Abstract
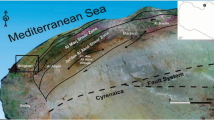
Chamshir Dam site is located in southwest of Iran, on Zuhreh River, 20 km southeast of Gachsaran city. The study area mainly covered by evaporite formations of Fars Group especially Gachsaran Formation. Dam axis is located on limestone beds of Mishan Formation but nearly two-thirds of the dam reservoir is in contact with the Gachsaran Formation. The reservoir and dam site have been brecciated by several faults such as Dezh Soleyman thrust and Chamshir fault zone that lead to development of karst in this region. The region has a wide variety of developed karstic features such as karrens, dissolution dolines, karstic springs and cavities. These karst features can compromise on the ability of Chamshir Dam to hold water in the reservoir, and can even cause collapse of the dam. Gypsum karst in the Chamshir Dam reservoir may develop the solution channels and cavities which cause water to flow toward downstream of the dam reservoir. Therefore, to eliminate these problems, construction of cutoff wall or clay blanket is proposed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benito G, Perez-Gonzalez A, Gutierrez F, Machado MJ (1998) River response to Quaternary subsidence due to evaporite solution (Gallego River, Ebro Basin, Spain). Geomorphology 22:243–263
Benito G, Gutierrez F, Perez-Gonzalez A, Machado MJ (2000) Geomorphological and sedimentological features in Quaternary fluvial system affected by solution-induced subsidence (Ebro Basin NE-Spain). Geomorphology 33(3–4):209–224
Berberian M (1995) Master “Blind” thrust faults hidden under the Zagros folds: active basement tectonics and surface morphotectonics. Tectonophysics 241:193–224
Berbrian M, King GCP (1981) Towards a paleogeography and tectonic evolution of Iran. Can J Earth Sci 18:210–265
Birk S (2002) Characterisation of karst systems by simulating aquifer genesis and spring responses: model development and application to gypsum karst. TGA Reihe C Nr 60, University of Tu¨bingen, p 122
Boğli A (1980) Karst hydrology and physical speleology. Springer, Berlin, p 284
Calaforra JM, Pulido-Bosch A (1999) Gypsum karst features as evidence of diapiric processes in the Betic Cordillera Southern Spain. Geomorphology 29:251–264
Calaforra JM, Pulido-Bosch A (2003) Evolution of the gypsum karst of Sorbas (SE Spain). Geomorphology 50:173–180
Cooper AH, Calow RC (1998) Avoiding gypsum geohazards: guidance for planning and construction. British Geological Survey, p 57
Cooper AH, Sauro U (eds) (1997) Gypsum karst of the world. Int J Speleol 5(1–2) 1996 Thematic Issue
Cooper AH, Waltham AC (1999) Subsidence caused by gypsum dissolution at Ripon North Yorkshire. Q J Eng Geol 32:305–320
Cucchi F, Zini L (2003) Gypsum karst of Zagros Mountains (I.R. IRAN). Acta Carsologica 32(1):69–82
Doğan U, Yeşilyurt S (2004) Gypsum karst south of Imran IV. Cave Karst Sci 31(1):7–14
Ford DC, Williams PW (1989) Karst geomorphology and hydrology. Unwin Hyman, London, p 601
Gill WD, Ala MA (1972) Sedimentology of Gachsaran Formation (lower Fars series), Southwest Iran. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 56:1965–1974
Gutierrez-Elorzo M, Gutierrez-Santolalla F (1998) Geomorphology of the tertiary gypsum formations in the Ebro depression (Spain). Geoderma 87:1–29
Hessami K, Koyi HA, Talbot CJ (2001a) The significance of strike slip faulting in the basement of the Zagros fold–thrust belt. J Pet Geol 24:5–28
Hessami K, Koyi HA, Talbot CJ, Tabasi H, Shabanian E (2001b) Progressive unconformities within an evolving foreland fold–thrust belt, Zagros Mountains. J Geol Soc Lond 158:969–981
Jassim SZ, Jibril AS, Numan NMS (1997) Gypsum karstification in the Middle Miocene Fatha Formation Mosul area, Northern Iraq. Geomorphology 18:137–149
Jeschke AA, Vosbeck K, Dreybrodt W (2001) Surface-controlled dissolution rates of gypsum in aqueous solutions exhibit nonlinear dissolution kinetics. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65(27):34
Kashfi MS (1980) Stratigraphy and environmental sedimentology of lower Fars group (Miocene), South–Southwest Iran. Am Assoc Pet Geol Bull 64:2095–2107
Klimchouk AB (1996) The dissolution and conversion of gypsum and anhydrite. Int J Speleol 25(3–4):21–36
Klimchouk AB, Ford DC, Palmer AN, Dreybrodt W (eds) (2000) Speleogenesis, evolution of karst aquifers. National Speleological Society, p 527
Maramathas A, Maroulis Z, Marinos-Kouris D (2003) Brackish karstic springs model: application to Almiros spring in Crete. Ground Water 41(6):728
Meinzer OE (1923) The occurrence of ground water in the United States with a discussion of principles. US Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 489, Washington, DC
Motiei H (1993) Stratigraphy of Zagros. Geological Survey of Iran, p 536 (in Persian)
Paukštys B, Cooper HA, Arustiene J (1999) Planning for gypsum geohazards in Lithuania and England. Eng Geol 52:99–103
Setudehnia A (1972) Stratigraphic Lexicon of Iran. Union International des Sciences Geologiques, vol 3. ASIE, South-West Iran, pp 320–321
Setudehnia A, OB-Perry GT (1966) Geological map of Gachsaran, Iranian Oil Operating Companies (IOOC), 1:100,000
Stocklin J (1968) Structural history and tectonics of Iran: a review. AAPG Bull 52:1229–1258
Stöcklin J (1968) Salt deposits of the Middle East. In: Mattox RB (ed) Saline deposits: s symposium based on papers from the International Conference on Saline Deposits. Geological Society of America, Special Paper 88, Houston
Torabi-Kaveh M (2011) Study of evaporative rocks solubility in Gachsaran Formation in the Chamshir Dam site. Unpublished MSc Dissertation, Bu-Ali Sina University (in Persian)
Veress M (2010) Karst environments; Karren Formation in High Mountains. Springer, Heidelberg, p 230
Waltham T (2002) Gypsum karst near Sivas Turkey. Cave Karst Sci 29(1):39–44
White WB (1988) Geomorphology and hydrology of Karst Terrains. Oxford University Press, Oxford, p 464
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. Hamid Reza Zarei for the valuable help in the field. We also would like to thank the Bu-Ali Sina University for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torabi-Kaveh, M., Heidari, M. & Miri, M. Karstic features in gypsum of Gachsaran Formation (case study; Chamshir Dam reservoir, Iran). Carbonates Evaporites 27, 291–297 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-012-0090-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-012-0090-9