Abstract
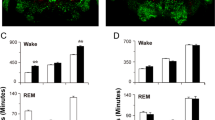
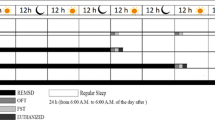
REM sleep is a crucial component of sleep. Animal studies indicate that rapid eye movement (REM) sleep deprivation elicits changes in gene expression. Downregulatory antagonist modulator (DREAM) is a protein which downregulates other gene transcriptions by binding to the downstream response element site. The aim of this study is to examine the effect of REM sleep deprivation on DREAM expression in ventrobasal thalamic nuclei (VB) of rats. Seventy-two male Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into four major groups consisting of free-moving control rats (FMC) (n = 18), 72-h REM sleep-deprived rats (REMsd) (n = 18), 72-h REM sleep-deprived rats with 72-h sleep recovery (RG) (n = 18), and tank control rats (TC) (n = 18). REM sleep deprivation was elicited using the inverted flower pot technique. DREAM expression was examined in VB by immunohistochemical, Western blot, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) studies. The DREAM-positive neuronal cells (DPN) were decreased bilaterally in the VB of rats deprived of REM sleep as well as after sleep recovery. The nuclear DREAM extractions were increased bilaterally in animals deprived of REM sleep. The DREAM messenger RNA (mRNA) levels were decreased after sleep recovery. The results demonstrated a link between DREAM expression and REM sleep deprivation as well as sleep recovery which may indicate potential involvement of DREAM in REM sleep-induced changes in gene expression, specifically in nociceptive processing.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida TF, Roizenblatt S, Tufik S (2004) Afferent pain pathways: a neuroanatomical review. Brain Res 1000:40–56
Andersen ML, Ribeiro DA, Bergamaschi CT, Alvarenga TA, Silva A, Zager A, Campos RR, Tufik S (2009) Distinct effects of acute and chronic sleep loss on DNA damage in rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33(3):562–567
Benkovic SA, McGowan EM, Rothwell NJ, Hutton M, Morgan DG, Gordon MN (1997) Regional and cellular localization of presenilin-2 RNA in rat and human brain. Exp Neurol 145(2 Pt 1):555–564
Biswas S, Mishra P, Mallick BN (2006) Increased apoptosis in rat brain after rapid eye movement sleep loss. Neuroscience 142(2):315–331
Blažetić S, Labak I, Viljetić B, Balog M, Vari SG, Krivošíková Z, Gajdoš M, Kramárová P, Kebis A, Vuković R, Puljak L, Has-Schön E, Heffer M (2014) Effects of high fat diet, ovariectomy, and physical activity on leptin receptor expression in rat brain and white fat tissue. Croat Med J 55(3):228–238
Carrión AM, Mellström B, Naranjo JR (1998) Protein kinase A-dependent derepression of the human prodynorphin gene via differential binding to an intragenic silencer element. Mol Cell Biol 18:6921–6929
Carrión AM, Link WA, Ledo F, Mellström B, Naranjo JR (1999) DREAM is a Ca2+-regulated transcriptional repressor. Nature 398(6722):80–84
Cheng HY, Pitcher GM, Laviolette SR, Whishaw IQ, Tong KI, Kockeritz LK, Wada T, Joza NA, Crackower M, Goncalves J, Sarosi I, Woodgett JR, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Ikura M, van der Kooy D, Salter MW, Penninger JM (2002) DREAM is a critical transcriptional repressor for pain modulation. Cell 108:31–43
Cirelli C, Gutierrez CM, Tononi G (2004) Extensive and divergent effects of sleep and wakefulness on brain gene expression. Neuron 41(1):35–43
Cirelli C, Faraguna U, Tononi G (2006) Changes in brain gene expression after long-term sleep deprivation. J Neurochem 98(5):1632–1645
Costigan M, Woolf CJ (2002) No DREAM, no pain. Closing the spinal gate. Cell 108(3):297–300
Everson CA, Crowley WR (2004) Reductions in circulating anabolic hormones induced by sustained sleep deprivation in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 286(6):E1060–E1070
Guindalini C, Andersen ML, Alvarenga T, Lee K, Tufik S (2009) To what extent is sleep rebound effective in reversing the effects of paradoxical sleep deprivation on gene expression in the brain? Behav Brain Res 201(1):53–58
Gulyani S, Mallick BN (1995) Possible mechanism of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation induced increase in Na-K ATPase activity. Neuroscience 64(1):255–260
Guzman-Marin R, Bashir T, Suntsova N, Szymusiak R, McGinty D (2007) Hippocampal neurogenesis is reduced by sleep fragmentation in the adult rat. Neuroscience 148(1):325–333
