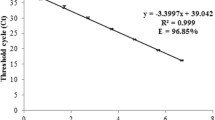
Abstract
Harmful algal blooms recently have been under the spotlight throughout the world, because of their negative impact on the marine environment, aquaculture, fisheries as well as public health. The development of methods for rapid and precise identification and quantification of causative species is essential for the warning andmonitoring of blooms, among which the techniques based on taxonomic probes are themost favored. In this study, two harmful algae, i.e., Prorocentrum minimum and Karenia mikimotoi were taken into consideration. The partial large subunit rDNA (D1-D2) of both species were firstly PCR-amplified, cloned and sequenced. The obtained sequences were then introduced to carry out alignment analysis for gene specific regions. Three respective candidate probes for each species were designed and used to screen the optimal probe by performing fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) tests. The results showed that the probes Pmin0443 and Kmik0602 displayed the best hybridization for P. minimum and K. mikimotoi, respectively. Both the specific (taxonomic) (Pmin0443 and Kmik0602) and the control probes (UniC0512 and UniR0499) were used for cross-reactivity tests with other microalgae in our laboratory. The probes Pmin0443 and Kmik0602 are specific and could be served as taxonomic probes introduced into the techniques targeting rRNA, such as FISH, sandwich hybridization, and DNA-microarray assay of P. minimum and K. mikimotoi in the future. Finally, FISH analyses with both probes were performed on the simulated field samples. The probes could hybridize exclusively with the target cells well, and no significant difference (p >0.05) was observed in the cell densities of the samples determined by FISH and light microscopy (LM). All suggest that the probes are specific and could be introduced into FISH for the monitoring of both harmful algae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Kandari M A, Highfield A C, Hall M J, et al. 2011. Molecular tools separate harmful algal bloom species, Karenia mikimotoi, from different geographical regions into distinct sub-groups. Harmful Algae, 10: 636–643
Adachi M, Sako Y, Ishida Y. 1996. Identification of the toxic dinoflagellates Alexandrium catenella and A. tamarense (Dinophyceae) using DNA probes and whole cell hybridization. J Phycol, 32: 1049–1052
Cembella A D, Taylor F J R. 1985. Biochemical variability within the Protogonyaulax tamarensis/catenella species complex. In: Anderson DM, White AW, Baden D G, eds. Toxic Dinoflagellates. New York: Elsevier Science Press, 55–60
Chen Guofu, Wang Guangce, Zhang Chunyun, et al. 2008. Development of rRNA and rDNA targeted probes for fluorescence in situ hybridization to detect Heterosigma akashiwo (Raphidophyceae). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol, 355: 66–75
Chen Guofu, Zhang Chunyun, Wang Guangce, et al. 2009. Advances in molecular detection techniques for red tide algae. High Tech Lett (in Chinese), 19: 314–322
Cai Qingsong, Li Rongxiu, Zhen Yu. 2006. Detection of two Prorocentrum species using sandwich hybridization integrated with nuclease protection assay. Harmful Algae, 5: 300–309
Diercks S, Medlin L K, Metfies K. 2008. Colorimetric detection of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum using sandwich hybridizationin a microtiter plate assay. Harmful Algae, 7: 137–145
Embley T M, Finlay B J, Thomas R H, et al. 1992. The use of rRNA sequences and fluorescent probes to investigate the phylogenetic positions of the anaerobic ciliate Metopus palaeformis and its archaeobacterial endosymbiont. J Gen Microbiol, 138: 1479–1487
Field K G, Olsen G J, Lane D J, et al. 1998. Molecular phylogeny of the animal kingdom. Science, 239: 748–753
Fuchs B M, Wallner G, Beisker W, et al. 1998. Flow cytometric analysis of the in situ accessibility of Escherichia coli 16S rRNA for fluorescently labeled oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol, 64: 4973–4982
Galluzzi L, Cegna A, Casabianca S, et al. 2011. Development of an oligonucleotide microarray for the detection and monitoring of marine dinoflagellates. J Microbiol Meth, 84: 234–242
Gas F, Pinto L, Baus B, et al. 2009. Monoclonal antibody against the surface of Alexandrium minutum used in a whole-cell ELISA. Harmful Algae, 8: 538–545
Gescher C, Metfies K, Medlin L K. 2008. The Alex chip-development of a DNA chip for identification and monitoring of Alexandrium. Harmful Algae, 7: 485–494
Guillard R R L. 1975. Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH, eds. Culture of Marine Invertebrate Animals. New York: Plenum Press, 29–60
Hallegraeff G M. 2003. Harmful algal blooms: a global overview. In: Hallegraeff G M, Anderson D M, Cembella A D, eds. Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae. Paris: UNESCO, 25–49
Handy SM, Demir E, Hutchins D A. 2008. Using quantitative real-time PCR to study competition and community dynamics among Delaware Inland Bays harmful algae in field and laboratory studies. Harmful Algae, 7: 599–613
Hosoi-Tanabe S, Sako Y. 2006. Development and application of fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) method for simple and rapid identification of the toxic dinoflagellates Alexandrium tamarense and Alexandrium catenella in cultured and natural seawater. Fish Sci, 72: 77–82
