Abstract
This study aims to analyze the impact of digital marketing on urban courier companies in the municipality of Valledupar, Colombia. It also aims to propose strategies for smart delivery in urban courier companies in developing countries and identify barriers to be overcome in these activities. A quantitative approach with a descriptive research design is used. Given the nested nature of the data, a correlation analysis was performed to gather information on the relationship between the variables studied and the strength and direction of those relationships. A correlation analysis was conducted to identify the correlation coefficient between two specific variables. The ordinary least squares (OLS) regression method examined the relationship between the dependent and independent variables. The results indicate that the use of social media has a significant positive impact on the dependent variable. In contrast, the use of email and websites does not show statistical significance. The proposed strategies include real-time tracking of shipments, personalized notifications, scheduled delivery, integration of augmented reality, use of smart lockers, and geolocation technology. As barriers to be overcome in urban courier activities in developing countries, the following are identified infrastructure limitations, limited access to technology, costs associated with technology adoption, digital divide and skills, and resistance to change. The study was conducted in small and medium-sized courier companies in developing countries, so the implications of the results should be generalized to only some companies worldwide. The research highlights the importance of developing digital marketing skills and addressing barriers to implementing smart delivery strategies. Strategies such as real-time tracking of shipments, personalized notifications, scheduled delivery, augmented reality integration, smart lockers, and geolocation technology are proposed. It is concluded that digital marketing can enhance urban courier services and provide competitive advantages to companies that adopt it. This study provides valuable insights to develop specific strategies and solutions that help improve the operational efficiency of urban courier companies, including website optimization, effective use of social media, and email, and increased visibility in search engines. It enhances service quality, providing a more satisfying customer experience and fostering customer loyalty. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of developing engaging and relevant content and establishing effective communication with customers through digital channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
In recent years, urban courier companies have seen the need to adopt digital marketing strategies due to the rapid growth of electronic commerce and the increasing demand for efficient and timely delivery services (Pandey et al., 2020). Digital marketing has significantly changed how companies reach their customers (Kumar & Sharma, 2022). The digital format, the availability of different contents, and interactivity allow fluid and personalized communication with the client (Rizvanović et al., 2023). Consumers who use digital resources in the purchase process tend to trust social networks (Dwivedi et al., 2023). Since companies from countries with emerging economies often have limited resources, are struggling to increase their customers, and present other growth challenges, digital marketing tools can be used to support digital interactions and impact the growth of companies (Rizvanović et al., 2023).
In the urban messaging industry, there is heavy reliance on worker delivery, which is less efficient and demands excessive time and resources. Many companies offer discounted or even free shipping to gain a competitive advantage. However, there are lingering doubts about the sustainability of this approach (Sham et al., 2023). To expand their marketing reach, enhance operational efficiency, gain customer insights, and create new business opportunities (Hoffman et al., 2021), small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly embracing digital marketing technologies such as e-commerce platforms (Cui et al., 2017), social networks (Chaker et al., 2022), and mobile applications (Ziółkowska, 2021). By continuously adapting technology from various public platforms and developing digital marketing portfolios, many small businesses have the potential to thrive, grow, and become market leaders (Ciarli et al., 2021; Zhang & Watson, 2020).
The appearance of the Internet and new technologies has transformed the role of marketing and its practice (Harrigan & Hulbert, 2011; Quinton & Simkin, 2017); consequently, it entered a space where all types of business organizations must invest resources in making products or services visible through digital media, becoming an essential tool for decision-making. These platforms have the potential to generate awareness, enhance brand reputation, attract new customers, improve customer service, increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, drive sales, and reduce expenses (Karjaluoto et al., 2015; Setkute & Dibb, 2022; Taiminen & Karjaluoto, 2015). However, owners of small service businesses often need to be more convinced about the value of digital marketing and social media (Cole et al., 2017).
The new marketing landscape has led companies to conditions that require them not only to exist in the conventional competitive field but also to exist in the field of digital marketing (Masrianto et al., 2022), which is why there is a great need to incorporate advertising innovations through digital media that have greater acceptance by customers or users. In SMEs, despite the evidence that business performance can be improved through digital marketing (Cenamor et al., 2019), adopting these practices remains low, and the reasons why are poorly understood (Quinton & Simkin, 2017; Quinton et al., 2018). That is why today, business organizations, to compete and remain over time, must establish digital marketing plans, which as a planning tool does not guarantee success, but does minimize risks.
The COVID-19 pandemic, in addition to having an impact on the increase in media consumption habits, also affected the rise in the number of Internet users, the use of digital devices, and the growth in activities online (Masrianto et al., 2022), which led to deepening virtual interaction and generating a communication channel between companies and consumers that can operate 24 h a day, 365 days a year. This situation has forced companies worldwide to restructure their operations and business strategies (Das & Ramalingam, 2023), including urban courier companies. In the city of Valledupar, Colombia, according to information provided by the Chamber of Commerce, before the year 2020, one hundred twenty-two (122) urban courier companies were formally registered in this municipality, and between the years 2020 and 2021, the formalization took place. Of one hundred and thirty-three (133) new urban courier companies, thus demonstrating that despite the crisis experienced between 2020 and 2021, an entrepreneurial opportunity was also generated based on a need for distance and to be able to acquire goods and services without leaving home.
This study is framed within the context of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021. During this period, social distancing measures significantly increased the need to acquire goods and services for family survival, thus driving substantial growth in urban courier companies in the area. It has brought about changes in our sense of well-being in public spaces, compelling us to adhere to appropriate COVID behavior and resort to online platforms for shopping and communication (Chuah et al., 2022; Verma et al., 2023). These circumstances had a significant impact on platform economies, sparking debates and speculations about the future of digital platforms and changes in everyday habits in post-pandemic cities (Ecker & Strüver, 2022).
Consequently, urban courier companies experienced remarkable growth, becoming a crucial option for product delivery. Digital marketing played a fundamental role during this stage, enabling these companies to interact and promote their services effectively through online business strategies. Despite this growth, urban courier entrepreneurs in developing countries face challenges in implementing digital marketing and smart delivery strategies. Questions linger about how shipping companies are adopting and adjusting online campaigns and the impact of these tactics on how they promote their services and how people access them. There is a need to better understand the obstacles and limitations when applying contemporary promotion practices and how to reach customers effectively in this specific context. This study aims to comprehend the particular challenges these companies face, whether in terms of resources, knowledge, or resistance to change, in fully embracing digital marketing practices and smart services. In addition to the aforesaid mentioned novelty factors, this study seeks to address the following research questions:
-
RQ1
-
How are urban courier companies utilizing electronic channels for their marketing strategies?
-
RQ2
-
What are the most effective smart delivery strategies implemented by urban courier companies in developing countries?
-
RQ3
-
What are the most significant barriers faced by urban courier activities in developing countries, and how can they be overcome?
The research has the potential to provide valuable insights into how local courier companies can optimize their online marketing strategies to adapt to changing market conditions, enhance service effectiveness, and strengthen their competitive position. Additionally, it can help fill the existing knowledge gap in this specific context. Our study reveals that the use of social media plays a significant role in digital marketing, boosting consumer purchasing intent, in contrast to the limited influence exerted by email and websites. The importance of developing digital marketing skills and addressing barriers to implementing smart delivery strategies is emphasized.
Among the proposed strategies are real-time tracking, personalized notifications, scheduled delivery, augmented reality integration, use of smart lockers, and geolocation technology. It is emphasized that digital marketing can enhance urban courier services, offering competitive advantages and improving customer retention and satisfaction. Despite barriers such as limited knowledge and operational challenges, the article highlights the opportunity to educate urban courier companies and address logistical challenges to ensure a successful transition. Overcoming these barriers is essential to maximize the impact of digital marketing and provide more efficient services tailored to customer needs, especially in countries with emerging economies like Colombia.
The summary of this article is structured as follows: the introduction is followed by the theoretical framework and the formulation of hypotheses. The research methodology and data analysis are described next. Results and related discussion are then provided. Opportunities for digital marketing and smart delivery and barriers to overcome in urban courier activities in developing countries are identified. The article concludes with a summary of the study’s theoretical and practical contributions, limitations and future work, and conclusions.
Theoretical Background
Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
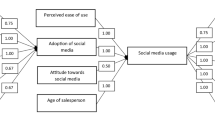
The TAM lists three factors explaining user motivation: perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and attitude toward use. Therefore, TAM includes both behavioral intention and the two central beliefs, perceived effectiveness and ease of use, which significantly influence the user’s attitude (Taherdoost, 2018). These can be interpreted as both favorable and unfavorable attitudes toward the system. The TAM model sometimes considers external variables such as user training, system characteristics, user participation in design, and the nature of the implementation process (Lin et al., 2011).
Technology acceptance models focus on the implementation stage within organizations after the decision to adopt technology has already been made. Analyzing how consumers and courier companies use and adapt to digital technologies in the context of product delivery (Shachak et al., 2019; Zhu et al., 2022). This could include studying factors influencing the speed of adopting new technologies and the barriers and facilitators of digital solution adoption. This research proposes the following hypotheses:
-
H1. Increased activity on social media and communication through email can lead to an increase in the number of customers for urban courier companies.
