Abstract
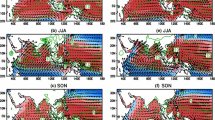
The asymmetry of sea surface temperature anomaly (SSTA) amplitudes between the positive and negative phases of the Indian Ocean dipole (IOD) are studied. The dynamic effects on it are analyzed using a hybrid coordinate ocean model (HYCOM). It suggests that the IOD is still asymmetric even when forced by a symmetric wind stress, and the asymmetry of the SSTA in the eastern pole is strong while that in the western pole is almost insignificant during the mature phase (September-November (SON)). Thus, the IOD asymmetry is primarily caused by the asymmetry in the IODE. A heat budget analysis is also conducted for the mixed-layer temperature in the eastern Indian Ocean (IODE), which indicates that a nonlinear ocean advection cools both the positive and negative IOD events. Therefore, the nonlinear ocean advection is responsible for the asymmetry of the IOD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan Robert J, Chambers, Don, et al. 2001. Is there an equatorial Indian Ocean SST dipole, independent of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation? CLIVAR Exchanges, 6(3): 18–22
An Soon II, Jin Fei Fei. 2004. Nonlinearity and asymmetry of ENSO. J Climate, 17(12): 2399–2412
Annamalai H, Liu Ping, Xie Shangping. 2005. Southwest Indian Ocean SST variability: its local effect and remote influence on Asian monsoons. J Climate, 18(20): 4150–4167
Annamalai H, Murtugudde R, Potemra J, et al. 2003. Coupled dynamics over the Indian Ocean: spring initiation of the zonal mode. Deep-Sea Res Pt II, Topical Studies in Oceanography, 50(12–13): 2305–2330
Behera S K, Yamagata T. 2003. Influence of the Indian Ocean dipole on the Southern Oscillation. JMeteor Soc JPN, 81(1): 169–177
Bjerknes J. 1969. Atmospheric teleconnections from the equatorial Pacific. MonWea Rev, 97(3): 163–172
Bleck R, Halliwell G, Wallcraft A, et al. 2002. Hybrid coordinate ocean model (HYCOM) User’s Manual: Details of the Numerical Code. Miami, Florida: University of Miami. http://hycom.org/attachments/063_hycom_users_manual.pdf
Chang P, Yamagata T, Schopf P, et al. 2006. Climate fluctuations of tropical coupled systems-the role of ocean dynamics. J Climate, 19(20): 5122–5174
Dong Buwen. 2005. Asymmetry between El Niño and La Niña in a global coupled GCMwith an eddy-permitting ocean resolution. J Climate, 16(18): 3373–3387
Hastenrath S. 2002. Dipoles, temperature gradients, and tropical climate anomalies. Bull AmerMeteor Soc, 83(5): 735–740
Huang Bohua, James L, Kinter III. 2002: The interannual variability in the tropical IndianOcean. JGeophys Res, 107(C11): 20-1ĺC20-26
Huang Bohua, Shukla J. 2007a. Mechanisms for the interannual variability in the tropical Indian Ocean. Part I: The role of remote forcing fromthe tropical Pacific. J Climate, 20(13): 2917–2936
Huang Bohua, Shukla J. 2007b. Mechanisms for the interannual variability in the tropical Indian Ocean. Part II: Regional Processes. J Climate, 20(13): 2937–2960
Hong Chi-Cherng, Li Tim, Lin Ho, et al. 2008. Asymmetry of Indian Ocean dipole. Part I: Observational analysis. J Climate, 21(18), 4834–4848
Hong Chi-Cherng, Li Tim, Luo Jing-Jia. 2008. Asymmetry of Indian Ocean dipole. Part II: Model diagnosis. J Climate, 21(18): 4849–4858
Hong Chi-Cherng, Lu Mong-Ming, Masao Kanamitsu. 2008. Temporal and spatial characteristics of positive and negative Indian Ocean dipole with and without ENSO. J Geophys Res, 113(D8): D08107
Jin Fei Fei, An Soon-II, Timmermann Axel, et al. 2003. Strong El Ni?o events and nonlinear dynamical heating. Geophys Res Lett, 30(3): 1120–1123
Kalnay E, Kanamitsu M, Kistler R, et al. 1996. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull AmerMeteor Soc, 77(3): 437–470
Kang In-Sik, Kug Jong-Seong. 2002. El Niño and La Niña sea surface anomalies: asymmetry characteristics associated with their wind stress anomalies. J Geophys Res, 107(D19): 4372
Levitus S, Boyer T P. 1994. World Ocean Atlas Temperature. Washington, US: National Environmental Satellite, Data, and Information Service, Volume 4
Li Tim, Wang Bin, Chang C P, et al. 2003. A theory for the Indian Ocean dipole-zonal mode. J Atmos Sci, 60(17): 2119–2135
Li Tim, Zhang Yongsheng, Lu Er, et al. 2002. Relative role of dynamic and thermodynamic processes in the development of the Indian Ocean dipole: an OGCMdiagnosis. Geophys Res Lett, 29(23): 2110–2113
Murtugudde R, McCreary J P, Busalacchi A J. 2000. Oceanic processes associated with anomalous events in the Indian Ocean with relevance to 1997-1998. J Geophys Res, 105(C2): 3295–3306
Saji N H, Goswami B H, Vinayachandran P N, et al. 1999. A dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Nature, 401(6751): 360–363
Saji N H, Yamagata T. 2003a. Possible impacts of Indian Ocean dipole mode events on global climate. Climate Res, 25: 151–169
Saji N H, Yamagata T. 2003b. Structure of SST and surface wind variability during Indian Ocean dipole mode events: COADS observation. J Climate, 16(16): 2735–2751
Schott Friedrich A, Xie Shangping, McCreary Julian P. 2009. Indian Ocean circulation and climate variability. Rev Geophys, 47(1): RG1002, 46
Wang Dongxiao, Liu Qinyan, Liu Yun, et al. 2004. Connection between interannual variability of the western Pacific and eastern Indian Oceans in the 1997–1998 El Niño event. Progress in Natural Science, 14(5): 423–429
Wang Dongxiao, Qin Yinghao, Xiao Xianjun, et al. 2012. El Niño and El Niño Modoki variability based on a new ocean reanalysis. Ocean Dynamics, 62(9): 1311–1322
Wang Weiwen, Wang Dongxiao, Zhou Wen, et al. 2011. Impact of the South China Sea Through flow on the Pacific Low-Latitude Western Boundary Current: a numerical study for seasonal and interannual time scales. Adv Atmos Sci, 28(6): 1367–1376
Webster P J, Moore A M, Loschnigg J P, et al. 1999. Coupled ocean-atmosphere dynamics in the Indian Ocean during 1997–98. Nature, 401(6751): 356–360
White Glenn H. 1980. Skewness, kurtosis and extreme values of Northern Hemisphere geopotential heights. Mon Wea Rev, 108(9): 1446–1455
Xie Shang-ping, Annamalai H, Schott Friedrich A, et al. 2002. Structure and mechanisms of south Indian Ocean climate variability. J Climate, 15(8): 864–878
Zheng Xiaotong, Xie Shang-ping, Vecchi Gabriel A, et al. 2010. Indian Ocean dipole response to global warming: analysis of ocean-atmospheric feedbacks in a coupled model. J Climate, 23(5): 1240–1253
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 41276011, 41221063 and 41130859; the National Basic Research Program of China under contract No. 2012CB417404.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Lan, J. & Cui, F. Effect of nonlinear advection on the Indian Ocean diploe asymmetry. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 33, 77–82 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0420-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-014-0420-y