Abstract
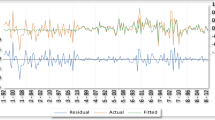
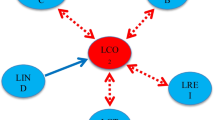
The recent COVID-19-induced global economic recession has led to lower natural resource prices, thereby reducing energy demand. Amid this concern, renewable energy projects have become uncompetitive and an obstacle to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Following Pesaran et al.’s (Journal of Applied Econometrics, 16, 289–326, 2001) ARDL approach, green finance, renewable energy generation, and private energy investment have strong incremental effects on short-term and long-term renewable energy investment in China during 1980–2022. The findings also show that green finance, renewable electricity output, renewable energy consumption, and the square of gross domestic product (GDP2) have a significant negative impact, while gross domestic product (GDP) has a significant positive impact on China’s long-term CO2 emissions. The positive association between GDP and carbon dioxide emissions and the negative relationship between GDP2 and carbon dioxide emissions rationalize the inverted U-shaped EKC hypothesis for China. The vector error correction model (VECM) Granger causality test indicates that renewable energy investment, green finance, renewable energy consumption, CO2 emission, and gross domestic product (GDP) have long-term causality. Policies must aim to control volatility and promote investment in renewable energy investment, green finance, and renewable electricity output for sustainable growth and the environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in World 489 Development Indicator page published by World Bank (2020), at https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world490 development-indicators.
References
Adebayo, T. S., Adedoyin, F. F., & Kirikkaleli, D. (2021). Toward a sustainable environment: Nexus between consumption-based carbon emissions, economic growth, renewable energy and technological innovation in Brazil. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(37), 52272–52282.
Aktar, M. A., Alam, M. M., & Al-Amin, A. Q. (2021). Global economic crisis, energy use, CO2 emissions, and policy roadmap amid COVID-19. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 26, 770–781.
Al Mamun, M., Sohag, K., Shahbaz, M., & Hammoudeh, S. (2018). Financial markets, innovations and cleaner energy production in OECD countries. Energy Economics, 72, 236–254.
Ali, A., Radulescu, M., Lorente, D. B., & Hoang, V. N. V. (2022). An analysis of the impact of clean and non-clean energy consumption on economic growth and carbon emission: Evidence from PIMC countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(34), 51442–51455.
Ali, A., Radulescu, M., & Balsalobre-Lorente, D. (2023). A dynamic relationship between renewable energy consumption, nonrenewable energy consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emissions: Evidence from Asian emerging economies. Energy & Environment, 34(8), 3529–3552. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X231151684
Arain, H., Sharif, A., Akbar, B., & Younis, M. (2020). Dynamic connection between inward foreign direct investment, renewable energy, economic growth and carbon emission in China: Evidence from partial and multiple wavelet coherence. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(32), 40456–40474.
Azhgaliyeva, D., & Liddle, B. (2020). Introduction to the special issue: Scaling up green finance in Asia. Journal of Sustainable Finance & Investment, 10(2), 83–91.
Ben Jebli, M., & Kahia, M. (2020). The interdependence between CO2 emissions, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energies, and service development: Evidence from 65 countries. Climatic Change, 162(2), 193–212.
Ben Jebli, M., Ben Youssef, S., & Apergis, N. (2019). The dynamic linkage between renewable energy, tourism, CO2 emissions, economic growth, foreign direct investment, and trade. Latin American Economic Review, 28(1), 1–19.
Chen, C., Hu, Y., Karuppiah, M., & Kumar, P. M. (2021). Artificial intelligence on economic evaluation of energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies. Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, 47, 101358.
Dalia, S., & Vitaliy, K. (2021). Green finance and the economic threats during COVID-19 pandemic. Terra Economicus, 19(2), 105–113.
De Atholia, T., Flannigan, G., & Lai, S. (2020). Renewable energy investment in Australia. RBA Bulletin, March.
Dikau, S., & Volz, U. (2021). Central bank mandates, sustainability objectives and the promotion of green finance. Ecological Economics, 184, 107022.
Elliott, G., Rothenberg, T. J., & Stock, J. H. (1992). Efficient tests for an autoregressive unit root, 64, 813–836. https://doi.org/10.3386/t0130
Engle, R. F., & Granger, C. W. J. (2015). Co-integration and error correction: Representation, estimation, and testing. Applied Economics, 39, 107–135. https://doi.org/10.2307/1913236
Falcone, P. M. (2020). Environmental regulation and green investments: The role of green finance. International Journal of Green Economics, 14(2), 159–173.
Granger, C. W. (1969). Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica: journal of the Econometric Society, 37, 424-438
Halicioglu, F. (2007). The demand for new housing in Turkey: An application of ARDL model. Global Business and Economics Review, 9(1), 62–74.
Haug, A. (2002). Temporal aggregation and the power of cointegration tests: A Monte Carlo study. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 64, 399–412.