-
H2. Companies with greater knowledge and skills in digital marketing also tend to be more active on social media and adopt digital marketing strategies more effectively.
-
H3. The more active companies are on social media, the more likely they will use digital marketing strategies effectively. The reliability of the instrument was determined through Cronbach’s alpha coefficient, applied to closed-ended questions using a 5-point.
Conceptual Development
The reason behind this theory lies in the fact that social media allows companies to establish direct and continuous contact with their customers, facilitating the dissemination of information, promotion of offers, and the creation of an online community (Masrianto et al., 2022; Yaseen et al., 2019). Companies that can generate meaningful interactions on social media are expected to be able to use digital marketing techniques more effectively as well. Ongoing interaction with customers on social media can reveal crucial information about their preferences, needs, and behaviors. This can create more effective and adaptable digital marketing strategies (De Vries et al., 2017).
Content Marketing
Content marketing is crucial in establishing urban courier companies as thought leaders and industry experts, as it generates significant benefits and impacts almost every sector and context (Binh Nguyen et al., 2023). By creating and sharing relevant and valuable content such as blog posts, articles, videos, and infographics, these companies can educate their target audience, demonstrate their expertise, and build trust and credibility. With the rise of content-based social commerce, designing marketing content that better stimulates consumer purchasing behaviors has become increasingly essential (Wang et al., 2023a, 2023b). In addition to driving consumer engagement behaviors (e.g., likes, shares, and comments) (Roy et al., 2018; Zheng et al., 2022), another goal of social commerce content marketing is to encourage consumers to make a direct purchase after consuming the content (Mu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023a, 2023b). Content marketing also improves search engine rankings, attracts inbound traffic, and nurtures leads throughout the customer journey.
Digital Marketing Strategies
Digital marketing emerged as a natural response from businesses to leverage and benefit from the substantial concentration of consumers on the Internet. Various types of organizations, including businesses, hospitals, schools, professional associations, councils, and NGOs, employ digital marketing as a key component of their marketing strategies and implementation programs (Miklosik et al., 2019).
Digitalization has reshaped the business landscape in several industries, including logistics. Urban courier companies responsible for delivering packages and merchandise within metropolitan areas have recognized the importance of digital marketing as a fundamental driver of growth and success in an increasingly competitive market. Digital marketing strategies, search engine optimization (SEO), social media promotion, content creation, email usage, and paid advertising stand out. These tactics are implemented to sustain and increase the customer base.
Search Engine Optimization
Search engines can classify websites based on keywords, descriptions, and content, allowing for easy access to desired content. SEO is a widely used technique to improve website accessibility effectively (Yalçın & Köse, 2010). SEO is crucial in improving the visibility and ranking of urban courier companies in search engines. These companies can attract more visitors or potential customers and achieve higher financial returns by optimizing their website content, using relevant keywords, and enhancing the user experience (Erdmann et al., 2022). SEO techniques allow urban courier companies to target specific geographical areas and enhance their visibility among potential customers in urban locations (Lin et al., 2014).
Social Media Marketing
Social media platforms have become powerful tools for urban courier companies to connect with customers, promote their image and brand, and offer services (Park et al., 2021). Social media marketing allows these companies to establish a solid online presence and foster customer loyalty by creating engaging content, targeted advertising, and effective customer engagement (Hanaysha, 2022). Kar and Kushwaha (2021) identify consumers who are interested in obtaining necessary information about a specific company or brand; they tend to search through social media. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn provide opportunities for urban courier companies to showcase their offerings, share updates, and respond promptly to customer inquiries. The growing interconnectedness of social media with the metaverse has forged a new digital connection between users and community-building platforms. The increased accessibility of social media via smartphones provides opportunities for enhanced social interaction, facilitating users’ engagement in online interactions (G et al., 2023).
Email Marketing
Email marketing remains an effective channel for urban courier companies to communicate with their current and potential customers (Goic et al., 2021). By sending targeted and personalized email campaigns, these companies can share updates, special offers, and personalized recommendations (Nobile & Cantoni, 2023). Research has identified several positive effects of personalization, such as positive consumer attitudes toward the brand, increased purchase intention, and willingness to pay (de Groot, 2022; Tomczyk et al., 2022). Email marketing automation tools allow urban courier companies to optimize their communication processes, track customer interactions, and measure the effectiveness of their campaigns.
Paid Advertising
Paid advertising, such as pay-per-click advertising and display advertising, allows urban courier companies to reach a wider audience and drive targeted traffic to their website. Additionally, to enhance advertising efficiency, e-commerce platforms make specific promotional efforts (Hao & Yang, 2022). Although paid advertising is a significant investment for some companies (Symitsi et al., 2022), these companies can improve brand visibility, increase website traffic, and generate qualified leads by strategically investing in paid advertising campaigns. Proper monitoring and optimization of the movement are essential to maximize the return on investment of paid advertising efforts.
Methodology
The research was conducted using a quantitative approach with a descriptive research design. Given the nested nature of the data, a correlation analysis was performed to gather information on the relationship between the variables studied and the strength and direction of those relationships. A correlation analysis was conducted to identify the correlation coefficient between two specific variables. The ordinary least squares (OLS) regression method examined the relationship between the dependent and independent variables. A non-experimental cross-sectional design was used as the data was collected during a single period from a specific population of 133 urban courier companies. After obtaining their consent to participate in the data collection instrument, only 29 companies agreed, resulting in a non-probabilistic sample of 29 out of the total population.
Key informants for the study included administrative and operational personnel who possess specific knowledge of organizational functioning and can provide insights into the implementation of digital marketing. Additionally, vehicle operators, who have direct contact with service users, were also considered vital informants in the study. The chosen technique was a survey, and the data collection instrument was a 19-item questionnaire, which was administered virtually after establishing validity by three experts who determined its relevance to the objectives, variables, and indicators, as well as its wording to align with the appropriate language and aesthetics for the level of study. Likert scale (never, rarely, sometimes, often, always) as a result of a pilot test conducted with 10 urban courier companies in the municipality of Valledupar, Colombia. Reliability was established using the following formula:
- α:
-
Reliability coefficient of the questionnaire
- k:
-
Number of items in the instrument
- \({\sum }_{i=1}^{k}{S}_{i}^{ 2}\):
-
Sum of item variances
- \({S}_{i}^{ 2}\):
-
Total variance of the instrument
A reliability of 0.78 was obtained, indicating a level of excellent reliability. In OLS regression, the goal is to find the straight line that best fits the data by minimizing the sum of squared differences between the observed values and the values predicted by the model. The OLS model was solved in Python. The summary of the model results provided information about the regression coefficients, standard errors, t-statistics, p-values, and other relevant details for assessing the significance of the independent variables about the dependent variable. The research aims to address the following questions:
-
RQ1. Which smart delivery strategies in urban courier companies can be applicable in developing countries?
-
RQ2. What are the main barriers to implementing technology in urban courier services in developing countries?
Results
The survey assessed the knowledge of the participating companies regarding the concept of smart delivery. This evaluation aimed to determine the companies’ familiarity with the latest trends and technologies in the urban courier industry. The survey also investigated the digital marketing skills possessed by the participating companies and gathered information about the existing knowledge and competencies in the field of digital marketing within the urban courier sector. The survey examined the utilization of social media, email, and websites as digital marketing strategies among the surveyed courier companies. Likewise, at the end of the study, space was provided for general observations that offered valuable insights into the crucial informants’ perceptions regarding the sector’s myths and realities. This analysis allowed to identify the most utilized channels and understand their impact on the marketing strategies employed by urban courier companies. Table 1 presents the correlation matrix among the variables under study.
Each number in the matrix represents the correlation coefficient between two specific variables. The values range from − 1 to 1, where a value of 1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, meaning that the variables are highly related and move in the same direction; a matter of − 1 shows a perfect negative correlation, meaning that the variables are positively related but move in opposite directions; and a value close to 0 indicates a weak or null correlation, meaning that the variables are not related or have a fragile relationship.
The Use of Social Media variable shows a high positive correlation with all the other variables, indicating that it is related to the use of email, the use of websites, the impact on the number of clients, the knowledge of smart delivery, the adequate digital marketing skills, social media activity, the adoption of social media, and the use of digital marketing in urban courier companies. The Use of Email has a high positive correlation with the Use of Social Media, suggesting a strong relationship between these two variables. This could indicate that individuals who use social media more also tend to use email more.
The Use of Website variable shows very low correlations with the other variables, as most values are close to 0. This indicates a weak or null relationship between the use of websites and the other variables.
The Impact of Social Media on the Number of Customers shows a high positive correlation between the Use of Social Media and Email. This indicates a strong relationship between the impact of social media on the number of customers and the use of social media and email.
