Abstract
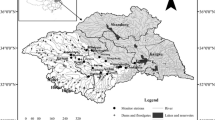
The Dawu water source is the most important urban water supply source in Zibo City, Shandong Province, China. In this paper, the karst water level, precipitation, exploitation and flood discharge data during 2012–2018 were used to study and explore the characteristics and factors that control and influence the dynamic evolution of the karst water level in the Dawu water source area. The results showed that the dynamic evolution of the karst water level from 2012 to 2018 can be divided into three stages: (1) from 2012 to 2013, the karst water levels were relatively stable and maintained at approximately 36 m. (2) However, the karst water levels decreased from 30.5 to 4.2 m with a decline rate of 6.58 m/a from 2014 to 2017, and the rapid decrease caused a change in the runoff of the karst water flow field. (3) The karst water flow was restored to the original mode of south to north flow with the increase in the karst water level in 2018. The results of the correlation analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis showed that flood discharge, precipitation and exploitation all influence karst water level dynamic changes in the Dawu water source area. Among them, the increase in exploitation was the main reason for the karst water level decline, the flood discharge from the Taihe reservoir is the most direct and effective recharge source. The results of the principal component analysis showed that the influencing intensity of the three factors was constantly changing with time. The main factor that influenced the karst water level dynamic changes in the Dawu water source area was flood discharge in 2012 and 2013, exploitation in 2015 and 2016 and precipitation in 2018. Although in 2014 and 2017, the main factors were the combination of precipitation, exploitation and flood discharge.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barthel R, Rojanschi V, Wolf J (2016) Groundwater contour maps for the alluvial aquifers of the Upper Danube Basin, pp 207–213. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-16751-0_26
Brenner S, Coxon G, Howden NJK, Freer J, Hartmann A (2018) Process-based modelling to evaluate simulated groundwater levels and frequencies in a Chalk catchment in south-western England. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 18:445–461. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-18-445-2018
Carretero SC, Kruse EE (2012) Relationship between precipitation and water–table fluctuation in a coastal dune aquifer: northeastern coast of the Buenos Aires province, Argentina. Hydrogeol J 20:1613–1621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-012-0890-y
Chen Y, Zhu X, Zhu X (1999) Evolution of the groundwater flow field and its influencing factors in the Dawu water source area of Zibo City. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 3:32–47. https://doi.org/10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.1999.03.011
Dai R (1989) The water resources of the Dawu water source are gradually weakening. Qilu Petrochem Technol 3:74–75
Eltarabily MG, Negm AM, Yoshimura C, Takemura J (2018) Groundwater modeling in agricultural watershed under different recharge and discharge scenarios for quaternary aquifer Eastern Nile Delta, Egypt. Environ Model Assess 23:289–308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10666-017-9577-z
Gao Z, Sun J, Lu T, Wang X, Yang L, Liu Z (2019) Types and assessment of organic pollutants in groundwater of Dawu source area in Zibo. J Shandong Univ Sci Technol (Nat Sci) 38:1–9. https://doi.org/10.16452/j.cnki.sdkjzk.2019.04.001
Giri A, Bharti VK, Kalia S, Kumar K, Raj T, Chaurasia OP (2019) Utility of multivariate statistical analysis to identify factors contributing river water quality in two different seasons in cold-arid high-altitude region of Leh-Ladakh. India Appl Water Sci 9(2):26–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-019-0902-3
Guo W, Zhao J, Yin L, Kong D (2016) Simulating research on pressure distribution of floor pore water based on fluid–solid coupling. Arab J Geosci 10(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2770-6
Haque MN, Keramat M, Shahid S, Mohsenipour M, Wang XJ (2017) Groundwater dynamics and balance in the western part of Greater Kushtia District of Bangladesh. KSCE J Civ Eng 21(5):1595–1606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0801-1
Howladar MF, Al Numanbakth MA, Faruque MO (2017) An application of Water Quality Index (WQI) and multivariate statistics to evaluate the water quality around Maddhapara Granite Mining Industrial Area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ Syst Res 6(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-017-0090-9