Huang, Y., Xue, L., & Khan, Z. (2021). What abates carbon emissions in China: Examining the impact of renewable energy and green investment. Sustainable Development, 29(5), 823–834.
Husted, B. W., & de Sousa-Filho, J. M. (2017). The impact of sustainability governance, country stakeholder orientation, and country risk on environmental, social, and governance performance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 155, 93–102.
Johansen, S., & Juselius, K. (1990). Maximum likelihood estimation and inference on cointegration—with appucations to the demand for money. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and statistics, 52(2), 169–210.
Khan, Z., Sisi, Z., & Siqun, Y. (2019). Environmental regulations an option: Asymmetry effect of environmental regulations on carbon emissions using non-linear ARDL. Energy Sources, Part a: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 41(2), 137–155.
Kirikkaleli, D., & Adebayo, T. S. (2021). Do public-private partnerships in energy and renewable energy consumption matter for consumption-based carbon dioxide emissions in India? Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28(23), 30139–30152.
Kwiatkowski, D., Phillips, P. C., Schmidt, P., & Shin, Y. (1992). Testing the null hypothesis of stationarity against the alternative of a unit root: How sure are we that economic time series have a unit root?. Journal of Econometrics, 54(1–3), 159–178.
Li, M., Hamawandy, N. M., Wahid, F., Rjoub, H., & Bao, Z. (2021). Renewable energy resources investment and green finance: Evidence from China. Resources Policy, 74, 102402.
Li, Z., Kuo, T. H., Siao-Yun, W., & Vinh, L. T. (2022). Role of green finance, volatility and risk in promoting the investments in renewable energy resources in the post-COVID-19. Resources Policy, 76, 102563.
Liu, X., Kong, H., & Zhang, S. (2021). Can urbanization, renewable energy, and economic growth make environment more eco-friendly in Northeast Asia? Renewable Energy, 169, 23–33.
Luo, Y., Guo, C., Ali, A., & Zhang, J. (2022). A dynamic analysis of the impact of FDI, on economic growth and carbon emission, evidence from China, India and Singapore. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(54), 82256–82270.
Meo, M. S., & AbdKarim, M. Z. (2022). The role of green finance in reducing CO2 emissions: An empirical analysis. Borsa Istanbul Review, 22(1), 169–178.
Mngumi, F., Shaorong, S., Shair, F., & Waqas, M. (2022). Does green finance mitigate the effects of climate variability: Role of renewable energy investment and infrastructure. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 29(39), 59287–59299.
Moorthy, K., Patwa, N., & Gupta, Y. (2019). Breaking barriers in deployment of renewable energy. Heliyon, 5(1), e01166.
Mostafaeipour, A., Bidokhti, A., Fakhrzad, M. B., Sadegheih, A., & Mehrjerdi, Y. Z. (2022). A new model for the use of renewable electricity to reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Energy, 238, 121602.
Ng, S., & Perron, P. (2001). Lag length selection and the construction of unit root tests with good size and power. Econometrica, 69(6), 1519–1554.
Paris, International Energy Agency. (2019). World energy investment 2019—Data tables. Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-investment-2019
Park, Y., Meng, F., & Baloch, M. A. (2018). The effect of ICT, financial development, growth, and trade openness on CO2 emissions: An empirical analysis. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(30), 30708–30719.
Peimani, H. (2019). Financial barriers for development of renewable and green energy projects in Asia. In Handbook of green finance (pp. 15–34). Singapore.
Pesaran, M. H., Shin, Y., & Smith, R. J. (2001). Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 16(3), 289–326.
Phillips, P., & Perron, P. (1988). Testing for a unit root in time series analysis. Biometrika, 75, 335–346.
Probst, B., Westermann, L., Anadón, L. D., & Kontoleon, A. (2021). Leveraging private investment to expand renewable power generation: Evidence on financial additionality and productivity gains from Uganda. World Development, 140, 105347.
Pyka, I., & Nocoń, A. (2021). Responsible lending policy of green investments in the energy sector in Poland. Energies, 14(21), 7298.
Ragosa, G., & Warren, P. (2019). Unpacking the determinants of cross-border private investment in renewable energy in developing countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 235, 854–865.
Rasoulinezhad, E., & Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. (2022). Role of green finance in improving energy efficiency and renewable energy development. Energy Efficiency, 15(2), 1–12.
Ren, X., Shao, Q., & Zhong, R. (2020). Nexus between green finance, non-fossil energy use, and carbon intensity: Empirical evidence from China based on a vector error correction model. Journal of Cleaner Production, 277, 122844.
Saleem, H., Khan, M. B., & Shabbir, M. S. (2020). The role of financial development, energy demand, and technological change in environmental sustainability agenda: Evidence from selected Asian countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(5), 5266–5280.
Saud, S., Chen, S., & Haseeb, A. (2020). The role of financial development and globalization in the environment: Accounting ecological footprint indicators for selected one-belt-one-road initiative countries. Journal of Cleaner Production, 250, 119518.