The Use of Website variable shows very low correlations with the other variables, as most values are close to 0. This indicates a weak or null relationship between the use of websites and the other variables. The Impact of Social Media on the Number of Customers shows a high positive correlation between the Use of Social Media and Email. This indicates a strong relationship between the impact of social media on the number of customers and the use of social media and email. Knowledge of Smart Delivery, Adequate Digital Marketing Skills, Activity on Social Media, Adoption of Social Media, and Use of Digital Marketing in Urban Courier Companies have high correlations, indicating strong relationships between these variables. Barriers to Digital Marketing have low correlations with the other variables, except for a moderate correlation with the Use of Email. This suggests a weaker relationship between barriers to digital marketing and the other variables studied. Table 2 presents the OLS regression results on digital marketing in urban courier companies.
In the OLS, the dependent variable is the use of digital marketing in urban courier companies. The independent variables are Use of Social Media, Use of Email, Use of Website, Impact of Social Media on Number of Customers, Knowledge of Smart Delivery, Adequate Digital Marketing Skills, Activity on Social Media, Barriers to Digital Marketing, and Adoption of Social Media. The independent variables and their assigned values are as follows: For the variables Use of Social Media, Use of Email, Impact of Social Media on Number of Customers, Knowledge of Smart Delivery, Adequate Digital Marketing Skills, Activity on Social Media, Barriers to Digital Marketing, and Adoption of Social Media, the values ranged from 1 to 5, indicating the frequency or intensity of social media use by urban courier companies, with 1 showing lower intensity and 5 displaying higher intensity.
OLS provides coefficients for each of the independent variables, along with their standard error, t-value, p-value, and 95% confidence intervals. For const, the coefficient is 2.8081, indicating the expected value of the dependent variable when all independent variables are 0.
Social media platforms have become powerful tools for urban courier companies to connect with their target audience, create brand awareness, and promote their services (Park et al., 2021). Through engaging content, targeted advertising, and effective customer engagement, social media marketing allows these companies to establish a strong online presence and foster customer loyalty (Hanaysha, 2022). According to Kar and Kushwaha (2021), when consumers are interested in obtaining necessary information about a brand, they tend to search through social media.
Regarding the use of Social Media, the coefficient is 0.2058, which means that a one-unit increase in social media use is associated, on average, with a 0.2058 increase in the dependent variable. The p-value is less than 0.001, indicating that this variable is statistically significant in the model. Email Use has a coefficient of 0.0349, but the p-value is more significant than 0.05 (0.904), indicating that this variable is not statistically significant in the model. There is insufficient evidence to suggest a significant relationship between email and digital marketing. Website Use has a coefficient of − 0.3385, but the p-value is more significant than 0.05 (0.555), indicating that this variable is not statistically significant in the model. There is insufficient evidence to suggest a significant relationship between websites and digital marketing.
The impact of social media on the number of customers, knowledge of smart delivery, adequate digital marketing skills, activity on social media, and adoption of social media: All these variables have the same coefficient of 0.2058, and the p-value is less than 0.001 for all of them. This indicates that a one-unit increase in these variables is associated, on average, with a 0.2058 increase in the dependent variable. These variables are statistically significant in the model.
Barriers to digital marketing have a coefficient of 0.03, and the p-value is more significant than 0.05 (0.895), indicating that this variable is not statistically significant in the model. There is insufficient evidence to suggest a significant relationship between barriers to digital marketing and digital marketing use. The significant variables in the model are Social Media Use, Impact of Social Media on the Number of Customers, Knowledge of Smart Delivery, Adequate Digital Marketing Skills, Activity on Social Media, and Adoption of Social Media. These variables have positive coefficients, suggesting a positive relationship with digital marketing use in urban courier companies in developing countries. Furthermore, there is a tendency for small businesses to focus on digital marketing as a set of tools rather than guiding the strategy (Quinton & Simkin, 2017), with the use of social media and digital communication platforms being more tactical than strategic (Bocconcelli et al., 2018). Email Use, Website Use, and Barriers to Digital Marketing are not statistically significant in the model.
This analysis allows us to infer that digital marketing can be crucial in improving urban courier services. Developing digital marketing skills is essential to adopting strategies that enhance efficiency (Hoffman et al., 2021), quality, and visibility of courier services. In terms of barriers, although limited knowledge about smart delivery strategies is not a determining factor in adopting digital marketing, it is essential to note that there is an opportunity to educate and train urban courier companies in this area. Additionally, operational and logistical challenges that may arise when implementing smart delivery strategies need to be addressed, along with a situational analysis of security issues present in emerging economies such as Colombia, which often limit the implementation of innovative approaches to ensure a successful transition. Overcoming barriers, such as lack of knowledge and operational challenges, is essential to maximize the impact of digital marketing in these companies and provide more efficient and tailored services to customer needs.
Discussion
The study is framed within the TAM approach to understand the perceptions and attitudes of urban courier companies regarding the implementation of digital marketing and smart delivery in developing countries. The study highlights the importance of perceived usefulness and ease of use in technological adoption. In the context of the research, opportunities for implementing digital marketing strategies are identified in terms of utility to improve operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and other relevant aspects.
The results show that the opportunities with the highest impact and recurrence are linked to digital strategy and smart delivery. This finding suggests that the benefits of digital marketing in urban courier companies are perceived primarily at an external level (digital strategy and smart delivery) rather than at an internal level (human and organizational capabilities and internal and operational organization) (Le-Dain et al., 2023).
On the other hand, when a company successfully assimilates digital technologies, the resulting value proposition and strategic vision enable it to gain a competitive advantage and ultimately optimize its costs sustainably (Kohli, 2017). Innovations in digital products and digital marketing (i.e., innovations in the distribution, promotion, and pricing elements of the marketing mix) have allowed companies to compete in fundamentally new ways (Varadarajan et al., 2022).
Through the TAM, in the discussion with the focus group participants, perceived barriers are identified by urban courier companies that could affect technological adoption and the implementation of digital marketing. Among the identified barriers, the lack of knowledge, resistance to change, associated costs, and other challenges specific to developing contexts are highlighted.
Concerning the posed H1, it is found that the Impact of Social Media on the Number of Customers will be positively correlated with the Use of Social Media and Use of Email. This hypothesis was based on understanding how digital marketing strategies and online presence can influence customer attraction and retention in urban courier services. The results are consistent with findings identified by Chakraborty et al. (2023b), who point out that increased accessibility of social media through smartphones provides opportunities for enhanced social interaction and facilitates user engagement online. Companies that actively utilize social media are believed to leverage a powerful tool to engage with their audiences. These companies can effectively connect with their current and potential customers through participation and interaction on social media platforms. By sharing relevant posts, responding to inquiries and comments, and implementing targeted promotions, companies can remain at the forefront of their customer’s minds and foster closer and more positive relationships.
The variable of Use of Email is linked to direct communication with customers through email. This can include sending relevant updates, exclusive promotions, and informative newsletters. Companies employing effective email strategies are expected to have more direct and personalized communication with their customers. This can impact brand perception and customer loyalty. The variable Impact of Social Media on Number of Customers indicates how actions taken on social media can increase the number of customers. A positive relationship was found between this variable and the other two, as more significant activity and effective communication on social media and through email can amplify company exposure, generate interest, and convert potential customers into actual customers. This supports the notion that increased use of social media and email can enhance the customer base of urban courier companies. The benefits of using social media include increasing awareness and communicating the brand online (Dwivedi et al., 2023).
For H2, Knowledge of Smart Delivery, Adequate Digital Marketing Skills, Activity on Social Media, Adoption of Social Media, and Use of Digital Marketing in Urban Courier Companies will be positively correlated. Companies with more excellent knowledge and skills in digital marketing also tend to be more active on social media and adopt digital marketing strategies more effectively. These variables’ synergistic and interdependent nature forms the basis of this hypothesis. Companies are believed to have a strong foundation to implement digital strategy effectively if they possess a solid and up-to-date understanding of digital marketing practices and concepts, represented by Knowledge of Smart Delivery and Adequate Digital Marketing Skills. This knowledge and skill base may enable them to identify opportunities, make informed decisions, and adapt to the changing dynamics of the digital environment. An important implication of this finding is that, while digital marketing adoption is widely recommended by researchers such as Gibson (2018) and Bala & Verma (2018), companies will gain a competitive advantage only if digital marketing adoption is combined with digital transformation and ecosystem readiness (Masrianto et al., 2022).
Regarding H3, it was identified that a positive and significant relationship exists between increased Use of Social Media and higher adoption of digital marketing strategies. This hypothesis was grounded in the idea that social media has become a crucial communication channel for interacting with customers and promoting products and services. Companies that are more active and engaged on social media are more likely to use digital marketing strategies effectively. Although specific social media engagement strategies for urban courier companies have not been identified in the literature, various studies have explored social media adoption, usage, and impact in the business-to-business (B2B) context (Dwivedi et al., 2023). Some of these studies examine how social media strategies influence online user engagement (McShane et al., 2019). Others focus on developing the process of social media adoption through a three-phase engagement strategy, including coordination, cooperation, and co-production (Chirumalla et al., 2018). Additionally, research has delved into the use of Twitter by both B2B and business-to-consumer (B2C) companies to predict factors influencing messaging strategies (Swani et al., 2013). The rationale behind this theory is that social media allows companies to establish direct and continuous contact with their customers, facilitating information dissemination, promotion of offers, and creation of an online community. Companies capable of generating meaningful interactions on social media will also be more adept at utilizing digital marketing techniques (Masrianto et al., 2022). Ongoing interaction with customers on social media can reveal crucial insights into their preferences, needs, and behaviors. This can impact the devising of more effective and adaptable digital marketing strategies.
