Abstract
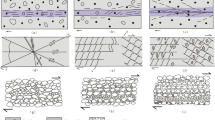
Karst-related issues have become serious in the Three Gorges reservoir area, where the bank slopes consist of marlite. In this paper, the mineralogical and petrological properties and internal micro-structure development mechanism of the marlite were analyzed to determine its dissolution and weathering characteristics. In addition, the application of high-power electron microscopy identified micro-cracks in the marlite and micro-dissolution vugs on both sides of the micro-cracks. Montmorillonite was shown to be the dominant clay mineral accumulated at the edges of the vugs. Based on the test results of the rock mechanics and the natural dissolution processes, the concept of dissolution coefficient was proposed to describe the strength change pattern of the marlite. Next, the change pattern between the dissolution and strength weakening of the marlite was characterized with the typical four stages of rock compression and deformations. It was also shown that long-term water–rock interactions resulted in unique deformation characteristics in the slopes, while, vertically, the slope bodies could be divided into a strong dissolution zone, medium dissolution zone, and weak dissolution zone.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao H, Zhai Y, Lan H, Zhang KK, Qi Q, Yan CG (2019) Distribution characteristics and controlling factors of vertical joint spacing in sand-mud interbedded strata. J Struct Geol 128:103886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2019.103886
Bian K, Liu J, Zhang W, Zheng XQ, Ni SH, Liu ZP (2019) Mechanical behavior and damage constitutive model of rock subjected to water-weakening effect and uniaxial loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(1):97–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1580-4
Chen ZY (2006) The influences of water–rock interaction on the strength of limestone rock mass in the limestone in Jin Sha Zhou section of line 6 of Guangzhou underground railway. Guangzhou Archit 5:62–65 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cheng YG (2016) Mechanism analysis of water–rock interaction for slope failure. Subgrade Eng 1:3–5 (in Chinese)
Deng HF, Hu AL, Li JL, Zhang XJ, Hu Y, Chang DL, Zhu M (2017) Statistical damage constitutive model of sandstone under water–rock interaction. Rock Soil Mech 38(3):631–639 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Duperret A, Taibi S, Mortimore RN, Daigneault M (2005) Effect of groundwater and sea weathering cycles on the strength of chalk rock from unstable coastal cliffs of NW France. Eng Geol 78:321–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.01.004
Eang KE, Igarashi T, Kondo M, Nakatani T, Tabelin CB, Fujinaga R (2018) Groundwater monitoring of an open-pit limestone quarry: water–rock interaction and mixing estimation within the rock layers by geochemical and statistical analyses. Int J Min Sci Technol 28:849–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2018.04.002
Erguler ZA, Ulusay R (2009) Water-induced variations in mechanical properties of clay-bearing rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):355–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.07.002
Gao F, Zhou KP, Luo XW, Zhai JB (2012) Effect of induction unloading on weakening of rock mechanics properties. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 22(2):419–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61193-X(English Edition)
Guo JQ, Liu XL, Qiao CS (2014) Experimental study of mechanical properties and energy mechanism of karst limestone under natural and saturated states. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 33(2):296–308 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He CM, Guo JC (2013) Mechanism study of acid on mechanical properties of limestone. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 32(2):3016–3021 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He MC, Wu X, Lu C (2003) Research on experimental method for identification of rock body within sliding masses of landslide. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 22(4):630–632 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang D, Gu DM (2017) Influence of filling-drawdown cycles of the Three Gorges reservoir on deformation and failure behaviors of anaclinal rock slopes in the Wu Gorge. Geomorphology 295:489–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.07.028
Lebedev M, Wilson MEJ, Mikhaltsevitch V (2014) An experimental study of solid matrix weakening in water-saturated Savonnieres limestone. Geophys Prospect 62:1253–1265. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2478.12168
Liu HY, Li ZX, Fang QH, Hu XH, Lv DW (2008) Analysis the Karst form character of marlite under 5%HCl condition—a case study from the marlite of middle Triassic Badong group in Fengjie area, Sichuan provience. Carsologica Sinica 27(4):377–381 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu XS, Ning JG, Tan YL, Gu QH (2016) Damage constitutive model based on energy dissipation for intact rock subjected to cyclic loading. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 85:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.03.003
