, Yuan DX, Shi YK, Chen B, Shen SZ (2020) A high-resolution Middle to Late Permian paleotemperature curve reconstructed using oxygen isotopes of well-preserved brachiopod shells. Earth Planet Sci Lett 540:116245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116245
Wei HY, Wei XM, Qiu Z, Song HY, Shi G (2016) Redox conditions across the G-L boundary in South China: evidence from pyrite morphology and sulfur isotopic compositions. Chem Geol 440:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.07.009
Xiao D, Cao J, Luo B, Zhang Y, Xie C, Chen SL, Gao GH, Tan XC (2020a) Mechanism of ultra-deep gas accumulation at thrust fronts in the Longmenshan mountains, lower Permian Sichuan Basin, China. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 83:103533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103533
Xiao D, Cao J, Luo B, Tan XC, Liu H, Zhang BJ, Yang X, Li Y (2020b) On the dolomite reservoirs formed by dissolution: differential eogenetic versus hydrothermal in the lower Permian Sichuan Basin, southwestern China. Am Asso Petrol Geol Bull 104(7):1405–1438. https://doi.org/10.1306/02262018242
Xie SC, Algeo TJ, Zhou WF, Ruan XY, Luo GM, Huang JH, Yan JX (2017) Contrasting microbial community changes during mass extinctions at the middle/late Permian and Permian/Triassic boundaries. Earth Planet Sci Lett 460:180–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.12.015
Xu YG, Chung SL, Shao H, He B (2010) Silicic magmas from the Emeishan large igneous province, Southwest China: petrogenesis and their link with the end-Guadalupian biological crisis. Lithos 119:47–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2010.04.013
Xu H, Zhou W, Cao Q, Xiao C, Zhou QM, Zhang HT, Zhang YY (2018) Differential fluid migration behaviour and tectonic movement in lower silurian and lower Cambrian shale gas systems in China using isotope geochemistry. Mar Pet Geol 89:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.03.027
Yao X, Zhou YQ, Hinnov LA (2015) Astronomical forcing of a middle Permian chert sequence in Chaohu, South China. Earth Planet Sci Lett 422:206–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.04.017
Yin HF, Song HJ (2013) Mass extinction and Pangea integration during the Paleozoic-Mesozoic transition. Sci China Earth Sci 56(11):1791–1803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-013-4624-3
Yu H, Wei HY (2015) A Kungurian oceanic upwelling on Yangtze platform: evidenced by δ13Corg and authigenic silica in the lower Chihsia formation of Enshi section in south China. Journal of Earth Science 26(2):211–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0533-z
Yu Y, Lin L, Deng X, Wang Y, Li Y, Guo Y (2020) Geochemical features of the middle-upper Permian cherts and implications for origin, depositional environment in the Sichuan Basin. SW China Geol J 55(2):1493–1506. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3511
Zhang YZ, Xu SL, Chen HD, Lin LB, Dong YX, Yu Y, Zhang Y (2018) Geochemical characteristic and paleo-environmental implications of Middle Permian Qixia Formation in Wangcang, north Sichuan. Petr Geol Exp 40(2):210–217 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang BL, Yao SP, Mills BJW, Wignall PB, Hu WX, Liu B, Ren YL, Li LL, Shi G (2020) Middle Permian organic carbon isotope stratigraphy and the origin of the Kamura Event. Gondwana Res 79:217–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2019.09.013
Zhou JG, Yao GS, Yang G, Gu MF, Yao QY, Jiang QC, Yang L, Yang YR (2016) Lithofacies paleogeography and favorable gas exploration zones of Qixia and Maokou Fms in the Sichuan Basin. Nat Gas Ind B 3(3):226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ngib.2016.05.007
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the four anonymous reviewers whose comments/suggestions helped improve and clarify this manuscript. The authors thank Drs. Zhi-Qiang Shi, James Ogg, Zhong-Qiang Chen, Sheng-Xian Zhu, Guo-Qiang Luan, Jie Li and Xin Jin for their valuable and constructive suggestions during the performance of this research work. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 41872109), the Everest Scientific Research Program of Chengdu University of Technology (grant no. 2020ZF11402), and the Open Fund (grant no. PLC20180507) of the State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation (Chengdu University of Technology).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant/award numbers: 41402104 and 41602118; Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation (Chengdu University of Technology), grant/award numbers: PLC20180507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13146_2021_743_MOESM1_ESM.xlsx
Supplementary file1 Elemental and isotopic geochemical compositions of Luduba section carbonates. Values preceded by the sign “<” are below the detection limit (XLSX 5675 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Azmy, K., Yang, S. et al. Early-Middle Permian carbon-isotope stratigraphy of marine carbonates in the northern edge of the South China: implications for global correlation. Carbonates Evaporites 37, 1 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00743-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00743-4