Opportunities for Digital Marketing and Smart Delivery
The implementation of digital marketing strategies in urban courier companies in developing countries is not without challenges, and according to key informants perception, there must be a complementary commitment from government entities to guarantee improvements in infrastructure, mobility, and security that contribute to the overall development of the city and, consequently, the urban courier industry sector. These companies face limited marketing budgets (Faruk et al., 2021), intense competition, rapidly evolving technology, and the need to adapt to changing customer preferences (Shree et al., 2021). However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation, differentiation, and creating unique value propositions.
The nature of the competitive landscape also influences the use of digital marketing practices within these companies (Cenamor et al., 2019; O’Dwyer et al., 2009; Shaltoni, 2017). However, such pressures are less likely to apply in environments where digital marketing is the norm. As such, the way these small companies practice marketing can be profoundly influenced by both their operational context (O’Dwyer et al., 2009; Quinton et al., 2018) and their more limited impact on the market (Gilmore et al., 2001; Miller et al., 2021). Implementing digital marketing strategies in urban courier companies allows them to leverage emerging technologies, increase their potential customers, expand their market niches, enhance the customer experience, and optimize their operations.
Real-Time Package Tracking
An intelligent strategy to implement in urban courier services would be the adoption of real-time tracking systems that allow customers to track the status or progress of their shipments through a mobile application or Internet-enabled computer (Steever et al., 2019). This can enhance trust in the courier service by providing customers with peace of mind about the status of their delivery (Zhang et al., 2014). Real-time tracking of packages would enable the company to manage shipments better and help resolve any potential issues. In the event of delays or incidents during delivery, courier companies can quickly detect them and take corrective measures. These situations improve customer confidence by providing prompt responses and timely solutions to unforeseen circumstances. In a highly competitive environment, real-time tracking becomes a key differentiating factor for urban courier companies. With the development of location-based technology and the widespread use of smartphones, it is now possible to quickly obtain sufficient location information about a shipment (Pick et al., 2017).
A person who acquires a service from a company expects, at the very least, to receive reliable and efficient services. Providing customers with the ability to track their shipments in real time builds trust and can attract new customers. Small details supported by technological solutions can influence customer decisions when choosing one courier company over another. To successfully implement real-time tracking, courier companies must invest in technology, such as tracking and real-time communication systems, and ensure their staff is trained to use these tools effectively. Similarly, it is essential to communicate effectively to customers about the availability of real-time tracking and how to access these applications quickly, conveniently, and efficiently.
Personalized Notifications to Customers
Automated personalized notifications can be a digital marketing strategy to keep customers informed about the status of their shipments. Instant messaging applications have gained significant market share in the last decade and have become one of the most widely used applications worldwide by users(Davis et al., 2022). These notifications could be sent via email, text messages, or chat applications and could include updates on the location, estimated delivery time, and any potential changes in the itinerary. These activities would improve communication with users and provide a personalized experience for each shipment.
Personalized notifications have the potential to create a positive perception of trust that facilitates the adoption of companies’ offerings (Dang et al., 2020). In this context, urban courier companies should strive to build trust with consumers to encourage the use of these services. Trust can have a significant influence on customer retention and the generation of a sustained revenue stream (Chakraborty et al., 2023c).
Scheduled Delivery
Current research on urban logistics often claims that the increase in e-commerce and associated courier deliveries is inherently responsible for urban traffic congestion, disruptions, and delays within cities (Kummer et al., 2021). Implementing the option of scheduled delivery is a valuable strategy to optimize routes and delivery schedules by allowing customers to select a specific date and time for the delivery of their shipments according to their availability and preferences. This flexibility would increase customer satisfaction, improve operational efficiency in the process, and reduce transportation costs; as in developing countries, deliveries are directly made to individuals, and shipments are not left at the doorstep of houses and establishments due to higher security conditions (theft and crime) in these territories compared to developed countries.
Integration of Augmented Reality in Delivery
To attract and retain customers, many companies have implemented augmented reality (Wang et al., 2023a, 2023b). As such, augmented reality has evolved from a nice-to-have feature to a standout technology for companies seeking to differentiate themselves from the competition by offering customers a unique and engaging experience. Augmented reality applications provide an immersive experience that combines digital enhancements with the real-world environment in real time (Carmigniani & Furht, 2011). An innovative strategy could be to use augmented reality to enhance the delivery experience. Understanding whether and why consumers adopt or resist innovations is important for firms developing new products and services (Savas-Hall et al., 2020). For example, customers could scan a code on the package and visualize additional information, such as usage instructions or special promotions, directly on their mobile devices. This would add an interactive and surprising element to the package delivery process.
Delivery with Smart Lockers
An innovative strategy would be to implement smart lockers in strategic locations throughout the city through partnerships with chain supermarkets, private security companies providing local security, and community action boards, among others. These parcel lockers serve as pickup points and specific intermediate delivery points (dos Santos et al., 2022). Various studies address the integration of lockers into the delivery system (Iwan et al., 2016; Janjevic et al., 2019; Veenstra et al., 2018), highlighting that the use of lockers for packages can contribute to a reduction in delivery costs and in gas emissions (Lemke et al., 2016; Song et al., 2013), mainly when they are located according to user preferences (Lin et al., 2020; Yuen et al., 2018). With the use of a code system or mobile applications, customers could collect their packages at any convenient time, thus avoiding unnecessary waits and improving delivery efficiency (Rohmer & Gendron, 2020). The proposed shared use of locker facilities by customers who prefer to pick up their orders and as a transfer depot for customers who prefer home delivery will contribute to better utilizing an already available storage capacity (dos Santos et al., 2022).
Use of Geolocation Technology
The integration of geolocation technology in delivery vehicles could be an efficient strategy. This would allow for more accurate management of delivery routes, optimizing times and reducing delays. Additionally, geolocation technology could be used to identify the exact location of the customer when making the delivery, facilitating timely and accurate delivery.
Effective digital marketing strategies offer numerous benefits and outcomes for urban courier companies. These include increased brand awareness, expanded customer reach (Karjaluoto et al., 2015), higher customer engagement and retention (Setkute & Dibb, 2022), improved customer satisfaction (Taiminen & Karjaluoto, 2015), enhanced operational efficiency, and ultimately, increased revenue and profitability. By leveraging digital marketing tools and techniques, urban courier companies can position themselves as industry leaders and gain a competitive edge. To gain a competitive advantage, the digital marketing adoption strategy must be dynamically and effectively adapted (Su et al., 2023). However, customer digital readiness is necessary, which can be achieved by assessing customer digital readiness by analyzing aspects such as customer digital service awareness, co-creation of digital value, and contractual agreements for digital services (Tabares et al., 2023).
Offering Payment for Services Through an App
Considering the economic limitations faced by Colombian families, especially in intermediate cities, it is essential to facilitate the option for customers to make payment offers for urban courier services, similar to what occurs in some digital urban transportation applications. The accelerated growth of digital transactions observed during the coronavirus pandemic, aiming to retain customers and promote continued use of digital payments, was crucial for the continuity of many businesses (Savitha et al., 2022). A mobile payment app is software specifically designed to function on various compatible devices and is used to execute financial payments for services using a mobile or computer device (Chakraborty et al., 2022; Liao & Yang, 2020) and has enjoyed increasing popularity and significant growth (Tew et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023). The frequent use of applications can make consumers familiar with the purchasing process, motivating them to derive immediate benefits from service providers (Chakraborty et al., 2023a).
Payments made through apps primarily consist of transactions related to e-commerce and retail, providing multiple benefits to users through their technological interface and quickly becoming a convenient payment method, even in developing countries (Mohammadi, 2015). Urban courier companies need to identify the benefits of adopting mobile payment applications, as this would enable companies to make decisions based on the cost–benefit relationship of the distances and routes that delivery operators must travel. In this way, a service that aligns with the economic realities of families would be provided, fostering greater loyalty from customers and users in general.
Barriers to Overcome Urban Courier Activities in Developing Countries
The delivery of products through courier services in developing countries faces significant challenges due to economic, environmental, and social issues. These challenges include a shortage of workforce, unstable traffic conditions, limited storage capacity, high fuel consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, among others (Kader et al., 2023). Kaya et al. (2019) demonstrated that delivery delays harm consumer-seller relationships, company reputation, and customer satisfaction. Moreover, poor distribution management, characterized by late and inconvenient deliveries, motivates consumers to seek alternative options in the market. The difficulty in achieving efficient and effective delivery poses a challenge in attracting and retaining customers in an increasingly competitive environment where customer loyalty is hard to attain (Kader et al., 2023).
