Abstract
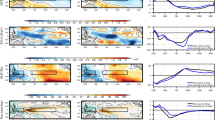
In the past 20 a, the gulf-scale circulation in the Beibu Gulf has been commonly accepted to be driven by a wind stress or density gradient. However, using three sensitive experiments based on a three-dimensional baroclinic model that was verified by observations, the formation mechanisms were revealed: the circulation in the northern Beibu Gulf was triggered by the monsoon wind throughout a year; whereas the southern gulf circulation was driven by the monsoon wind and South China Sea (SCS) circulation in winter and summer, respectively. The force of heat flux and tidal harmonics had a strong effect on the circulation strength and range, as well as the local circulation structures, but these factors did not influence the major circulation structure in the Beibu Gulf. On the other hand, the Beibu Gulf Cold Water Mass (BGCWM) would disappear without the force of heat flux because the seasonal thermocline layer was generated by the input of heat so that the vertical mixing between the upper hot water and lower cold water was blocked. In addition, the wind-induced cyclonic gyre in the northern gulf was favorable to the existence of the BGCWM. However, the coverage area of the BGCWM was increased slightly without the force of the tidal harmonics. When the model was driven by the monthly averaged surface forcing, the circulation structure was changed to some extent, and the coverage area of the BGCWM almost extended outwards 100%, implying the circulation and water mass in the Beibu Gulf had strong responses to the temporal resolution of the surface forces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blumberg A F, Mellor G L. 1987. A description of a three-dimensional coastal ocean circulation model, in three-dimensional coastal ocean models. In: Heaps N, ed. Coastal Estuarine Stud. Washington D C: American Geophysical Union, 4: 1–16
Cao Deming, Fang Guohong. 1990. A Numerical model of the tides and tidal currents in Beibu Bay. Chin J Oceanol Limnol (in Chinese), 21(2): 105–113
Chu Peter C, Chen Yuchun, Lu Shihua. 1998. Wind-driven South China Sea deep basin warm-core/cool-core eddies. J Oceanogr, 54(4): 347–360
Dale W L. 1956. Wind and drift current in the South China Sea. The Malayan Journal of Tropical Geography, 8: 1–31
Durski S M, Glenn S M, Haidvogel D B. 2004. Vertical mixing scheme in the coastal ocean: comparison of the level 2.5 Mellor-Yamada scheme with an enhanced version of the K-profile parameterization. J Geophys Res, 109: C01015, doi:10.1029/2002JC001702
Flather R A. 1976. A tidal model of the northwest European continental shelf. Memories de la Societe Royale des Sciences de Liege, 6(10): 141–164
Gan Jianping, Li H, Curchitser E N, et al. 2006. Modeling South China Sea circulation: Response to seasonal forcing regimes. J Geophys Res, 111: C06034, doi: 10.1029/2005JC003298
Gao Jingsong, Xue Huijie, Chai Fei, et al. 2013. Modeling the circulation in the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea. Oce Dyn, 63(8): 979–993
Huang Zhida, Hu Jianyu, Sun Zhenyu, et al. 2009. Distributions of temperature, salinity and density in the eastern Beibu Gulf in spring 2007. In: Li Yan, Hu Jianyu., eds. The Essay Collection of the Researches on the Ocean Science in the Gulf of Tonkin PT II (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 92–99
Hu Jianyu, Kawamura H, Tang Danling. 2003. Tidal front around the Hainan Island, northwest of the South China Sea. J Geophys Res, 108: 3342, doi:10.1029/2003JC001883
Li Jiaxun, Wang Guihua, Xie Shangping. 2012. A winter warm pool southwest of the Hainan Island due to the orographic wind wake. J Geophys Res, 117: C08036, doi:10.1029/2012JC008189
Li Shuhua. 1986. A numerical modeling of the tidal wave in the Gulf of Tonkin. Trop Oceanogr (in Chinese), 5(3): 7–14
Li Shuhua. 1987. Preliminary study on the Eulerian current in the Gulf of Tonkin. Trans Oceanol Limnol (in Chinese), 3: 8–14
Liu Aiju, Zhang Yanting. 1997. Numerical prediction and analysis of the tide in Beibu Bay. Chin J Oceanol Limnol (in Chinese), 28(6): 640–645
Liu Fengshu, Yu Tianchang. 1980. Preliminary study on the oceanic circulation in Beibu Bay. Trans Oceanol Limnol (in Chinese), 1: 9–15
Liu Qinyu, Kaneko A, Su Jilan. 2008. Recent progress in studies of the South China Sea circulation. J Oceanogr, 64: 753–762
Lu Xinggang, Qiao Fangli, Wang Guanshuo, et al. 2008. Upwelling off the west coast of Hainan Island in summer: its detection and mechanisms. Geophys Res Lett, 35: L02604, doi: 10.1029/2007GL032440
Manh D V, Yanagi T. 2000. A study on the residual flow in the Gulf of Tonkin. J Oceanogr, 56: 59–68
Mellor G L, Yamada T. 1982. Development of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev Geophys Space Phys, 20: 851–875
Ren Huijun, Zhan Jieming. 2005. A numerical study on the seasonal variability of the Yellow Sea cold water mass and the related dynamics. J of Hydrodyn, 20: 887–896.
