Abstract
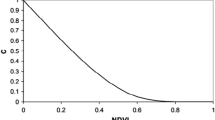
To study the influence of rainfall on soil and water loss in karst rocky desertification region, the characteristics and correlations of rainfall, runoff and sediment yield were analyzed under 56 erosive rainfalls from April 2018 to August 2019 in Guanling–Huajiang rocky desertification region of southwestern China. The results showed that the erosive rainfall is mainly rainfall in the study area, and rainstorm’s frequencies and accumulated rainfall were the most in the five erosive rainfalls. Increasing vegetation coverage or reducing bedrock bare rate could effectively reduce the amount of soil and water loss in runoff plots. The rainfall-runoff depth in the runoff plot linearly increased with the increase of rainfall. With the increase of the rainfall kinetic energy, the sediment yield modulus increased approximately linearly, and the relevance of rainfall-sediment yield was weaker than that of rainfall runoff. With the increase of surface runoff, soil loss first increased and then gradually stabilized. The runoff sediment carrying capacity gradually increased with the decrease of vegetation coverage and the increase of bedrock exposure rate. These study results are expected to provide guidance for the control of soil erosion in karst rocky desertification region.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Y, Liu Q, Gu Z et al (2017) The dissolution mechanism and karst development of carbonate rocks in karst rocky desertification area of Zhenfeng–Guanling–Huajiang County, Guizhou, China. Carbonate Evaporite 9:1–7
Cai X, Wang J, An Y, et al (2010) Laboratorial simulation on soil erosion under different vegetation coverage in Southwest Karst Area, [C]//China. IEEE 1–5.
Cai H, Yang X, Wang K et al (2014) Is forest restoration in the southwest China karst promoted mainly by climate change or human-induced factors. Remote Sens 6(10):9895–9910
Dai Q, Peng X, Yang Z et al (2017) Runoff and erosion processes on bare slopes in the Karst Rocky Desertification Area. Catena 152:218–226
Feng Q, Ma H, Jiang X et al (2015) What Has caused desertification in China. Sci Rep 5:1–8
Fu XT (2012) Research on slope length effect on runoff and sediment yield and dynamics processes. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, pp 23–25
Gu LB, Zhang XQ, Yang GX et al (2015) Characteristics of slope runoff and sediment production under rainfall events in the plateau area of western Guizhou. Sci Soil Water Conserv 13(1):23–28
Hu K, Chen H, Nie Y et al (2015) Seasonal recharge and mean residence times of soil and epikarst water in a small karst catchment of southwest China. Sci Rep 5:1–12
Kheir RB, Abdallah C, Khawlie M (2008) Assessing soil erosion in Mediterranean karst landscapes of Lebanon using remote sensing and GIS. Eng Geol 99(3–4):239–254
Licznar P, Nearing MA (2003) Artificial neural networks of soil erosion and runoff prediction at the plot scale. Catena 51(2):89–114
Liu Q, Gu ZF, Lu YR et al (2015) Weathering processes of the dolomite in Shibing (Guizhou) and formation of collapse and stone peaks. Environ Earth Sci 74(2):1823–1831
Liu Q, Deng DP, Yao BJ et al (2020) Analysis of the karst springs’ supply sources in rocky desertification area of Guanling-Huajiang, Guizhou China. Carbonate Evaporite 35(90):1–11
Lu Y (2010) Karst in China—a world of improbable peaks and wonderful caves. Higher Education Press, Beijing, pp 36–37
Luo W, Jiang Z, Yang Q et al (2018) The features of soil erosion and soil leakage in karst peak-cluster areas of Southwest China. J Groundw Sci Eng 6(1):18–30
Ma Y, Xie HH, Li C (2014) experimental analysis on runoff and sediment from sloping lands in Karst Region. Adv Mater Res 1073–1076:1624–1629
Mariano MH, José MN, Luis MM et al (2010) Plot scale effects on runoff and erosion along a slope degradation gradient. Water Resour Res 46(4):475–478
Munroe JS, Farrugia G, Ryan PC (2007) Parent material and chemical weathering in alpine soils on Mt. Mansfield, Vermont, USA. Catena 70(1):39–48
Piedallu C, Guégout J, Bruand A et al (2011) Mapping soil water holding capacity over large areas to predict the potential production of forest stands. Geoderma 160(3):355–366
Tang Y, Sun K, Zhang X et al (2016) Microstructure changes of red clay during its loss and leakage in the karst rocky desertification area. Environ Earth Sci 75(6):537
Wei W, Chen L, Fu B et al (2007) The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China. J Hydrol 335(3–4):247–258
Wu XQ, Cai YL, Zhou T (2011) Effects of Land Use/Land cover changes on rocky desertification-a case study of a small karst catchment in southwestern China. Energy Procedia 5(22):1–5
Wu Q, Han G, Tao F et al (2012) Chemical composition of rainwater in a karstic agricultural area, Southwest China: the impact of urbanization. Atmos Res 111:71–78
Xie Y, Liu YB, Zhang WB (2000) Study on standard of erosive rainfall. J Soil Water Conserv 14(4):6–11 (in Chinese)
Xie LW, Zhong J, Chen FF et al (2015) Evaluation of soil fertility in the succession of karst rocky desertification using principal component analysis. Solid Earth 6(2):515–524
Xiong X, Li J, Zhang T et al (2021) Simulation of coupled transport of soil moisture and heat in a typical karst rocky desertification area, Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:4716–4730
Yan DC, Zhang XB, Wen AB et al (2012) Assessment of sediment yield in a small karst catchment by using 137Cs tracer technique. Int J Sedim Res 27(4):547–554
Yan Y, Dai QH, Yuan YF et al (2018) Effects of rainfall intensity on runoff and sediment yields on bare slopes in a karst area, SW China. Geoderma 330:30–40
Ying B, Xiao S, Xiong K et al (2014) Comparative studies of the distribution characteristics of rocky desertification and land use/land cover classes in typical areas of Guizhou province, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(2):631–645
Zhang WY, Wang BT, Yang GX et al (2014) Erosive rainfall and characteristics analysis of sediment yield on yellow soil area in karst mountainous. Ecol Environ Sci 23(11):1776–1782
Zheng Y, Yu G, Qian Y et al (2002) Simulations of regional climatic effects of vegetation change in China. Q J R Meteorol Soc 128(584):2089–2114
Zheng HJ, Yang J, Zuo CQ et al (2009) Analysis of the erosive rainfall and rainfall erosion energy on red-soil slopeland. Res Soil Water Conserv 16(03):30–33 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by research of the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0502603) and Grant 41772292 from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the 15th experimental teaching reform project of Tongji University (0200104457).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Deng, D., Liao, Q. et al. Analysis on the influence of rainfall characteristics on soil and water loss in rocky desertification region. Carbonates Evaporites 36, 77 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00742-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-021-00742-5