The experiences and approaches used in developed countries cannot be automatically applied to developing countries due to disparities in economic development and social, political, and cultural systems (Boom-Cárcamo & Peñabaena-Niebles, 2022; Relva et al., 2021; Stadelmann & Castro, 2014). Colombia is a developing country, and many limitations identified for making technological advancements in urban courier processes apply to other countries in the same category. The following difficulties in implementing technology in courier processes were identified within the study, and participating companies used the surveys.
Infrastructure Limitations
As an essential element of the business ecosystem, telecommunications infrastructure can effectively stimulate business activity (Li et al., 2023). Developing countries may need help with reliable communication infrastructure, such as high-speed and widespread Internet networks, which can hinder the adoption of technological solutions in the courier sector. Slow or unstable connections make real-time data transmission and efficient communication among the different actors involved in the delivery chain difficult (Pan et al., 2022).
Another unusual situation is the poor condition of transportation routes, which can cause delivery delays, difficulty accessing certain areas, and increased operational costs. This directly affects the ability to implement technology in courier processes, as solid and efficient transportation infrastructure is required to ensure the smooth operation of services (Tiznado-Aitken et al., 2022). The need for widespread access to mobile devices and communication technology can also be challenging in developing countries. Suppose customers and courier workers need help accessing devices like smartphones or computers. In that case, adopting technological solutions that could improve the efficiency and quality of courier services becomes difficult.
Limited Access to Technology
Mocnik and Sirec (2010) stated that access to the Internet is an essential tool for people to access information quickly. Access to technological devices and services, such as smartphones, computers, and Internet connection, can help adopt and utilize technology in courier processes. Access to information is part of adequately integrating developing countries into the global economy and increasing their level of development (Korkmaz et al., 2022).
In many developing countries, these devices and services may need more availability and affordability, creating a significant barrier for courier companies and their employees to fully leverage technology for efficient operations, real-time tracking, and seamless customer communication. Furthermore, the absence of reliable Internet connectivity in certain regions can further hinder the implementation of technology-driven solutions, as it restricts the ability to access online platforms, track shipments, and effectively communicate with customers. It is worth noting that access to the Internet significantly affects economic activity, mainly through its impact on productivity and social welfare (Jorgenson et al., 2008).
Costs Associated with Technology Adoption
Implementing technology in courier processes entails significant costs, including acquiring equipment, specialized software, and staff training. In developing countries, these investments can be challenging due to their economic limitations. The implementation poses considerable risks for SMEs in emerging economies, and developing strategies to effectively manage the risks of implementing new technologies in emerging economy contexts is crucial (Tamvada et al., 2022). Courier companies in these countries may need more financial resources to adopt the technology due to needing more financial resources (Costa et al., 2023). SMEs in emerging economies need more support in accessing capital and technology due to the high costs associated with acquisition and maintenance (Coad & Tamvada, 2012). This limits their ability to compete in the market and benefit from the efficiencies and operational improvements that technology can provide.
Regarding barriers to digitization and innovation, Ullah et al. (2021) identified high software and hardware costs is the second most important barrier in the technological domain. Mohanty et al. (2016) argued that the quantity of intelligent components or digital technologies depends on the cost and technological infrastructure available in the form of software and hardware that can be used to disseminate it. Similarly, according to Sepasgozar et al. (2019), transaction cost analysis theory should be integrated within the set of theories that emphasize socio-economic dimensions and explain the acceptance of digital technologies.
Digital Divide and Skills
New digital technologies are shaping the transformation of productive activities. This change process is characterized by increasing digitization, interconnectivity, and automation (Cirillo et al., 2023). While developed countries have greater access to technology and digital skills, developing countries need more infrastructure and resources to adopt and utilize technology in the courier sector fully. Several studies have indicated that companies face significant challenges in harnessing knowledge when they fail to effectively integrate their capabilities, skills, resources, and critical factors necessary for fostering innovation (Pedraza-Rodríguez et al., 2023). However, firms have to anticipate skill needs in preparation for particular technological options and are constrained in their technological choices by human capital endowments (Cirillo et al., 2023).
The lack of technical skills and knowledge in using technology is another significant barrier. Many workers in the courier sector in developing countries may not be familiar with the operation of digital tools or lack the necessary skills to use technological systems and applications in their daily work efficiently. This can hinder the adoption and utilization of available technical solutions; however, systematization, competencies in human talent management, and technological skills will be even more essential in the business structures of emerging economies (Amaris et al., 2022).
As a strategy to overcome these barriers, courier companies must invest in training programs and the development of digital skills. This involves providing access to technology education, training in digital tools, and promoting digital literacy overall. Additionally, collaboration is required between governments, businesses, and other relevant organizations to improve technological infrastructure and ensure equitable access to technology throughout the courier sector (Meng & Wang, 2023). Significant improvements in efficiency, service quality, and competitiveness of courier companies in developing countries can be achieved by addressing the digital divide and strengthening digital skills. Furthermore, technology adoption can open new opportunities for growth and development in the sector, aligning it with global trends and enabling greater integration into the digital economy.
Resistance to Change
Employees and established courier companies may resist the implementation of technological advancements for various reasons. Resistance to change can be a significant factor in the success or failure of changes (Warrick, 2023). From the employee’s perspective, there may be a fear of job displacement or changes in job roles and responsibilities (Burnes, 2015). How an individual responds to change depends on their attitude toward change and response to a specific shift. While some individuals adapt and accept differences, others reject them and prefer to maintain the status quo (Warrick, 2023). Resistance is likely to occur if self-interest or adverse effects are threatened. Some employees may need more skills or knowledge to adapt to new technologies, leading to resistance. Additionally, employees accustomed to traditional methods may feel comfortable with their current practices and must be more open to adopting new working methods.
At the organizational level, Ullah et al. (2021) identified that the higher likelihood of failure is due to the organizational unwillingness to invest in digital marketing. Low et al. (2020) insisted on the adoption of digital marketing, discussing that creating real-time interactions, developing key performance indicators to measure digital marketing, personalization, and fostering innovation in digital marketing paves the way for the use and adoption of digital technologies. Therefore, it is necessary to increase investments in this area (Kumar et al., 2021).
On the other hand, courier companies may resist change due to concerns about the cost of implementing new technologies, potential disruptions to existing operations, or a need to understand the benefits that technology can bring to their business. There may also be a reluctance to invest in training and development programs to enhance employees’ skills and equip them with the necessary digital competencies. Companies must provide clear and transparent communication about the reasons for adopting new technologies and the benefits they can bring, considering that human capital is the main component of business development and its primary resource (Bilichenko et al., 2022). Involving employees in decision-making and providing appropriate training and support can help alleviate their concerns and build trust (Vos & Rupert, 2018). Creating a culture of innovation and continuous improvement within the organization can also help overcome resistance and encourage employees and companies to embrace technological changes to enhance their operations and competitiveness.
Theoretical and Practical Implications
This study contributes specifically to the literature in the context of digital marketing in urban courier companies. While scholars have shown interest in understanding how digital marketing evolved (Faruk et al., 2021), the digital marketing capability of companies (Masrianto et al., 2022), barriers to digital marketing in small B2B firms (Setkute & Dibb, 2022), and how market pressures and organizational readiness drive the evolution of digital marketing adoption strategies in small and medium enterprises (Su et al., 2023), to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study examining barriers and opportunities for digital marketing implementation in urban courier companies in developing countries. Therefore, our empirical research makes a noteworthy contribution that enriches the emerging but limited research on the topic, in addition to providing valuable insight into how local courier companies can optimize their online marketing strategies to adapt to changing market conditions, enhancing the effectiveness of their services and strengthening their competitive position.
On the other hand, the research provides specific recommendations for improving operational efficiency, integrating digital technologies, and overcoming logistical obstacles in market entry. Simultaneously, the study could lead to significant changes in public policy and regulation concerning urban courier transportation in developing countries. Identifying specific barriers could result in suggestions on creating a more conducive environment for innovation and the adoption of digital technologies in this sector.
On a business level, the research could serve as a valuable guide for urban courier companies in formulating digital marketing and smart delivery strategies. It could help them enhance efficiency, reach new customers, and stay competitive in a constantly changing business market. The research would be beneficial for companies in this sector as well as for public policies aimed at developing urban courier services in developing countries.
Limitations and Future Work
These results should be approached with caution for several reasons. Our findings stem from a focus group involving urban courier companies in Colombia, and while they provide strong inferences supported by the literature, generalizing to specific business contexts could be challenging. Considering the characteristics of the courier companies in the focus group and the respondents, the results of this study are particularly relevant to such companies operating in traditional areas of developing countries, aspiring to enhance their strategic and operational processes supported by digital marketing.
Developing countries provide a particularly critical field research context for studies like this, where issues, underlying causes, possible solutions, and development directions are analyzed. It should be noted that the identified barriers for urban courier activities in this situation are by no means extrapolatable to other regions or countries with different socio-economic situations and logistical conditions. The proposed study and its recommendations are specifically aimed at improving courier operations in specific environments within developing countries and may require considerable adaptations for application in more diverse or industrialized contexts.
