Abstract
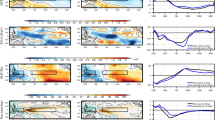
The major feature, interannual variability and variation cause of the Mindanao Eddy and its impact on the thermohaline structure are analyzed based on the Argo profiling float data, the history observed data and the SODA data. The analysis results show that the Mindanao Eddy is a permanent cyclonic meso-scale eddy and spreads vertically from about 500 m depth upward do about 50 m depth. In addition to its strong seasonal variability, the Mindanao Eddy displays a remarkable interannual variability associated with ENSO. It strengthens and expands eastward during El Niño while it weakens and retreats westward during La Niña. The interannual variability in the Mindanao Eddy may be caused by the North Equatorial Counter Current, the North Equatorial Current, the Mindanao Current and the Indonesian Through Flow. The eddy variability can have a great influence on the thermohaline structure pattern in the local upper ocean. When the eddy is strong, the cold and low salinity water inside the eddy moves violently upward from deep layer, the thermocline depth greatly shoals, and the subsurface high salinity water largely decreases, with the upper mixed layer becoming thinner, and vice versa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akima H. 1970. A new method of interpolation and smooth curve fitting based on local procedures. J Assoc Comput Meth, 17: 589–603
Arruda W, Nof D. 2003. The Mindanao and Halmahera eddies—twin eddies induced by nonlinearities. J Phys Oceanogr, 33: 2815–2830
Chu P C, Li R F, Fan C W. 2003. Determination of the current system on isopycnal surface between Mindanao and New Guinea from GDEM. Chine J Oceanol Limnol, 21(3): 193–213
Ffield A, Gordon A L. 1992. Vertical mixing in the Indonesian thermocline. J Phys Oceanogr, 22: 184–195
Gao Libao, Yu Weidong. 2008. Observations and analysis on seasonal changes of western boundary currents and eddy structures in the western Pacific Ocean of the low latitudes. Advances of Marine Science (in Chinese), 26(3): 317–325
Guan Bingxian. 1989. Variation of the Mindanao Eddy and its relation with El Niño event. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica (in Chinese), 20(2): 131–137
Johnson G C, McPhaden M J. 1999. Interior pycnocline flow from the subtropical to the equatorial Pacific Ocean. J Phys Oceanogr, 29: 3071–3089
Koenuma K. 1937. On the hydrography of the southwestern part of the North Pacific and the Kuroshio. Part I: General oceanographic features of the region. The Imperial Marine Observatory Kobe, Japan, 6(1): 279–332
Lukas R, Firing E, Hacker P, et al. 1991. Observations of the Mindanao Current during the Western Equatorial Pacific Ocean circulation study. J Geophys Res, 96(C4): 173–185
Masuzawa J. 1968. Second cruise for CKS, Ryofu Maru, January to March 1968. Oceanogr Mag, 20: 173–185
Qu T, Mitsudera H, Yamagata T. 1999. A climatology of the circulation and water mass distribution near the Philippine coast. J Phys Oceanogr, 29: 1488–1505
Qu T, Mitsudera H, Yamagata T. 1998. On the western boundary currents in the Philippine Sea. J Geophys Res, 103(C4): 7537–7548
Takahashi T. 1959. Hydrographical researches in the western equatorial Pacific. Mem Fish Kagoshima Univ, 7: 141–147
Wang Fan, Zhang Ping, Hu Dunxin, et al. 2001. The tropical Pacific Ocean circulations and their seasonal variations. Science Bulletin (in Chinese), 46(23): 1998–2002
Wyrtki K. 1961. Physical oceanography of the Southeast Asian waters. NAGA Rep, 2: 195
Zhai Panmao, Li Xiaoyan, Ren Fumin. 2003. El Niño (in Chinese). Beijing: Meteorology Press: 17–32
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Basic Research Program of China “973” project under contract No. 2007CB816002; the innovative key project of Chinese Academy of Sciences under contract Nos KZCXZ-YW-201 and KZCX2-YW-Q11-02; the Fund of Key Laboratory of Global Change and Marine-Atmospheric Chemistry, SOA under contract No.GCMAC2010.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhou, H. & Liu, H. Interannual variability in the Mindanao Eddy and its impact on thermohaline structure pattern. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 31, 56–65 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-012-0247-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-012-0247-3