Huang Bangqin, Hou Jianjun, Lin Senjie, et al. 2008. Development of a PNA probe for the detection of the toxic dinoflagellate Takayama pulchella. Harmful Algae, 7: 495–503
Ki J S, Han M S. 2006. A low-density oligonucleotide array study for parallel detection of harmful algal species using hybridization of consensus PCR products of LSU rDNA D2 domain. Biosens Bioelectron, 21: 1812–1821
Lü Songhui, Hodgkiss I J. 2004. Harmful algal bloom causative collected from Hong Kong waters. Hydrobiologia, 512: 231–238
Metfies K, Berzano M, Mayer C, et al. 2007. An optimized protocol for the identification of diatoms, flagellated algae and pathogenic protozoa with phylochips. Mol Ecol Notes, 7: 925–936
Mikulski C M, Morton S L, Doucette G J. 2005. Development and application of LSU rRNA probes for Karenia brevis in the Gulf of Mexico, USA. Harmful Algae, 4: 49–60
Mikulski C M, Park Y T, Jones K L, et al. 2008. Development and field application of rRNA-targeted probes for the detection of Cochlodinium polykrikoides Margalef in Korean coastal waters using whole cell and sandwich hybridization formats. Harmful Algae, 7: 347–359
Miller P E, Scholin C A. 1998. Identification and enumeration of cultured and wild Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) using species-specific LSU rRNA-targeted fluorescent probes and filter-based whole cell hybridization. J Phycol, 34: 371–382
Miller P E, Scholin C A. 2000. On detection of Peseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) species using whole cell hybridization: sample fixation and stability. J Phycol, 36: 238–250
Park T G, Park Y T. 2010. Detection of Cochlodinium polykrikoides and Gymnodiniumimpudicum(Dinophyceae) in sediment samples from Korea using real-time PCR. Harmful Algae, 9: 59–65
Parsons M L, Scholin C A, Miller P E, et al. 1999. Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) species in Louisiana coastal waters: molecular probe field trials, genetic variability, and domoic acid analyses. J Phycol, 35: 1368–1378
Sako Y, Hosoi-tanabe S, Uchida A. 2004. Fluorescence in situ hybridization using rRNA-targeted probes for simple and rapid identification of the toxic dinoflagellates Alexandriumtamarense and A. catenella. J Phycol, 40: 598–605
Sako Y, Kim C H, Ninomiya H, et al. 1990. Isozyme and cross analysis of mating population in the Alexandrium catenella/tamarense species complex. In: Graneli E, Sundstrom B, Edler L, et al., eds. Toxic Marine Phytoplankton. New York: Elsevier, 320–323
Scholin C A, Buck K R, Britschgi T, et al. 1996. Identification of Pseudnizschia australis (Bacillariophyceae) using rRNA-targeted probes in whole cell and sandwich hybridization formats. Phycologia, 35: 190–197
Scholin C A, Herzog M, Sogin M, et al. 1994. Identification of groupand strain-specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (Dinophyceae): II. sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene. J Phycol, 30: 999–1011
Scholin C A, Miller P E, Buch K R, et al. 1997. Detection and quantification of Pseudo-nitzschia australis in cultured and natural populations using LSU rRNA-targeted probes. Limnol Oceanogr, 42: 1265–1272
Sherlock G. 2000. Analysis of large-scale gene expression data. Curr Opin Immunol, 12: 201–205
Shi Yanhong, Zhang Fengying, Ma Lingbo. 2010. Development of a real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and quantification of Heterocapsa circularisquama. J Fishery Sci China, 17: 267–273
Sun Ningbo, Sui Zhenghong, Bao Zhenming, et al. 2008. Study of three red tide algae using immuno-fluorescent technique. Acta Oceanologica Sinlca (in Chinese), 30: 132–139
Tyrrell J V, Bergquist P R, Bergquist P L, et al. 2001. Detection and enumeration of Heterosigma akashiwo and Fibrocapsa japonica (Raphidophyceae) using rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Phycologia, 40: 457–467
Ulrich R M, Casper E T, Campbell L, et al. 2010. Detection and quantification of Karenia mikimotoi using real-time nucleic acid sequence-based amplification with internal control RNA (ICNASBA). Harmful Algae, 9: 116–122
Wheeler Alm E, Oerther DB, Larsen N, et al. 1996. The oligonucleotide database project. Appl Environ Microb, 62: 3557–3559
Xiang C C, Chen Yidong. 2000. cDNA microarray technology and its applications. Biotechnol Adv, 18: 35–46
Zhang Fengying, Ma Linbo, Xu Zhaoli, et al. 2009. Sensitive and rapid detection of Karenia mikimotoi (Dinophyceae) by loopmediated isothermal amplification. Harmful Algae, 8: 839–842
Zhen Yu, Mi Tiezhu, Yu Zhigang. 2009. Detection of several harmful algal species by sandwich hybridization integrated with a nuclease protection assay. Harmful Algae, 8: 651–657
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Foundation item: Shandong Province Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund under contract No. BS2010HZ002; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 41106082 and 41176141; Key Laboratory of Marine Ecology and Environmental Science and Engineering, SOA under contract No. MESE-2011-06; the Basic Research of Harbin Institute of Technology Outstanding Talents Cultivation Plan of Class III.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G., Wang, Q., Zhang, C. et al. Development of taxonomic rRNA-targeted probes of two harmful algae: Prorocentrum minimum and Kareniamikimotoi by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 32, 66–75 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-013-0278-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-013-0278-4