For future research, it is proposed to explore how to adapt these smart delivery strategies to the specific contexts of developing countries, taking into account differences in community structures, regulations, and market demand. This approach can provide an understanding of how these strategies can be recalibrated to successfully address the social and economic needs of each location, potentially facilitating their implementation. Along the same lines, it is suggested to investigate the socio-economic impact of applying these strategies in small communities. By emphasizing job creation, service improvement, and enabling micro-businesses to integrate into the digital economy, this research direction could delve into how smart delivery strategies can contribute to boosting the local economy and fostering the digital transformation of urban courier services in developing countries.
Conclusions
Given the constant evolution of the urban courier sector, these companies must stay updated on the latest digital marketing trends and seek continuous innovation to meet the changing needs of their customers. The findings suggest that strategic utilization and active adoption of social media are critical elements in improving digital marketing in urban courier companies. Furthermore, the low adoption of websites is identified as an area for improvement in expanding online presence and enhancing company visibility. Urban courier companies are recommended to consider increasing their investment in digital marketing, developing effective social media strategies, and exploring the potential of websites as marketing tools (Chaker et al., 2022). These findings indicate that urban courier companies can benefit from strategically using social media and email in their digital marketing efforts. Additionally, they should improve their online presence through website optimization to maximize its impact as a marketing channel.
Implementing the proposed strategies in the Colombian context would require significant investment in technology, research, and development, as well as careful logistical planning and compliance with local regulations. However, by offering smart and innovative delivery solutions, urban courier companies in developing countries, can differentiate themselves in the market, generate customer interest, and position themselves as leaders in innovation within the sector, providing competitive advantages and improving the customer experience. By staying in tune with the latest trends and emerging technologies, companies can quickly adapt to market changes and stay ahead in the urban courier industry.
Digital marketing can be a catalyst for enhancing urban courier services. Identifying and overcoming barriers to implementing smart delivery strategies, such as limited knowledge and operational challenges, are crucial to capitalize on opportunities and maximize the impact of digital marketing in these companies. By examining the strategies employed, challenges faced, and outcomes achieved, a comprehensive understanding of the impact of digital marketing on the growth and sustainability of these companies can be achieved. The insights provided in this research will assist industry professionals and researchers in identifying best practices and future directions for digital marketing in the context of urban courier services.
References
Amaris, R. R. A., Molina, R. I. R., Ruiz, M. J. S., & Raby, N. D. L. (2022). Generic and technical skills of human talent supported by ICT: Systematization, scope, and reflections. Procedia Computer Science, 210, 378–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2022.10.168
Bala, M., & Verma, D. (2018). A critical review of digital marketing paper type: - Review and viewpoint. International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering, 8(10), 321–339.
Bilichenko, O., Tolmachev, M., Polozova, T., Aniskevych, D., & Mohammad, A. L. A. K. (2022). Managing strategic changes in personnel resistance to open innovation in companies. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(3), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc8030151
Binh Nguyen, P. M., Pham, X. L., & To Truong, G. N. (2023). A bibliometric analysis of research on tourism content marketing: Background knowledge and thematic evolution. Heliyon, 9(2), e13487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13487
Bocconcelli, R., Cioppi, M., Fortezza, F., Francioni, B., Pagano, A., Savelli, E., & Splendiani, S. (2018). SMEs and marketing: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Management Reviews, 20(2), 227–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12128
Boom-Cárcamo, E., & Peñabaena-Niebles, R. (2022). Opportunities and challenges for the waste management in emerging and frontier countries through industrial symbiosis. Journal of Cleaner Production, 363, 132607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132607
Burnes, B. (2015). Understanding resistance to change – Building on Coch and French. Journal of Change Management, 15(2), 92–116. https://doi.org/10.1080/14697017.2014.969755
Carmigniani, J., & Furht, B. (2011). Augmented reality: An overview. Handbook of Augmented Reality (pp. 3–46). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0064-6_1
Cenamor, J., Parida, V., & Wincent, J. (2019). How entrepreneurial SMEs compete through digital platforms: The roles of digital platform capability, network capability and ambidexterity. Journal of Business Research, 100, 196–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.03.035
Chaker, N. N., Nowlin, E. L., Pivonka, M. T., Itani, O. S., & Agnihotri, R. (2022). Inside sales social media use and its strategic implications for salesperson-customer digital engagement and performance. Industrial Marketing Management, 100, 127–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2021.10.006
Chakraborty, D., Siddiqui, A., Siddiqui, M., Rana, N. P., & Dash, G. (2022). Mobile payment apps filling value gaps: Integrating consumption values with initial trust and customer involvement. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 66, 102946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.102946
Chakraborty, D., Babu Singu, H., Kumar Kar, A., & Biswas, W. (2023a). From fear to faith in the adoption of medicine delivery application: An integration of SOR framework and IRT theory. Journal of Business Research, 166, 114140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.114140
Chakraborty, G. S., Polisetty, D., Khorana, A., & Buhalis, D. (2023b). Use of metaverse in socializing: Application of the big five personality traits framework. Psychology & Marketing, 40(10), 2132–2150. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21863
Chakraborty, D., Siddiqui, M., Siddiqui, A., Paul, J., Dash, G., & Mas, F. D. (2023c). Watching is valuable: Consumer views – Content consumption on OTT platforms. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 70, 103148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103148
Chirumalla, K., Oghazi, P., & Parida, V. (2018). Social media engagement strategy: Investigation of marketing and R&D interfaces in manufacturing industry. Industrial Marketing Management, 74, 138–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2017.10.001
Chuah, S.H.-W., Aw, E.C.-X., & Cheng, C.-F. (2022). A silver lining in the COVID-19 cloud: Examining customers’ value perceptions, willingness to use and pay more for robotic restaurants. Journal of Hospitality Marketing and Management, 31(1), 49–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/19368623.2021.1926038
Ciarli, T., Kenney, M., Massini, S., & Piscitello, L. (2021). Digital technologies, innovation, and skills: Emerging trajectories and challenges. Research Policy, 50(7), 104289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2021.104289
Cirillo, V., Fanti, L., Mina, A., & Ricci, A. (2023). The adoption of digital technologies: Investment, skills, work organisation. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 66, 89–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2023.04.011
Coad, A., & Tamvada, J. P. (2012). Firm growth and barriers to growth among small firms in India. Small Business Economics, 39(2), 383–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11187-011-9318-7
Cole, H. S., DeNardin, T., & Clow, K. E. (2017). Small service businesses: Advertising attitudes and the use of digital and social media marketing. Services Marketing Quarterly, 38(4), 203–212. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332969.2017.1394026
Costa, A., Crupi, A., De Marco, C. E., & Di Minin, A. (2023). SMEs and open innovation: Challenges and costs of engagement. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 194, 122731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122731
Cui, M., Pan, S. L., Newell, S., & Cui, L. (2017). Strategy, resource orchestration and e-commerce enabled social innovation in rural China. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 26(1), 3–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2016.10.001
Dang, V. T., Nguyen, N., & Pervan, S. (2020). Retailer corporate social responsibility and consumer citizenship behavior: The mediating roles of perceived consumer effectiveness and consumer trust. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102082
Das, M., & Ramalingam, M. (2023). To praise or not to praise- Role of word of mouth in food delivery apps. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 74, 103408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2023.103408
Davis, M., McInnes, B., & Ahmed, I. (2022). Forensic investigation of instant messaging services on Linux OS: Discord and Slack as case studies. Forensic Science International: Digital Investigation, 42, 301401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsidi.2022.301401
de Groot, J. I. M. (2022). The personalization paradox in Facebook advertising: The mediating effect of relevance on the personalization–brand attitude relationship and the moderating effect of intrusiveness. Journal of Interactive Advertising, 22(1), 57–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/15252019.2022.2032492
De Vries, L., Gensler, S., & Leeflang, P. S. H. (2017). Effects of traditional advertising and social messages on brand-building metrics and customer acquisition. Journal of Marketing, 81(5), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1509/jm.15.0178
dos Santos, A. G., Viana, A., & Pedroso, J. P. (2022). 2-Echelon lastmile delivery with lockers and occasional couriers. Transportation Research Part e: Logistics and Transportation Review, 162, 102714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2022.102714
Dwivedi, Y. K., Ismagilova, E., Rana, N. P., & Raman, R. (2023). Social media adoption, usage and impact in business-to-business (B2B) context: A state-of-the-art literature review. Information Systems Frontiers, 25, 971–993. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10106-y
Ecker, Y., & Strüver, A. (2022). Towards alternative platform futures in post-pandemic cities? A case study on platformization and changing socio-spatial relations in on-demand food delivery. Digital Geography and Society, 3, 100032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diggeo.2022.100032
Erdmann, A., Arilla, R., & Ponzoa, J. M. (2022). Search engine optimization: The long-term strategy of keyword choice. Journal of Business Research, 144, 650–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.01.065
Faruk, M., Rahman, M., & Hasan, S. (2021). How digital marketing evolved over time: A bibliometric analysis on Scopus database. Heliyon, 7(12), e08603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08603
Gibson, C. (2018). The most effective digital marketing strategies & approaches: A review of literature. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, 8(2), 12.