Guzman-Marin R, Suntsova N, Bashir T, Nienhuis R, Szymusiak R, McGinty D (2008) Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation contributes to reduction of neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Sleep 31(2):167–175
Hammond PI, Craig TA, Kumar R, Brimijoin S (2003) Regional and cellular distribution of DREAM in adult rat brain consistent with multiple sensory processing roles. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 111:104–110
Hao S, Takahata O, Mamiya K, Iwasaki H (2002) Sevoflurane suppresses noxious stimulus-evoked expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat spinal cord via activation of endogenous opioid systems. Life Sci 71:571–580
Hayati AA, Zalina I, Myo T, Badariah AA, Azhar A, Idris L (2008) Modulation of formalin-induced fos-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord by swim stress-induced analgesia, morphine and ketamine. Ger Med Sci 6:Doc05
Heusner AA (1985) Body size and energy metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 5:267–293
Hipólide DC, D’Almeida V, Raymond R, Tufik S, Nobrega JN (2002) Sleep deprivation does not affect indices of necrosis or apoptosis in rat brain. Int J Neurosci 112(2):155–166
Hipólide DC, Suchecki D, de Carvalho P, Pinto A, Chiconelli Faria E, Tufik S, Luz J (2006) Paradoxical sleep deprivation and sleep recovery: effects on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity, energy balance and body composition of rats. J Neuroendocrinol 18(4):231–238
Kanosue K, Nakayama T, Ishikawa Y, Hosono T, Kaminaga T, Shosaku A (1985) Responses of thalamic and hypothalamic neurons to scrotal warming in rats: non-specific responses? Brain Res 328(2):207–213
Kanosue K, Nakayama T, Andrew PD, She Z, Sato M (1986) Neuronal activities in ventrobasal complex of thalamus and in trigeminal main sensory nucleus during EEG desynchronization in anesthetized rats. Brain Res 379:90–97
Koban M, Stewart CV (2006) Effects of age on recovery of body weight following REM sleep deprivation of rats. Physiol Behav 87(1):1–6
Koban M, Swinson KL (2005) Chronic REM-sleep deprivation of rats elevates metabolic rate and increases UCP1 gene expression in brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 289(1):E68–E74
Koban M, Le WW, Hoffman GE (2006) Changes in hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone, neuropeptide Y, and proopiomelanocortin gene expression during chronic rapid eye movement sleep deprivation of rats. Endocrinology 147(1):421–431
Koban M, Sita LV, Le WW, Hoffman GE (2008) Sleep deprivation of rats: the hyperphagic response is real. Sleep 31(7):927–933
Li Y, Zhang Y, Han JS, Wang Y (2008) Distinct responses of DREAM to electroacupuncture stimulation with different frequencies during physiological and inflammatory conditions in rats. Neurochem Res 33(10):2070–2077
Lilliehook C, Bozdagi O, Yao J, Gomez-Ramirez M, Zaidi NF, Wasco W, Gandy S, Santucci AC, Haroutunian V, Huntley GW, Buxbaum JD (2003) Altered Abeta formation and long-term potentiation in a calsenilin knock-out. J Neurosci 23:9097–9106
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Machado RB, Hipólide DC, Benedito-Silva AA, Tufik S (2004) Sleep deprivation induced by the modified multiple platform technique: quantification of sleep loss and recovery. Brain Res 1004:45–51
Majumdar S, Mallick BN (2003) Increased levels of tyrosine hydroxylase and glutamic acid decarboxylase in locus coeruleus neurons after rapid eye movement sleep deprivation in rats. Neurosci Lett 338:193–196
Majumdar S, Mallick BN (2005) Cytomorphometric changes in rat brain neurons after rapid eye movement sleep deprivation. Neuroscience 135:679–690
Mallick BN, Adya HV (1999) Norepinephrine induced alpha-adrenoceptor mediated increase in rat brain Na-K ATPase activity is dependent on calcium ion. Neurochem Int 34:499–507
Mallick BN, Gulyani S (1996) Alterations in synaptosomal calcium concentrations after rapid eye movement sleep deprivation in rats. Neuroscience 75:729–736
Mallick BN, Adya HV, Faisal M (2000) Norepinephrine-stimulated increase in Na+, K+-ATPase activity in the rat brain is mediated through alpha1A-adrenoceptor possibly by dephosphorylation of the enzyme. J Neurochem 74:1574–1578
Mallick BN, Majumdar S, Faisal M, Yadav V, Madan V, Pal D (2002) Role of norepinephrine in the regulation of rapid eye movement sleep. J Biosci 27(5):539–551
Mallick BN, Singh S, Singh A (2010) Mechanism of noradrenaline-induced stimulation of Na-K ATPase activity in the rat brain: implications on REM sleep deprivation-induced increase in brain excitability. Mol Cell Biochem 336:3–16
