Abstract
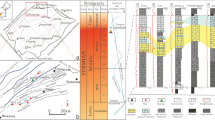
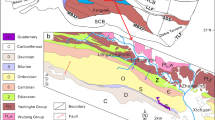
Dolomite is the most important component of the prolific reservoirs in the Ma55 to Ma51 submembers of the Ordovician Majiagou Formation in the central Yishan Slope, Ordos Basin. However, the origins of the different types of dolomite are unclear because of the different diagenetic environments and complex diagenetic fluids. This paper mainly focuses on the diagenetic environment and diagenetic fluid associated with the dolomite. The petrographic features of the dolomite were studied on the basis of core observation and thin section identification. Geochemical characteristics were analyzed according to the O, C and Sr stable isotopes and major and trace elements. The results demonstrate that, petrographically, the dolomite can be divided into four types, namely, type 1, type 2, type 3 and type 4. Type 1 is mainly characterized by dolomite with gypsum and salt dissolution as well as breccia structures with no clay minerals filling between breccia clasts. Type 2 is characterized by powder-fine crystalline dolomite with apparent residual textures and residual intergranular and intercrystal pores. Type 3 is characterized by leopard limestone or dolomite with leopard textures and massive bioborings. Finally, type 4 is characterized by karst breccia dolomite with many fractures and caves filled by abundant terrigenous clay minerals. In combination with the petrographic data, analysis of the geochemical data reveals that the type 1 dolomite formed in an early near-surface diagenetic environment and the diagenetic fluid might have been early freshwater. Type 2 and type 3 dolomite formed in a shallow-burial diagenetic environment. The diagenetic fluid of type 2 dolomite might have been hypersaline brine that was influenced by freshwater, but that of type 3 dolomite might have been a mixed fluid consisting of seawater and freshwater, which was less saline than the type 2 dolomite fluid. Type 4 dolomite formed in an epidiagenetic near-surface environment and the diagenetic fluid might have been superficial freshwater carrying abundant terrigenous clay minerals. The study shows that the analysis of the diagenetic environment and fluid of dolomite has great significance for research on dolomite origins. The porosity and permeability values of the four types of dolostone reservoirs indicate that type 1 dolomite reservoirs are the best reservoir, type 2 dolomite reservoirs have good physical properties, type 4 dolomite reservoirs are relatively good reservoirs, and the worst reservoir is the type 3 dolomite reservoirs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JE, Rhodes ML (1960) Dolomitization by seepage refluxion. Bull Am Assoc Pet Geol 44:1912–1920
Alhelal AB, Whitaker FF, Spycher N, Xiao Y (2012) Modeling brine reflux using the Pitzer ion-interaction model in Toughreact. In: Proceedings of the TOUGH Symposium. Lawrence Berkeley Notional Laboratory, Berkeley, California, pp 841–847
Allan JR, Matthews RK (1982) Isotope signatures associated with early meteoric diagenesis. Sedimentology 29:797–817
Allan JR, Wiggins WD (1993) Dolomite reservoirs- geochemical techniques for evaluating origin and distribution. AAPG 36:129
Al-Aasm IS (2000) Chemical and isotopic constraints for recrystallization of sedimentary dolomites from the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. Aquat Geochem 6:227–248
Banner JL, Hanson GN, Meyers WJ (1988) Determination of initial Sr isotopic compositions of dolostones from the Burlington-Keokuk Formation (Mississippian) constraints from cathodoluminescence, glauconite paragenesis, and analytical methods. J Sediment Res 58:673–687
Bao HP, Yang F, Cai ZH, Wang QP, Wu CY (2017) Origin and reservoir characteristics of Ordovician dolostones in the Ordos Basin. Nat Gas Ind 37:32–46 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Braithwaite CJR (1991) Dolomites, a review of origins, geometry and textures. Earth Environ Sci Trans R Soc Edinb 82:99–112
Budd DA (1997) Cenozoic dolomites of carbonate islands: their attributes and origin. Earth Sci Rev 42:1–47
Carballo JD, Land LS, Miser DE (1987) Holocene dolomitization of supratidal sediments by active tidal pumping, Sugarloaf Key, Florida. J Sediment Pet 57:153–165
Chappell J, Shackleton NJ (1986) Oxygen isotopes and sea level. Nature 324:137–140