Keshavarzi M, Baker A, Kelly BFJ, Andersen MS (2017) River–groundwater connectivity in a karst system, Wellington, New South Wales, Australia. Hydrogeol J 25:557–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1491-y
Lee S, Lee KK, Yoon H (2019) Using artificial neural network models for groundwater level forecasting and assessment of the relative impacts of influencing factors. Hydrogeol J 27:567–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1866-3
Li Y (2018) Study on groundwater evolution under changing enviroment in Zhongmou county. North China University of Water resources and Electric Power
Li M, Wang W, Ren S, Wang J, Li J (2014) Screening typical pollutants by modified comprehensive evalution method: a case study of typical pollutants screening in groundwater of Dawu water source. Environ Pollut Control 36:72–77. https://doi.org/10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2014.11.015
Li H, Ma C, Zhou WB, Yan Q, Song Y (2018) Characterizing the evolution of groundwater flow field and its driving forces in Xi'an, China. J Hydrol Eng 23(8):11. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)he.1943-5584.0001668
Li C, Zhang X, Gao X, Qi S, Wang Y (2019) The potential environmental impact of PAHs on soil and water resources in air deposited coal refuse sites in Niangziguan Karst Catchment, Northern China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:1368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081368
Lin P, Li SC, Xu ZH, Wang J, Huang X (2019) Water Inflow Prediction during Heavy Rain While Tunneling through Karst Fissured Zones. Int J Geomech 19(8):10. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0001478
Liu J, Xie X, Ma Z, Fang G, He H, Du M (2018a) A multiple-iterated dual control model for groundwater exploitation and water level based on the optimal allocation model of water resources. Water 10:28. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040432
Liu Z, Zhao Y, Han Y, Wang C, Wang F (2018b) Driving factors of the evolution of groundwater level in People's Victory Canal Irrigation District, China. Desalin Water Treat 112:325–333. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2018.22334
Liu J, Gao Z, Wang M, Li Y, Shi M, Zhang H, Ma Y (2019) Hydrochemical characteristics and possible controls in the groundwater of the Yarlung Zangbo River Valley, China. Environ Earth Sci 78:76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8101-y
Lv C, Ling M, Wu Z, Gu P, Guo X, Di D (2019) Analysis of groundwater variation in the Jinci Spring area, Shanxi Province (China), under the influence of human activity. Environ Geochem Health 41:921–928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0189-6
Meng FW, Zhang Z, Yan X, Ni P, Liu WH, Fan F, Xie GW (2017) Stromatolites in Middle Ordovician carbonate–evaporite sequences and their carbon and sulfur isotopes stratigraphy, Ordos Basin, northwestern China. Carbonates Evaporites 34(33):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-017-0367-0
Pathak AA, Dodamani BM (2019) Trend analysis of groundwater levels and assessment of regional groundwater drought: Ghataprabha River Basin, India. Nat Resour Res 28:631–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-018-9417-0
Patle GT, Singh DK, Sarangi A, Rai A, Khanna M, Sahoo RN (2015) Time series analysis of groundwater levels and projection of future trend. J Geol Soc India 85:232–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-015-0209-4
Qi X, Yang L, Han Y, Shang H, Xing L (2012) Cross wavelet analysis of groundwater level regimes and precipitation-groundwater level regime in Ji’nan Spring Region. Adv Earth Sci 27:969–978. https://doi.org/10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2012.09.0969
Seferli S, Modis K, Adam K (2019) Interpretation of groundwater hydrographs in the West Thessaly basin, Greece, using principal component analysis. Environ Earth Sci 78:257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8262-8
Shang Y (2013) Study on karst water level dynamic change for many years of Dawu water resource area in Zibo city Shandong. Land Resour 29:44–47. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2013.09.010
Shi M, Gao Z, Feng J, Zhang H, Cui Y, Fang S, Liu J (2019a) Characteristics and effects of fluorine release from shallow high-fluoride soils. Environ Earth Sci 78:604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8618-0
Shi M, Gao Z, Wan L, Guo H, Zhang H, Liu J (2019b) Desalination of saline groundwater by a weakly permeable clay stratum: a case study in the North China Plain. Environ Earth Sci 78:547. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8558-8