Maloney KJ, Mainville L, Jones BE (1999) Differential c-Fos expression in cholinergic, monoaminergic, and GABAergic cell groups of the pontomesencephalic tegmentum after paradoxical sleep deprivation and recovery. J Neurosci 19:3057–3072
Maret S, Dorsaz S, Gurcel L, Pradervand S, Petit B, Pfister C, Hagenbuchle O, O’Hara BF, Franken P, Tafti M (2007) Homer1a is a core brain molecular correlate of sleep loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(50):20090–20095
Matsu-ura T, Konishi Y, Aoki T, Naranjo JR, Mikoshiba K, Tamura TA (2002) Seizure-mediated neuronal activation induces DREAM gene expression in the mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 109:198–206
May ME, Harvey MT, Valdovinos MG, Kline RH 4th, Wiley RG, Kennedy CH (2005) Nociceptor and age specific effects of REM sleep deprivation induced hyperalgesia. Behav Brain Res 159:89–94
Nakanishi H, Sun Y, Nakamura RK, Mori K, Ito M, Suda S, Namba H, Storch FI, Dang TP, Mendelson W, Mishkin M, Kennedy C, Gillin JC, Smith CB, Sokoloff L (1997) Positive correlations between cerebral protein synthesis rates and deep sleep in Macaca mulatta. Eur J Neurosci 9(2):271–279
Nakhate KT, Kokare DM, Singru PS, Subhedar NK (2011) Central regulation of feeding behavior during social isolation of rat: evidence for the role of endogenous CART system. Int J Obes (Lond) 35(6):773–784
O’Hara BF, Watson FL, Srere HK, Kumar H, Wiler SW, Welch SK, Bitting L, Heller HC, Kilduff TS (1999) Gene expression in the brain across the hibernation cycle. J Neurosci 19(10):3781–3790
Paxinos G, Watson C (2006) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 6th edn. Academic Press, New York
Rechtschaffen A, Bergmann BM (1995) Sleep deprivation in the rat by the disk-over-water method. Behav Brain Res 69(1–2):55–63
Squire LR, Berg D, Bloom FE, Du Lac S, Ghosh A, Spitzer NC (2008) Fundamental neuroscience, 3rd edn. Academic Press Title, Burlington
Steriade M (1970) Ascending control of thalamic and cortical responsiveness. Int Rev Neurobiol 12:87–144
Suchecki D, Antunes J, Tufik S (2003) Palatable solutions during paradoxical sleep deprivation : reduction of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and lack of effect on energy imbalance. J Neuroendocrinol 15(9):815–821
Takami K, Terai K, Matsuo A, Walker DG, McGeer PL (1997) Expression of presenilin-1 and −2 mRNAs in rat and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Brain Res 748(1–2):122–130
Terao A, Greco MA, Davis RW, Heller HC, Kilduff TS (2003) Region-specific changes in immediate early gene expression in response to sleep deprivation and recovery sleep in the mouse brain. Neuroscience 120(4):1115–1124
Terao A, Wisor JP, Peyron C, Apte-Deshpande A, Wurts SW, Edgar DM, Kilduff TS (2006) Gene expression in the rat brain during sleep deprivation and recovery sleep: an Affymetrix GeneChip study. Neuroscience 137(2):593–605
Terao A, Huang ZL, Wisor JP, Mochizuki T, Gerashchenko D, Urade Y, Kilduff TS (2008) Gene expression in the rat brain during prostaglandin D2 and adenosinergically-induced sleep. J Neurochem 105(4):1480–1498
Tufik S, Andersen ML, Bittencourt LR, Mello MT (2009) Paradoxical sleep deprivation: neurochemical, hormonal and behavioral alterations. Evidence from 30 years of research. An Acad Bras Cienc 81(3):521–538
Willis WD, Westlund KN (1997) Neuroanatomy of the pain system and of the pathways that modulate pain. J Clin Neurophysiol 14:2–31
Woo HN, Chang JW, Choi YH, Gwon AR, Jung YK, Jo DG (2008) Characterization of subcellular localization and Ca2+ modulation of calsenilin/DREAM/KChIP3. Neuroreport 19(12):1193–1197
You HJ, Lei J, Niu N, Yang L, Fan XL, Tjølsen A, Li Q (2013) Specific thalamic nuclei function as novel ‘nociceptive discriminators’ in the endogenous control of nociception in rats. Neuroscience 232C:53–63
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Research University Grant from Universiti Sains Malaysia (1001/PPSK/812021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siran, R., Ahmad, A.H., Abdul Aziz, C.B. et al. REM sleep deprivation induces changes of Down Regulatory Antagonist Modulator (DREAM) expression in the ventrobasal thalamic nuclei of Sprague–Dawley rats. J Physiol Biochem 70, 877–889 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0356-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0356-x