Chen J, Wang HN (2004) Geochemistry. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Chen ZY, Ma ZF, Zhang JQ (1998) Genesis of the dolomite in M5 subinterval Ordovician in central Ordos Basin. Pet Explor Dev 25(6):20–22 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Choquette PW, Hiatt EE (2008) Shallow-burial dolomite cement: a major component of many ancient sucrosic dolomites. Sedimentology 55:423–460
Dawans JM, Swart PK (1988) Textural and geochemical alternations in Late Cenozoic Bahamian dolomites. Sedimentology 35:385–403
Duan J, Zhang SN, Ding XQ, Xiang L, Huang QY (2008) The Lower Paleozoic group in the western margin of the Ordos Basin. Acta Geol Sichuan 28:272–275 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Emery D, Robinson A (1993) Inorganic geochemistry: applications to petroleum geology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Enos P, Sawatsky LH (1981) Pore networks in Holocene carbonate sediments. J Sediment Res 51:961–985
Farr MR (1989) Compositional zoning characteristics of late dolomite cement in the Cambrian Bonneterre Formation, Missouri: implications for parent fluid migration pathways. Carbonates Evaporites 4:177–194
Fu JH, Wang BQ, Sun LY, Bao HP, Xu B (2011) Dolomitization of Ordovician Majiagou Formation in Sulige region, Ordos Basin. Pet Geol Exp 33:266–273 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gabellone T, Whitaker F, Katz D, Griffiths G, Sonnenfeld M (2016) Controls on reflux dolomitisation of epeiric-scale ramps: insights from reactive transport simulations of the Mississippian Madison Formation (Montana and Wyoming). Sediment Geol 345:85–102
Geske A, Zorlu J, Richter DK, Buhl D (2012) Impact of diagenesis and low grade metamorphosis on isotope (26Mg, S13C, 18O and 87Sr/86Sr) and elemental (Ca, Mg, Mn, Fe and Sr) signatures of Triassic sabkha dolomites. Chem Geol 332–333:45–64
Gingras MK, Pemberton SG, Muelenbachs K, Machel HG (2004) Conceptual models for burrow-related, selective dolomitization with textural and isotopic evidence from the Tyndall Limestone, Canada. Geobiology 2:21–30
Gregg JM, Bish DL, Kaczmarek SE, Machel HG (2015) Mineralogy, nucleation and growth of dolomite in the laboratory and sedimentary environment:a review. Sedimentology 62:1749–1769
He J, Fang SX, Hou FH, Yan RH, Zhao ZJ, Yao J, Tang XJ, Wu GR (2013) Vertical zonation of weathered crust ancient karst and the reservoir evaluation and prediction—a case study of M55–M51sub-members of Majiagou Formation in gas fields, central Ordos Basin, NW China. Pet Explor Dev 40(5):534–542 (in Chinese with English abstract)
He XY, Shou JF, Shen AJ, Wu XN, Wang YS, Hu YY, Zhu Y, Wei XD (2014) Geochemical characteristics and origin of dolomite: a case study from the middle assemblage of Majiagou Formation Member 5 of the west of Jingbian Gas Field, Ordos Basin, North China. Pet Explor Dev 41:375–384 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hips K, Haas J, Poros Z, Kele S, Budai T (2015) Dolomitization of Triassic microbial mat deposits (Hungary): origin of microcrystalline dolomite. Sediment Geol 318:113–129
Hou FH, Fang SX, Zhao JS, Dong ZX, Li L, Wu Y, Chen YN (2002) Depositional environment model of middle Ordovician Majiagou Formation in Ordos Basin. Mar Origin Pet Geol 7:38–46 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang SJ (1992) Relationship between cathodoluminescence and concentration of iron and manganese in carbonate minerals. J Mineral Petrol 12:76–81 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang SJ (2010) Diagenesis of carbonates. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Huang QY, Zhang SN, Ding XQ, Duan J, Xiang L (2010) Origin of dolomite of Ordovician Majiagou Formation, western and southern margin of the Ordos basin. Pet Geol Exp 32:147–153 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang ZL, Bao HP, Ren JF, Bai HF, Wu CY (2011) Characteristics and genesis of dolomite in Majiagou Formation of Ordovician south of Ordos Basin. Geoscience 25:925–930 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jacquemyn C, Desouky HE, Hunt D, Casini G, Swennen R (2014) Dolomitization of the Latemar platform: fluid flow and dolomite evolution. Mar Pet Geol 55:43–67
Jones GD, Rostron BJ (2000) Analysis of fluid flow constraints in regional-scale reflux dolomitization: constant versus variable-flux hydrogeological models. Bull Can Pet Geol 48:230–245
Jones B, Luth RW, Macneil AJ (2001) Powder X-ray diffraction analysis of homogeneous and heterogeneous sedimentary dolostones. J Sediment Res 71:790–799
Jones GD, Whitaker FF, Smart PL, Sanford WE (2002) Fate of reflux brines in carbonate platforms. Geology 30:371–374