Shaw Pingtung, Chao Shennyu. 1994. Surface circulation in the South China Sea. Deep-Sea Res Pt I, 40 (11/12): 1663–1683
Shi Maochong, Chen Changsheng, Xu Qichun, et al. 2002. The role of Qiongzhou Strait in the seasonal variation of the South China Sea circulation. J Phys Oceanogr, 32: 103–121, doi: 10.1175/1520-0485(2002)032〈0103:TROQSI〉2.0.CO;2
Su Jilan, Yuan Yeli. 2005. Hydrography of China Seas (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 285-294
Sun Hongliang, Huang Weimin, Zhao Junsheng. 2001. Threedimensional numerical simulation of tide-induced, wind-driven and thermohaline residual currents in the Beibu Bay. Acta Oceanol Sin (in Chinese), 32(5): 1–8
van Maren D S, Hoekstra P. 2004. Seasonal variation of hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics in a shallow subtropical estuary: the Ba Lat River, Vietnam. Estuar Coast Shelf S, 60: 529–540
Wang Daoru. 1998. Study of the dynamic-thermodynamic mechanic of Beibu Bay cool water masses [dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China
Wang Jianfeng, Wang Yi, Sun Shuangwen. 2009. Tidal currents and residual currents in the southeastern Beibu Gulf in spring (in Chinese). In: Li Yan, Hu Jianyu, eds. The Essay Collection of the Researches on the Ocean Science in the Gulf of Tonkin Pt II. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 47–55
Wong Laian, Chen Jaychong, Xue Huijie, et al. 2003. A model study of the circulation in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE) and its adjacent coastal waters: 1. Simulations and comparison with observations. J Geophys Res, 108(C5): 3156, doi: 10.1029/2002JC001451
Wu Chauron, Shaw Pingtung, Chao Shennyu. 1998. Seasonal and interannual variations in the velocity field of the South China Sea. J Oceanogr, 54(4): 361–372
Wu Dexing, Wang Yue, Lin Xiaopei, et al. 2008. The mechanism of the cyclonic circulation in the Gulf of Tonkin in the summer. J Geophys Res, 113: C09029, doi: 10.1029/2007JC004208
Wu Ziku, Wong Laian, Lü Xianqing, et al. 2003. A numerical model of tides in the Gulf of Tonkin by adjoint method. Acta Oceanol Sin, 25(2): 128–135
Wyrtki K. 1961. Physical oceanography of the Southeast Asian water. In: NAGA Report, Scientific Result of Marine Investigation of the South China Sea and Gulf of Thailand 1959–1961, La Jolla, California: Scripps Institution of Oceanography, 2: 195
Xia Huayong, Li Shuhua, Shi Maochong. 2001. Three-D numerical simulation of wind-driven current and density current in the Gulf of Tonkin. Acta Oceanol Sin, 20(4): 455–472
Xue Huijie, Chai Fei. 2002. Coupled Physical-Biological Model for the Pearl River Estuary: A Phosphate Limited Subtropical Ecosystem. In: Spaulding M L ed. Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Estuarine and Coastal Modeling, 913–928
Xue Huijie, Chai Fei, Pettigrew N, et al. 2004. Kuroshio intrusion and the circulation in the South China Sea. J Geophys Res, 109: C02017, doi:10.1029/2002JC001724
Yang Haijun, Liu Qinyu, Liu Zhengyu, et al. 2002. A general circulation model study of the dynamics of the upper ocean circulation of the South China Sea. J Geophys Res, 107(C7): 3085, doi: 10.1029/2001JC001084
Yu Lisan, Jin Xiangze, Weller R A. 2008. Multidecade global flux datasets from the objectively analyzed air-sea Fluxes (OAFlux) project: latent and sensible heat fluxes, ocean evaporation, and related surface meteorological variables. In: OAFlux Project Technical Report. Woods Hole Massachusetts: Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution
Zhang Huaming, Bates J J, Reynolds R W. 2006. Assessment of composite global sampling: Sea surface wind speed. Geophys Res Lett, 33: L17714, doi: 10.1029/2006GL027086
Zhang Guorong, Ma Teng, Pan Weiran, et al. 2009. The characteristics of low-frequency flow in the west mouth of Qiongzhou Strait and its response to the seasonal wind field. In: Li Yan, Hu Jianyu, eds. The Essay Collection of the Researches on the Ocean Science in the Gulf of Tonkin Pt II (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 64–76
Zhong Huanliang. 1995. Analysis of circulations in northern part of Beibu Gulf of South China Sea in spring. Mar Sci Bull (in Chinese), 14(1): 81–85
Zu Tingting. 2005. Analysis of the current and its mechanism in the Gulf of Beibu [dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The Guangxi Natural Science Foundation under contract No. 2012GXNSFEA053001; the program of “The Beibu Gulf forecast circulation system construction and its application to the coastal pollution transport”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Shi, M., Chen, B. et al. Responses of the circulation and water mass in the Beibu Gulf to the seasonal forcing regimes. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 33, 1–11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0506-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0506-6