Shi S, Wei J, Xie D, Yin H, Zhang W, Li L (2019c) An attribute recognition model to predict the groundwater potential of sandstone aquifers in coal mines. J Earth Syst Sci 128:72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1100-2
Viaroli S, Di Curzio D, Lepore D, Mazza R (2019) Multiparameter daily time-series analysis to groundwater recharge assessment in a caldera aquifer: Roccamonfina Volcano, Italy. Sci Total Environ 676:501–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.327
Wang J, Xu G (1994) System analysis of Dawu water supply base in Zibo city, Shandong province. Syst Eng Theory Pract 14:15–19. https://doi.org/10.12011/1000-6788(1994)10-15
Wang X, He X, Qi F (2019) Dynamic Analysis and Relationship Research on Precipitation and Groundwater Depth in Zhenlai County. In: 4th International conference on advances in energy resources and environment engineering, vol 237. IOP Conference Series-Earth and Environmental Science. IOP Publishing Ltd, Bristol. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/237/2/022035
Wu Y, Bian N (2003) Optimization analysis of groundwater monitoring network of a karst aquifer. Earth Sci Front 10:637–643. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.030
Wu Q, Xing L, Ye C, Liu Y (2011) The influences of coal mining on the large karst springs in North China. Environ Earth Sci 64:1513–1523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0376-y
Wu Q, Guo Y, Zhai Y, Yin Z, Zhao H, Zhang J, Li C (2017) Dynamic variation characteristics of NO3–N in groundwater of Dawu water source and influencing factors. J China Hydrol 37:68–73. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2017.06.012
Xing Y, Dou M, Zhang Z, Fu B, Zhang Y (2008) Dynamic analysis and water quality evaluation of groundwater in Dawu headwaters ground. Henan Sci 26:80–87. https://doi.org/10.13537/j.issn.1004-3918.2008.01.014
Xing L, Huang L, Chi G, Yang L, Li C, Hou X (2018) A dynamic study of a Karst Spring based on wavelet analysis and the Mann–Kendall Trend Test. Water 10:698. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10060698
Yang Q, Wang Y, Zhang J, Martin J (2015) Stochastic simulation of groundwater dynamics based on grey theory and seasonal decomposition model in a coastal aquifer of South China. J Water Suppl Res Technol Aqua 64:947–957. https://doi.org/10.2166/aqua.2015.047
Yang W et al (2018) experimental study of influence of Karst Aquifer on the law of water inrush in tunnels. Water 10:1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091211
Yin H, Shi Y, Niu H, Ma C, Liu G, Zhai P, Zhang J (2018) Characteristics, detection, and prevention of karst sinkholes: a case study in Laiwu iron ore mine areas, Shandong Province. China Environ Earth Sci 77:136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7310-0
Yin H, Zhao H, Xie D, Sang S, Shi Y, Tian M (2019) Mechanism of mine water inrush from overlying porous aquifer in Quaternary: a case study in Xinhe Coal Mine of Shandong Province. China Arab J Geosci 12:163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4325-0
Zhang X, Liu Y, Zhou L (2018) Correlation analysis between landscape metrics and water quality under multiple scales. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15081606
Zhang H, Gao Z, Shi M, Fang S, Xu H, Cui Y, Liu J (2019) Study of the effects of land use on hydrochemistry and soil microbial diversity. Water 11:466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11030466
Zhao Z, Jia Z, Guan Z, Xu C (2019) The effect of climatic and non-climatic factors on groundwater levels in the Jinghuiqu Irrigation District of the Shaanxi Province. China Water 11:18. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050956
Zhu X, Liu J (2001) Numerical study of contaminants transport in fracture-karst water in Dawu well field, Zibo city, Shandong province. Earth Sci Front 8:171–178. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2001.01.022
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41641022 and No. 40772145), the International Visiting Foundation (No. 0103014) and the Graduate Technology Innovation Foundation (No. SDKDYC180317) of Shandong University of Science and Technology and the Shandong Geological Survey (No. SDLR-2017-138). The authors are grateful to colleagues and friends who shared their meteorological and hydrological data with us.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Zhang, H., Feng, J. et al. Dynamic evolution of karst water levels and its controlling and influencing factors in Northern China: a case study in the Dawu water source area. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 47 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00585-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00585-6