Gilmore, A., Carson, D., & Grant, K. (2001). SME marketing in practice. Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 19(1), 6–11. https://doi.org/10.1108/02634500110363583
Goic, M., Rojas, A., & Saavedra, I. (2021). The effectiveness of triggered email marketing in addressing browse abandonments. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 55, 118–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intmar.2021.02.002
Hanaysha, J. R. (2022). Impact of social media marketing features on consumer’s purchase decision in the fast-food industry: Brand trust as a mediator. International Journal of Information Management Data Insights, 2(2), 100102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjimei.2022.100102
Hao, C., & Yang, L. (2022). Platform advertising and targeted promotion: Paid or free? Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 55, 101178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elerap.2022.101178
Harrigan, P., & Hulbert, B. (2011). How can marketing academics serve marketing practice? The new marketing DNA as a model for marketing education. Journal of Marketing Education, 33(3), 253–272. https://doi.org/10.1177/0273475311420234
Hoffman, D. L., Moreau, C. P., Stremersch, S., & Wedel, M. (2021). The rise of new technologies in marketing: A framework and outlook. Journal of Marketing, 86(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/00222429211061636
Iwan, S., Kijewska, K., & Lemke, J. (2016). Analysis of parcel lockers’ efficiency as the last mile delivery solution - The results of the research in Poland. Transportation Research Procedia, 12, 644–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2016.02.018
Janjevic, M., Winkenbach, M., & Merchán, D. (2019). Integrating collection-and-delivery points in the strategic design of urban last-mile e-commerce distribution networks. Transportation Research Part e: Logistics and Transportation Review, 131, 37–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2019.09.001
Jorgenson, D. W., Ho, M. S., & Stiroh, K. J. (2008). A retrospective look at the U. S. productivity growth resurgence. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 22(1), 3–24. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.22.1.3
Kader, M. S., Rashaduzzaman, M., Huang, X., & Kim, S. (2023). Influencing factors toward e-shoppers’ adoption of green last-mile delivery. International Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, 51(2), 220–237. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJRDM-10-2021-0480
Kar, A. K., & Kushwaha, A. K. (2021). Facilitators and barriers of artificial intelligence adoption in business – Insights from opinions using big data analytics. Information Systems Frontiers. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-021-10219-4
Karjaluoto, H., Mustonen, N., & Ulkuniemi, P. (2015). The role of digital channels in industrial marketing communications. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 30(6), 703–710. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-04-2013-0092
Kaya, B., Behravesh, E., Abubakar, A. M., Kaya, O. S., & Orús, C. (2019). The moderating role of website familiarity in the relationships between e-service quality, e-satisfaction and e-loyalty. Journal of Internet Commerce, 18(4), 369–394. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332861.2019.1668658
Kohli, A. K. (2017). Market orientation in a digital world. Global Business Review, 18(3_suppl), S203–S205. https://doi.org/10.1177/0972150917700769
Korkmaz, Ö., Erer, E., & Erer, D. (2022). Internet access and its role on educational inequality during the COVID-19 pandemic. Telecommunications Policy, 46(5), 102353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.telpol.2022.102353
Kumar, B., & Sharma, A. (2022). Examining the research on social media in business-to-business marketing with a focus on sales and the selling process. Industrial Marketing Management, 102, 122–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.01.008
Kumar, S., Talasila, V., & Pasumarthy, R. (2021). A novel architecture to identify locations for real estate investment. International Journal of Information Management, 56, 102012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.09.008
Kummer, S., Hribernik, M., Herold, D. M., Mikl, J., Dobrovnik, M., & Schoenfelder, S. (2021). The impact of courier-, express- and parcel (CEP) service providers on urban road traffic: The case of Vienna. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, 9, 100278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trip.2020.100278
Le-Dain, M. A., Benhayoun, L., Matthews, J., & Liard, M. (2023). Barriers and opportunities of digital servitization for SMEs: The effect of smart product-service system business models. In Service Business (Vol. 17, Issue 1). Springer Berlin Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11628-023-00520-4
Lemke, J., Iwan, S., & Korczak, J. (2016). Usability of the parcel lockers from the customer perspective - The research in Polish cities. Transportation Research Procedia, 16, 272–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trpro.2016.11.027
Li, Y., Zhang, J., & Lyu, Y. (2023). Does telecommunications infrastructure promote entrepreneurship in developing countries? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment in China. Structural Change and Economic Dynamics, 66, 106–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2023.04.013
Liao, S.-H., & Yang, L.-L. (2020). Mobile payment and online to offline retail business models. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102230
Lin, C., Choy, K. L., Ho, G. T. S., Lam, H. Y., Pang, G. K. H., & Chin, K. S. (2014). A decision support system for optimizing dynamic courier routing operations. Expert Systems with Applications, 41(15), 6917–6933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2014.04.036
Lin, F., Fofanah, S. S., & Liang, D. (2011). Assessing citizen adoption of e-Government initiatives in Gambia: A validation of the technology acceptance model in information systems success. Government Information Quarterly, 28(2), 271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2010.09.004
Lin, Y. H., Wang, Y., He, D., & Lee, L. H. (2020). Last-mile delivery: Optimal locker location under multinomial logit choice model. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2020.102059
Low, S., Ullah, F., Shirowzhan, S., Sepasgozar, S. M. E., & Lee, C. L. (2020). Smart digital marketing capabilities for sustainable property development: A case of Malaysia. Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135402
Masrianto, A., Hartoyo, H., Hubeis, A. V. S., & Hasanah, N. (2022). Digital marketing utilization index for evaluating and improving company digital marketing capability. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(3), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc8030153
McShane, L., Pancer, E., & Poole, M. (2019). The influence of B to B social media message features on brand engagement: A fluency perspective. Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, 26(1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1080/1051712X.2019.1565132
Meng, F., & Wang, W. (2023). The impact of digitalization on enterprise value creation: An empirical analysis of Chinese manufacturing enterprises. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge, 8(3), 100385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jik.2023.100385
Miklosik, A., Kuchta, M., Evans, N., & Zak, S. (2019). Towards the adoption of machine learning-based analytical tools in digital marketing. IEEE Access, 7, 85705–85718. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2924425
Miller, K., McAdam, M., Spieth, P., & Brady, M. (2021). Business models big and small: Review of conceptualisations and constructs and future directions for SME business model research. Journal of Business Research, 131, 619–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.12.036
Močnik, D., & Širec, K. (2010). The determinants of Internet use controlling for income level: Cross-country empirical evidence. Information Economics and Policy, 22(3), 243–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infoecopol.2010.01.002
Mohammadi, H. (2015). A study of mobile banking usage in Iran. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 33(6), 733–759. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-08-2014-0114
Mohanty, S. P., Choppali, U., & Kougianos, E. (2016). Everything you wanted to know about smart cities. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 5(3), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCE.2016.2556879
Mu, J., Zhang, J., Borah, A., & Qi, J. (2022). Creative appeals in firm-generated content and product performance. Information Systems Research, 33(1), 18–42. https://doi.org/10.1287/ISRE.2022.1117
Nobile, T. H., & Cantoni, L. (2023). Personalisation (in)effectiveness in email marketing. Digital Business, 3(2), 100058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.digbus.2023.100058
O’Dwyer, M., Gilmore, A., & Carson, D. (2009). Innovative marketing in SMEs. European Journal of Marketing, 43(1), 46–61. https://doi.org/10.1108/03090560910923238
Pan, W., Xie, T., Wang, Z., & Ma, L. (2022). Digital economy: An innovation driver for total factor productivity. Journal of Business Research, 139, 303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.09.061
Pandey, N., Nayal, P., & Rathore, A. S. (2020). Digital marketing for B2B organizations: Structured literature review and future research directions. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 35(7), 1191–1204. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-06-2019-0283
Park, J., Hyun, H., & Thavisay, T. (2021). A study of antecedents and outcomes of social media WOM towards luxury brand purchase intention. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102272
Pedraza-Rodríguez, J. A., Ruiz-Vélez, A., Sánchez-Rodríguez, M. I., & Fernández-Esquinas, M. (2023). Management skills and organizational culture as sources of innovation for firms in peripheral regions. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 191, 122518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122518
Pick, J. B., Turetken, O., Deokar, A. V., & Sarkar, A. (2017). Location analytics and decision support: Reflections on recent advancements, a research framework, and the path ahead. Decision Support Systems, 99, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2017.05.016
Quinton, S., Canhoto, A., Molinillo, S., Pera, R., & Budhathoki, T. (2018). Conceptualising a digital orientation: Antecedents of supporting SME performance in the digital economy. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 26(5), 427–439. https://doi.org/10.1080/0965254X.2016.1258004
Quinton, S., & Simkin, L. (2017). The digital journey: Reflected learnings and emerging challenges. International Journal of Management Reviews, 19(4), 455–472. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijmr.12104
