Abstract
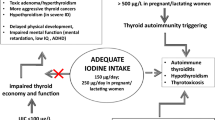
Currently, hypothyroidism is usually treated only with drugs; patients are never told that they could regulate their levels of iodine with dietary recommendations in a complementary way. The objective of this work was to explore the effect of a constant iodine intake through the diet in a postmenopausal woman with subclinical grade II hypothyroidism, who also had mild hypercholesterolemia and obesity. Baseline anthropometric nutritional, pharmacological, and habit data were obtained, then the woman was scheduled for 1 month a diet in which she was provided food naturally containing iodine, so that the recommended requirements (iodine 150 μg/day) were met. All the information about which foods contain this mineral was supplied and explained to the patient. This diet was also designed to help her to gradually lose weight, and was more balanced and closer to the nutritional recommendations. The results obtained in this work were satisfactory, having achieved improved blood levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (1.78 μIU/mL) and reduced total cholesterol levels (198 mg/dL). Statement of hypercholesterolemia was demoted. In addition, a significant improvement in relation to weight and body volume was reached (body mass index fell from 30.13 to 28.5 kg/m2), an important fact since it has impacted the overall well-being of the patient. In conclusion, it was demonstrated that a constant iodine intake through the diet for this patient with grade II hypothyroidism was very effective, and therefore, this aspect should be also considered during hypothyroidism treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TSH:
-
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
References
Bath S, and Rayman, M. (2016) Food fact sheet. British Dietetic Association (BDA). Available at www.bda.uk.com/foodfacts. Accesed 03.01.2016
Bürgi H (2010) Iodine excess. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 24(1):107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2009.08.010
Chandra AK (2010b) Goitrogen in food: cyanogenic and flavonoids containing plant foods in the development of goiter (chapter 42). In: Watson RR, Preedy VR (eds) Bioactive foods in promoting health: fruits and vegetables. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 691–716. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374628-3.00042-6
Fernández AC, Vidal A, Ballesteros MD (2012) Comparative study of total energy expenditure estimated by sense wear armband and Harris-Benedict equation in healthy ambulatory population; utility in clinical practice. Nutr Hosp 27(4):1244–1247. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2012.27.4.5823
Frank RA, Wilby KJ, Mamdani M (2014) Cross-national comparison of levothyroxine utilization in four developed countries. J Health Spec 2(4):152–155. https://doi.org/10.4103/1658-600X.142785
Garber JR, Cobin RH, Gharib H, Hennessey JV, Klein I, Mechanick JI, Pessah R et al (2012) Clinical practice guidelines for hypothyroidism in adults cosponsored by the American Association of clinical endocrinologists and the American thyroid association. Endocr Pract 6(18):988–1028
Gil A (2010) Tratado de Nutrición III: Nutrición Humana en el Estado de Salud, 2nd edn. Panamericana, Madrid
Lazarus JH (2015) The importance of iodine in public health. Environ Geochem Health 37(4):605–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9681-4
Mestres C, Durán M (2012) Farmacología en Nutrición, 1st edn. Panamericana, Madrid
Miranda JM (2006) Manual adjustement of diets. Universidad de Santiago de Compostela (unpublished)
Norton K, Olds T (1996) Anthropometrica. University of New South Wales Press, Sidney
Ortega R, López A, Andrés P, Requejo A, Aparicio A (2016) Programa Dial. Alce Ingeniería, informática y estadística en medicina y biología. Available at: https://www.alceingenieria.net/nutricion.htm (Calculadora nutricional dial) Accessed 01.15.2016
Ortega RM, Requejo AM (2015) Nutriguía, 2nd edn. Ed. Panamericana, Madrid
Pearce EN (2011) Iodine nutrition in the UK: what went wrong? Lancet 377(9782):1979–1980. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60741-1
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the woman of the case and to its family doctor for her essential help in data acquisition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
After obtaining the signed consent of the subject of the study, an anthropometric study was performed on her according to Norton and Olds [3]; a dietary history for 15 days, a food frequency questionnaire, and a 24-h recall questionnaire were also completed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article forms part of a special issue of the Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry entitled “Impact of lifestyles patterns on human health: Integrated approach from the child to the elderly.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopez, Y., Franco, C., Cepeda, A. et al. Constant iodine intake through the diet could improve hypothyroidism treatment: a case report. J Physiol Biochem 74, 189–193 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0605-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-017-0605-x