Jones GD, Smart PL, Whitaker FF, Rostron BJ, Machel HG (2003) Numerical modeling of reflux dolomitization in the Grosmont Platform Complex (Upper Devonian), western Canada Sedimentary Basin. AAPG Bull 87:1273–1298
Keith ML, Degens ET (1959) Geochemical indicators of marine and freshwater sediments. In: Abelson PH (ed) Researches in geochemistry. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 38–61
Krupenin MT, Michurin SV (2018) Indicator isotope—geochemical characteristics of sulfides from the satka magnesite ore field (South Urals Province). Dokl Earth Sci 478:108–111
Land LS (1980) The isotopic and trace element geochemistry of dolomite: the state of the art. In: Zenger DH, Dunham JB, Ethington RL (eds) Concepts and models of dolomitization. SEPM Spec Publ 28:87–110
Land LS, Moore CH (1980) Lithification, micritization and syndepositional diagenesis of biolithites on the Jamaican island slope. J Sediment Res 50:357–369
Li ZH, Yang YH (2005) Present situation and progress of research on dolomite genesis. Pet Geol Recovery Effi 11:9–12+85 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li GR, Si JX, Shi FZ (1997) The types and genetic mechanism of storage space in Ordovician Majiagou Formation, Ordos Basin. J Chengdu Univ Technol 24(1):17–23 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li WH, Chen Q, Li ZC, Wang RG, Wang Y, Ma Y (2012) Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Early Paleozoic in Ordos area. J Palaeogr 14:85–100 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li FJ, Du LC, Zhao JX, Li YG, Xiang F, Li FP (2016) Dolomite genesis in Member Ma55 of Majiagou Formation, Sudong area, Ordos Basin. Acta Pet Sin 37:328–338 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu YJ (1984) Element geochemistry. Science Press, Chengdu (in Chinese)
Liu DL, Sun XR, Li ZS, Tang NA, Tan Y, Liu B (2006) Analysis of carbon and oxygen isotope on the Ordovician dolostones in the Ordos Basin. Pet Geol Exp 28(2):155–161 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu C, Xie Q, Wang GW, Song YF, Qi KN (2016) Dolomite origin and its implication for porosity development of the carbonate gas reservoirs in the Upper Permian Changxing Formation of the eastern Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 35:775–797 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Lohmann KC (1988) Geochemical patterns of meteoric diagenetic systems and their application to studies of paleokarst. In: James NP, Philip WC (eds) Paleokarst. Springer, Berlin, pp 58–80
Machel HG (2004) Concepts and models of dolomitization: a critical reappraisal. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 235:57–63
Makhloufi Y, Samankassou E (2019) Geochemical constrains on dolomitization pathways of the Upper Jurassic carbonate rocks in the Geneva Basin (Switzerland and France). Swiss J Geosci 112:579–596
Mansour AS, Abd-Ellatif MT (2013) Dolomitization of the Miocene carbonates in Gebel Abu Shaar El Qiblie and Salum area, Egypt: a petrographical and geochemical comparative study. Carbonates Evaporites 28:347–363
Mazzullo SJ (1992) Geochemical and neomorphic alteration of dolomite: a review. Carbonates Evaporites 7:21–37
Mcarthur JM, Burnett J, Hancock JM (1992) Strontium isotopes at K/T boundary. Nature 355:28–28
Mcarthur JM, Howarth RJ, Bailey TR (2001) Stronti- um isotope stratigraphy: LOWESS Version 3: best fit to the marine Sr-isotope curve for 0–509 Ma and accompanying look-up table for deriving numerical age. J Geol 109:155–170
Morrow DW (1982) Diagenesis 2. Dolomite-part 2. Dolomitization models and ancient dolostones. Geosci Can 9:95–107
Nader F, Swennen R, Ellam RM (2007) Field geometry, petrography and geochemistry of a dolomitization front (late Jurassic, central Lebanon). Sedimentology 54:1093–1120
Ning M, Huang KJ, Lang XG, Ma HR, Yuan HL, Peng YB, Shen B (2019) Can crystal morphology indicate different generations of dolomites? Evidence from magnesium isotopes. Chem Geol 516:1–17
Ohde S, Elderfield H (1992) Strontium isotope stratigraphy of Kita-daito-jima Atoll, North Philippine Sea: implications for Neogene sea-level change and tectonic history. Earth Planet Sci Lett 113:473–486
Özkan AM, Dinç S (2018) Geochemical features of the Menteşe Formation dolostones (Rhaetian) in the Karacahisar-Kasımlar area (Isparta-Turkey). Arab J Geosci 11:449
Palmer MR, Edmond JM (1989) The strontium isotope budget of the modern ocean. Earth Planet Sci Lett 92:11–26
Pierson BJ (2010) The control of cathodoluminescence in dolomite by iron and manganese. Sedimentology 28:601–610