Relva, S. G., da Silva, V. O., Gimenes, A. L. V., Udaeta, M. E. M., Ashworth, P., & Peyerl, D. (2021). Enhancing developing countries’ transition to a low-carbon electricity sector. Energy, 220, 119659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119659
Rizvanović, B., Zutshi, A., Grilo, A., & Nodehi, T. (2023). Linking the potentials of extended digital marketing impact and start-up growth: Developing a macro-dynamic framework of start-up growth drivers supported by digital marketing. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 186, 122128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122128
Rohmer, S. U., & Gendron, B. (2020). A guide to parcel lockers in last mile distribution: Highlighting challenges and opportunities from an OR perspective. Cirrelt
Roy, S. K., Shekhar, V., Lassar, W. M., & Chen, T. (2018). Customer engagement behaviors: The role of service convenience, fairness and quality. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 44, 293–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2018.07.018
Savas-Hall, S., Koku, P. S., & Mangleburg, T. (2020). Consumers’ perception of service newness and its marketing implications. Services Marketing Quarterly, 41(1), 35–48. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332969.2019.1707373
Savitha, B., Hawaldar, I. T., & Kumar, K. N. (2022). Continuance intentions to use FinTech peer-to-peer payments apps in India. Heliyon, 8(11), e11654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11654
Sepasgozar, S. M. E., Hawken, S., Sargolzaei, S., & Foroozanfa, M. (2019). Implementing citizen centric technology in developing smart cities: A model for predicting the acceptance of urban technologies. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 142, 105–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.09.012
Setkute, J., & Dibb, S. (2022). Old boys’’ club”: Barriers to digital marketing in small B2B firms. Industrial Marketing Management, 102, 266–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.01.022
Shachak, A., Kuziemsky, C., & Petersen, C. (2019). Beyond TAM and UTAUT: Future directions for HIT implementation research. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103315
Shaltoni, A. M. (2017). From websites to social media: Exploring the adoption of internet marketing in emerging industrial markets. Journal of Business and Industrial Marketing, 32(7), 1009–1019. https://doi.org/10.1108/JBIM-06-2016-0122
Sham, R., Chong, H. X., Cheng-Xi Aw, E., Thangal, B. T., Abdamia, N.., & Binti. (2023). Switching up the delivery game: Understanding switching intention to retail drone delivery services. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 75, 103478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2023.103478
Shree, D., Kumar Singh, R., Paul, J., Hao, A., & Xu, S. (2021). Digital platforms for business-to-business markets: A systematic review and future research agenda. Journal of Business Research, 137, 354–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.08.031
Song, L., Guan, W., Cherrett, T., & Li, B. (2013). Quantifying the greenhouse gas emissions of local collection-and-delivery points for last-mile deliveries. Transportation Research Record, 2340, 66–73. https://doi.org/10.3141/2340-08
Stadelmann, M., & Castro, P. (2014). Climate policy innovation in the South - Domestic and international determinants of renewable energy policies in developing and emerging countries. Global Environmental Change, 29, 413–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2014.04.011
Steever, Z., Karwan, M., & Murray, C. (2019). Dynamic courier routing for a food delivery service. Computers & Operations Research, 107, 173–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2019.03.008
Su, J., Zhang, Y., & Wu, X. (2023). How market pressures and organizational readiness drive digital marketing adoption strategies’ evolution in small and medium enterprises. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 193, 122655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122655
Swani, K., Milne, G., Brown, P. B. (2013). Spreading the word through likes on Facebook. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 7(4), 269–294. https://doi.org/10.1108/JRIM-05-2013-0026
Symitsi, E., Markellos, R. N., & Mantrala, M. K. (2022). Keyword portfolio optimization in paid search advertising. European Journal of Operational Research, 303(2), 767–778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2022.03.006
Tabares, S., Parida, V., & Visnjic, I. (2023). Revenue models for digital services in the railway industry: A framework for choosing the right revenue model. Journal of Business Research, 165, 114041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.114041
Taherdoost, H. (2018). A review of technology acceptance and adoption models and theories. Procedia Manufacturing, 22, 960–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2018.03.137
Taiminen, H. M., & Karjaluoto, H. (2015). The usage of digital marketing channels in SMEs. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 22(4), 633–651. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSBED-05-2013-0073
Tamvada, J. P., Narula, S., Audretsch, D., Puppala, H., & Kumar, A. (2022). Adopting new technology is a distant dream? The risks of implementing Industry 4.0 in emerging economy SMEs. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 185, 122088. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122088
Tew, H.-T., Tan, G.W.-H., Loh, X.-M., Lee, V.-H., Lim, W.-L., & Ooi, K.-B. (2022). Tapping the next purchase: Embracing the wave of mobile payment. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 62(3), 527–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/08874417.2020.1858731
Tiznado-Aitken, I., Mora, R., Oyarzún, G., Vergara, J., & Vecchio, G. (2022). A bumpy ride: Structural inequalities, quality standards, and institutional limitations affecting cycling infrastructure. Transportation Research Part d: Transport and Environment, 110, 103434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2022.103434
Tomczyk, A. T., Buhalis, D., Fan, D. X. F., & Williams, N. L. (2022). Price-personalization: Customer typology based on hospitality business. Journal of Business Research, 147, 462–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2022.04.036
Ullah, F., Sepasgozar, S. M. E., Thaheem, M. J., & Al-Turjman, F. (2021). Barriers to the digitalisation and innovation of Australian Smart Real Estate: A managerial perspective on the technology non-adoption. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 22, 101527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2021.101527
Varadarajan, R., Welden, R. B., Arunachalam, S., Haenlein, M., & Gupta, S. (2022). Digital product innovations for the greater good and digital marketing innovations in communications and channels: Evolution, emerging issues, and future research directions. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 39(2), 482–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2021.09.002
Veenstra, M., Roodbergen, K. J., Coelho, L. C., & Zhu, S. X. (2018). A simultaneous facility location and vehicle routing problem arising in health care logistics in the Netherlands. European Journal of Operational Research, 268(2), 703–715. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2018.01.043
Verma, A., Chakraborty, D., & Verma, M. (2023). Barriers of food delivery applications: A perspective from innovation resistance theory using mixed method. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 73, 103369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2023.103369
Vos, J. F. J., & Rupert, J. (2018). Change agent’s contribution to recipients’ resistance to change: A two-sided story. European Management Journal, 36(4), 453–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2017.11.004
Wang, F., Xu, H., Hou, R., & Zhu, Z. (2023a). Designing marketing content for social commerce to drive consumer purchase behaviors: A perspective from speech act theory. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 70, 103156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103156
Wang, K.-Y., Ashraf, A. R., Tek Thongpapanl, N., & Nguyen, O. (2023b). Influence of social augmented reality app usage on customer relationships and continuance intention: The role of shared social experience. Journal of Business Research, 166, 114092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.114092
Warrick, D. D. (2023). Revisiting resistance to change and how to manage it: What has been learned and what organizations need to do. Business Horizons, 66(4), 433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2022.09.001
Yalçın, N., & Köse, U. (2010). What is search engine optimization: SEO? Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 9, 487–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.12.185
Yaseen, H., Al-Adwan, A. S., & Al-Madadha, A. (2019). Digital marketing adoption among smes in Jordan: A mixed-method approach. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 97(4), 1396–1407.
Yuen, K. F., Wang, X., Ng, L. T. W., & Wong, Y. D. (2018). An investigation of customers’ intention to use self-collection services for last-mile delivery. Transport Policy, 66, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranpol.2018.03.001
Zhang, J. Z., & Watson, G. F., IV. (2020). Marketing ecosystem: An outside-in view for sustainable advantage. Industrial Marketing Management, 88, 287–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.04.023
Zhang, Qi., Ariffin, S. K., Richardson, C., & Wang, Y. (2023). Influencing factors of customer loyalty in mobile payment: A consumption value perspective and the role of alternative attractiveness. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 73, 103302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2023.103302
Zhang, Q., Feng, D., & Wang, F. (2014). Courier: Multi-dimensional QoS guarantees for the consolidated storage system. Future Generation Computer Systems, 37, 97–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2013.06.013
Zheng, R., Li, Z., & Na, S. (2022). How customer engagement in the live-streaming affects purchase intention and customer acquisition, E-tailer’s perspective. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 68,. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103015
Zhu, Q., Bai, C., & Sarkis, J. (2022). Blockchain technology and supply chains: The paradox of the atheoretical research discourse. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2022.102824
Ziółkowska, M. J. (2021). Digital transformation and marketing activities in small and medium-sized enterprises. Sustainability, 13(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13052512
Funding
Open Access funding provided by Colombia Consortium
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Boom-Cárcamo, E., Molina-Romero, S., Galindo-Angulo, C. et al. Barriers and Strategies for Digital Marketing and Smart Delivery in Urban Courier Companies in Developing Countries. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01823-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01823-1