Lu YL, Wang LG, Sun XK, Wang J (2017) Experimental study of the influence of water and temperature on the mechanical behavior of mudstone and sandstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 76:645–660. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-016-0851-0
Patrick B, Zhu WL, Wong TF (2000) Failure mode and weakening effect of water on sandstone. J Geophys Res 105(B7):16371–16389. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000jb900087
Qi SW, Yue ZQ, Wu FQ, Chang ZH (2009) Deep weathering of a group of thick argillaceous limestone rocks near Three Gorges reservoir, Central China. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46:929–939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.03.006
Shen BT (2014) Coal mine roadway stability in soft rock: a case study. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47:2225–2238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-013-0528-y
Sun GH, Zheng H, Huang YY, Li CG (2016) Parameter inversion and deformation mechanism of Sanmendong landslide in the Three Gorges reservoir region under the combined effect of reservoir water level fluctuation and rainfall. Eng Geol 205:133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.10.014
Tugrul A, Zarif IH (2000) Engineering aspects of limestone weathering in Istanbul, Turkey. Bull Eng Geol Environ 58:191–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100640050075
Wang ZQ, Zhang LM, Sun H (2010) Experimental research on mechanical properties’ of limes containing natural joints under loading and unloading conditions. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 29(1):3308–3313 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang GL, Li TL, Xing XL, Zou Y (2015) Research on loess flow-slides induced by rainfall in July 2013 in Yan’an, NW China. Environ Earth Sci 73:7933–7944. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3951-9
Wu S, Liu YR, Li SJ (2013) Test and models of the mechanical properties of limestone under triaxial compression. J Yangtze River Sci Res Inst 30(3):30–34 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu J, Zhang JS, Liu TY (2019) Mesoscopic weakening feature of marble during water rock interaction. Geotech Geol Eng 37:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-0596-6olV)
Yang XQ, Liang WG, Yu YM, Zhang CD, Yu WD, Zhao YS (2014) Mechanical property weakening and the meso-mechanism of hard dissolved salt rock soaked in brine. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 33(1):134–143 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yao HY, Feng XT, Cui Q, Shen LF, Zhou H, Cheng CB (2009a) Experimental study of effect of chemical corrosion on strength and deformation of hard brittle limestone. Rock Soil Mech 30(2):338–344 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yao HY, Feng XT, Cui Q, Zhou H (2009b) Meso-mechanical experimental study of meso-fracturing process of limestone under coupled chemical corrosion and water pressure. Rock Soil Mech 30(1):59–67 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang JG (2004) Variation of mechanical property of marlite in process of karstification and weathering in Three Gorges region. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 23(7):1073–1077 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang JG (2005) Analysis on catastroph by karst weathering of marly limestone in population resettlement region of the Three Gorges. Carsologica Sinica 24(3):239–244 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang JZ, Miao LC, Yang ZF (2008) Research on rock degradation and deterioration mechanisms and mechanical characteristics under cyclic freezing-thawing. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 27(8):1688–1694 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang HQ, Xu JF, He YN, Han LJ, Jiang BS, Shao P (2012) Study of laboratory scale effect of limestone under uniaxial compression. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31(2):3491–3496 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang S, Xu Q, Hu ZM (2016) Effects of rainwater softening on red mudstone of deep-seated landslide, Southwest China. Eng Geol 204:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.01.013
Zhang JY, Wan LP, Pan HY, Li JL, Luo ZS, Deng HF (2017) Long-term stability of bank slope considering characteristics of water–rock interaction. Chin J Geotech Eng 39(10):1851–1858 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YC, Deng HF, Wang W, Duan LL, Zhi YY, Li JL (2018) The dynamic response law of bank slope under water–rock interaction. Adv Civ Eng 2018:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/1306575
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the research and innovation team support plan of Shandong University of Science and Technology (2018TDJH101) and the Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Depositional Mineralization & Sedimentary Mineral (DMSM201401).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Li, Z., Zhang, Y. et al. The weakening mechanisms of the rock mechanics of marlite bank slopes under water–rock interaction conditions. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 60 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00595-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00595-4