Pokrovsky BG, Chumakov NM, Melezhik VA, Bujakaite MI (2010) Geochemical properties of Neoproterozoic “cap dolomites” in the Patom paleobasin and problem of their genesis. Lithol Miner Resour 45:577–592
Rameil N (2008) Early diagenetic dolomitization and dedolomitization of Late Jurassic and earliest Cretaceous platform carbonates: a case study from the Jura Mountains (NW Switzerland, E France). Sediment Geol 212:70–85
Ren M, Jones B (2016) Spatial variations in the stoichiometry and geochemistry of Miocene dolomite from Grand Cayman: implications for the origin of island dolostone. Sediment Geol 342:15–30 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Sass E, Bein A (1988) Dolomites and salinity: a comparative geochemical study. In: Shukla V, Baker PA (eds) Sedimentology and geochemistry of dolostones. SEPM Spec Publ 43:223–233
Sheppard SMF, Schwarz HP (1970) Fractionation of carbon and oxygen isotopes and magnesium between metamorphic calcite and dolomite. Contrib Miner Petrol 26:161–198
Sibley DF, Gregg JM (1987) Classification of dolomite rock texture. J Sediment Res 57:967–975
Sperber CM, Wilkinson BH, Peacor DR (1984) Rock composition, dolomite stoichiometry, and rock/water reactions in dolomitic carbonate rocks. J Geol 92:609–622
Su ZT (2011) The study of dolomite genesis and diagenisis system of Majiagou Formation around Paleouplift, Ordos. Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu (in Chinese with English abstract)
Su ZT, Chen HD, Xu FY, Wei LB, Li J (2011) Geochemistry and dolomitization mechanism of Majiagou dolomites in Ordovician, Ordos, China. Acta Petrol Sin 27:230–238 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Su ZT, Chen HD, Xu FY, Jin XQ (2013) Genesis and reservoir property of lower Ordovician Majiagou dolostones in Ordos Basin. Mar Orig Pet Geol 18:15–22 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Swart PK, Cantrell DL, Westphal H, Handford CR, Kendall CG (2005) Origin of dolomite in the Arab-D reservoir from the Ghawar Field, Saudi Arabia: evidence from petrographic and geochemical constraints. J Sediment Res 75:476–491
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1985) The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p 312
Taylor TR, Sibley DF (1986) Petrographic and geochemical characteristics of dolomite types and the origin of ferroan dolomite in the Trenton Formation, Ordovician, Michigan Basin, U.S.A. Sedimentology 33:61–86
Tucker ME, Wright VP (1990) Carbonate sedimentology. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p 482
Vahrenkamp VC, Swart PK, Ruiz J (1991) Episodic dolomitization of late Cenozoic carbonates in the Bahamas: evidence from strontium isotopes. J Sediment Res 6:1002–1014
Wahlman GP (2010) Reflux dolomite crystal size variation in cyclic inner ramp reservoir facies, Bromide Formation (Ordovician), Arkoma Basin, Southeastern Oklahoma. Sediment Rec 8:4–9
Wang BQ, Qiang ZT, Zhang F, Wang XZ, Wang Y, Cao W (2009) Isotope characteristics of dolomite from the fifth member of the Ordovician Majiagou Formation, the Ordos Basin. Geochimica 38(5):472–479 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang QC, Zhao SP, Wei QL, Xiao L, Yang YH, Guo YQ, Niu MN (2012) Marine carbonate reservoir characteristics of the Middle Ordovician Majiagou Formation in Ordos Basin. J Paleogeogr 14:229–242 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang QC, Zhang Y, Xao L (2013) Carbon and oxygen stable isotopic features of diagenetic facies of Ordovician carbonate rocks in Ordos Basin. Oil Gas Geol 5:652–658 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang H, Gao X, Yang D, Li H, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhang L (2014) Genesis of dolomitic rock within the Lower Cretaceous lacustrine facies in Bayindulan Sag, Erlian Basin. Acta Sedimentol Sin 3:560–567 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang QC, Wei W, Zhao J, Ma Y, Ning B, Li BQ, Jin CG (2017) Geochemical characteristics of dolostone diagenetic facies of the Ordovician in Ordos Basin. J Paleogeogr 19(5):849–864 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ward WC, Halley RB (1985) Dolomitization in a mixing zone of near-seawater composition, late Pleistocene, northeastern Yucatan Peninsula. J Sediment Res 55:407–420
Warren JK (2000) Dolomite: occurrence, evolution and economically important associations. Earth Sci Rev 52:1–81