Shahbaz, M., Raghutla, C., Chittedi, K. R., Jiao, Z., & Vo, X. V. (2020). The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: Evidence from the renewable energy country attractive index. Energy, 207, 118162.
Shan, Y., Ou, J., Wang, D., Zeng, Z., Zhang, S., Guan, D., & Hubacek, K. (2021). Impacts of COVID-19 and fiscal stimuli on global emissions and the Paris Agreement. Nature Climate Change, 11(3), 200–206.
Shapiro, J. (2019). China’s environmental challenges. In Green Planet Blues (pp. 101–108). Routledge.
Solangi, Y. A., Longsheng, C., & Shah, S. A. A. (2021). Assessing and overcoming the renewable energy barriers for sustainable development in Pakistan: An integrated AHP and fuzzy TOPSIS approach. Renewable Energy, 173, 209–222.
Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., Yoshino, N., Mortha, A., & Sarker, T. (2019). Quality infrastructure and natural disaster resiliency (No. 991). ADBI Working Paper Series.
Taghizadeh-Hesary, F., Yoshino, N., & Phoumin, H. (2021). Analyzing the characteristics of green bond markets to facilitate green finance in the post-COVID-19 world. Sustainability, 13(10), 5719.
Umar, M., Ji, X., Kirikkaleli, D., & Xu, Q. (2020). COP21 Roadmap: Do innovation, financial development, and transportation infrastructure matter for environmental sustainability in China? Journal of Environmental Management, 271, 111026.
van Zyl, E. J. (2021). Redistributive populism versus strengthening property rights: A comparative study of Venezuela and Zimbabwe, and Uruguay and Botswana (Doctoral dissertation, Stellenbosch: Stellenbosch University).
Wang, L., Su, C. W., Ali, S., & Chang, H. L. (2020). How China is fostering sustainable growth: The interplay of green investment and production-based emission. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(31), 39607–39618.
Wang, Q., Ali, A., Chen, Y., & Xu, X. (2023). An empirical analysis of the impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on economic growth and carbon dioxide emissions: evidence from seven Northeast Asian countries. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30, 75041–75057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27583-0
World Bank. (2022). China’s transition to a low-carbon economy and climate resilience needs shifts in resources and technologies. https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2022/10/12/china-s-transition-to-a-low-carbon-economy-and-climate-resilience-needs-shifts-in-resources-and-technologies
Ye, J., Al-Fadly, A., Quang Huy, P., Quang Ngo, T., Phi Hung, D. D., & Hoang Tien, N. (2022). The nexus among green financial development and renewable energy: investment in the wake of the Covid19 pandemic. Economic research-Ekonomska istraživanja, 35(1), 5650–5675
Zahan, I., & Chuanmin, S. (2021). Towards a green economic policy framework in China: role of green investment in fostering clean energy consumption and environmental sustainability. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 28, 43618–43628
Zhang, D., Zhang, Z., & Managi, S. (2019). A bibliometric analysis on green finance: Current status, development, and future directions. Finance Research Letters, 29, 425–430.
Zhang, T., Yin, J., Li, Z., Jin, Y., Ali, A., & Jiang, B. (2023). A dynamic relationship between renewable energy consumption, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions: Evidence from Asian emerging economies. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 2721.
Zhao J, Zhang T, Ali A, Chen J, Ji H and Wang T (2023) An empirical investigation of the impact of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and economic growth on climate change, evidence from emerging Asian countries. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 10, 1085372. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2022.1085372
Zhou, X., Tang, X., & Zhang, R. (2020). Impact of green finance on economic development and environmental quality: A study based on provincial panel data from China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(16), 19915–19932.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.A. contributed to the conceptualization of the study, analysis, design, and conclusions; reviewed the manuscript; and approved the final submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The study obtained ethical approval from Central University of Finance and Economics, Chines Academy of Finance and Development, China.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
The authors have provided consent to publish this work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: Measurement, sources, and interpretation of variables in specifications
Appendix: Measurement, sources, and interpretation of variables in specifications
Variables | Description | Measurement | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
REI | Renewable energy investment | Current US$ | World Development Indicators (WDI) |
GF | Green finance | Current US$ | World Development Indicators (WDI) |
REO | Renewable electricity output | % of total electricity output | World Development Indicators (WDI) |
PEI | Private energy investment | Current US$ | World Development Indicators (WDI) |
REC | Renewable energy consumption | KG of oil equivalent | World Development Indicators (WDI) |
CO2 | Carbon emission | Metric tons per capita | World Development Indicators (WDI) |
GDP | Gross domestic product | Current US$ | World Development Indicators (WDI) |
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, X., Ali, A. & Zhang, L. The Influence of Green Finance and Renewable Energy Sources on Renewable Energy Investment and Carbon Emission: COVID-19 Pandemic Effects on Chinese Economy. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01732-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01732-3