Whitaker FF, Smart PL (1993) Circulation of saline ground water in carbonate platforms—a review and case study from the Bahamas. In: Horbury AD, Robinson AG (eds) Diagenesis and basin development. AAPG Stud Geol 36
Woody RE, Gregg JM, Koederitz LF (1996) Effect of texture on petrophysical properties of dolomite: evidence from the Cambrian–Ordovician of southeastern Missouri. AAPG Bull 80:119–132
Xie GA, Zhang QL, Guo LZ (2003) The genesis and hydrocarbon distribution of weatern and southern margins of Paleozoic foreland basin and central paleouplift in Ordos Basin. Acta Pet Sin 24(2):192–195 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiong Y, Li L, Wen CX, Hou YD, Xiao D, Zhong Y, Nie WC, Cao J, Tan XC (2016) Characteristics and genesis of Ordovician Ma51+2 sub-member reservoir in northeastern Ordos Basin. Oil Gas Geol 37:691–701 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang H, Fu JH, Wei XS, Ren JF (2011) Natural gas exploration domains in Ordovician marine carbonates, Ordos Basin. Acta Pet Sin 32:733–740 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang H, Wang BQ, Sun LY, Ren JF, Huang ZL, Wu CY (2012) Characteristics of oxygen and carbon stable isotopes for middle Ordovician Majiagou Formation carbonate rocks in the Ordos basin. Nat Gas Geosci 23:616–625 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang XY, Bao HP, Ren JF, Ma ZR (2015) Types of dolomites and characteristics of stable isotope from the Ma55 sub-member of Ordovician Majiagou Formation in Ordos Basin. Nat Gas Geosci 26:650–656 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yu Z, Ding ZC, Wu DX, Wei LB, Wei Y (2017) Geochemical characteristics and genetic model of dolomite in Majiagou Submember-55 of Ordovician in East-central Ordos Basin. Mar Origin Pet Geol 24:85–93 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang YS (2000) Mechanism of deep burial dolomitization of massive dolostones in the Middle Majiagou group of the Ordovician, Ordos Basin. Acta Sedimentol Sin 18(3):424–430 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang RX, Le CS (1981) Carbonate. Beijing Research Department, Wuhan Institute of Geology, Internal textbooks, vol 1, 2, pp 132–164 (in Chinese)
Zhang CL, Zhang YS, Kang QF, Luo J, Qi LS (2001) Dolomite genesis of Ordovician system in Formation Maliu, Southern Ordos Basin. Acta Pet Sin 22(3):22–26 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao WW, Wang BQ (2011) Geochemical characteristics of dolomite from 5th Member of the Ordovician Majiagou Formation in Sulige area, Ordos Basin. Acta Geosci Sin 32(6):681–690 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao JX, Chen HD, Zhang JQ, Liu XL, Fu ST (2005) Genesis of dolomite in the fifth member of Majiagou Formation in the middle Ordos Basin. Acta Pet Sin 26:38–47 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu S, Qin Y, Liu X, Wei C, Zhu X, Zhang W (2017a) Origin of dolomitic rocks in the Lower Permian Fengcheng Formation, Junggar Basin, China: evidence from petrology and geochemistry. Mineral Petrol 112:14–29 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu SF, Yue H, Zhu XM, Sun SY, Wei W, Liu X, Jia Y (2017b) Dolomitization of felsic volcaniclastic rocks in continental strata: a study from the Lower Cretaceous of the A'nan Sag in Er'lian Basin, China. Sediment Geol 353:13–27 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
We thank Senior Engineer Yihua Yang for the assistance of the thin sections identification. We are also grateful to the Lanzhou Center for Oil and Gas Resources, Institute of Geology, China for the analysis of major and trace elements and the carbon and oxygen stable isotopic compositions, the Geophysics and the State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University, China for strontium isotope analysis. Besides, thanks to Professor James W. LaMoreaux, editor-in-chief of Carbonate and Evaporite, and the review experts for their valuable suggestions on improving the quality of this article. This study was supported by the National “13th Five-Year” Plan for Science and Technology Major Project of China (2017ZX05005-002-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, B., Wang, Q. & Zhang, X. Petrographic and geochemical evidence of the diagenetic environment and fluid source of dolomitization of dolomite: a case study from the Ma55 to Ma51 submembers of the Ordovician Majiagou Formation, central Yishan Slope, Ordos Basin, China. Carbonates Evaporites 35, 36 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00569-6
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-020-00569-6