Abstract
Objectives
In recent years, the number of studies on the relationship between dispositional mindfulness (DM) facets and depression and anxiety symptoms has increased notably. The objective of this meta-analysis was to identify the longitudinal predictive associations from DM facets to depression and anxiety symptoms in both adult and adolescent samples.
Methods
Studies were eligible if they measured anxiety or depressive symptoms at least two times and DM during the first measurement. This meta-analysis seeks to clarify the proposed relationships, applying a Two-Stage Structural Equation Modeling method to data collected from adult and adolescent studies. In total, 34 studies were included.
Results
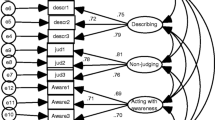
The results indicated that, in adult samples, the facets of Acting with Awareness, Non-Judging, Describing, and Non-Reacting covaried significantly with depression and anxiety symptoms at time one, but only Acting with Awareness and Non-Reacting facets predicted a decrease of symptoms over time. Due to the scarcity of studies using childhood and adolescent samples, only the role of Acting with Awareness predicting depression was evaluated, and the results indicated that this facet predicts a decrease in depression over time among adolescents.
Conclusions
These results provide insight into the longitudinal relationships between DM facets and depression and anxiety symptoms and suggest the importance of focusing attention on these facets in mindfulness interventions.
Trial Registration
The project was preregistered at the Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/ye4af).





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data are available at the Open Science Framework (https://osf.io/afgrj/https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/AFGRJ).
References
Note. References with an asterisk were included in the meta-analytic integration.
Ahmad, F., El Morr, C., Ritvo, P., Othman, N., Moineddin, R., & MVC Team (2020). An eight-week, web-based mindfulness virtual community intervention for students’ mental health: Randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mental Health, 7(2), e15520. https://doi.org/10.2196/15520
Andreotti, E., Antoine, P., Hanafi, M., Michaud, L., & Gottrand, F. (2017). Pilot mindfulness intervention for children born with esophageal atresia and their parents. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 26(5), 1432–1444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-017-0657-0
Antoine, P., Dauvier, B., Andreotti, E., & Congard, A. (2018). Individual differences in the effects of a positive psychology intervention: Applied psychology. Personality and Individual Differences, 122, 140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.10.024
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., & Allen, K. B. (2004). Assessment of mindfulness by self-report: The Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Skills. Assessment, 11(3), 191–191. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191104268029
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Hopkins, J., Krietemeyer, J., & Toney, L. (2006). Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment, 13(1), 27–45. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191105283504
Baer, R. A., Smith, G. T., Lykins, E., Button, D., Krietemeyer, J., Sauer, S., Walsh, E., Duggan, D., & Williams, J. M. G. (2008). Construct validity of the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment, 15(3), 329–342. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191107313003
Barnes, S. M., & Lynn, S. J. (2010). Mindfulness skills and depressive symptoms: A longitudinal study. Imagination, Cognition and Personality, 30(1), 77–91. https://doi.org/10.2190/ic.30.1.e
Barnhofer, T., & Crane, C. (2009). Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for depression and suicidality. In F. Didonna (Ed.), Clinical handbook of mindfulness (pp. 221–243). Springer.
Bergin, A. J., & Pakenham, K. I. (2016). The stress-buffering role of mindfulness in the relationship between perceived stress and psychological adjustment. Mindfulness, 7(4), 928–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-016-0532-x
Bergomi, C., Tschacher, W., & Kupper, Z. (2013). The assessment of mindfulness with self-report measures: Existing scales and open issues. Mindfulness, 4(3), 191–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-012-0110-9
Bergomi, C., Tschacher, W., & Kupper, Z. (2014). Konstruktion und erste Validierung eines Fragebogens zur umfassenden Erfassung von Achtsamkeit [Construction and first validation of a questionnaire for the comprehensive recording of mindfulness]. Diagnostica, 60(3), 111–125. https://doi.org/10.1026/0012-1924/a000109
Bishop, S. R., Lau, M., Shapiro, S., Carlson, L., Anderson, N. D., Carmody, J., Segal, Z. V., Abbey, S., Speca, M., Velting, D., G., & Devins. (2004). Mindfulness: A proposed operational definition. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 11(3), 230–241. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy/bph077
Black, D. S., Sussman, S., Johnson, C. A., & Milam, J. (2012). Testing the indirect effect of trait mindfulness on adolescent cigarette smoking through negative affect and perceived stress mediators. Journal of Substance Use, 17(5–6), 417–429. https://doi.org/10.3109/14659891.2011.587092
Boker, S., Neale, M., Maes, H., Wilde, M., Spiegel, M., Brick, T, Spies, J., Estabrook, R., Kenny, S., Bates, T., Mehta, P., & Fox, J. (2011). OpenMx: An open source extended structural equation modeling framework. Psychometrika, 76(2), 306–317. 10.1007%2Fs11336–010–9200–6
Boyle, C. C., Stanton, A. L., Ganz, P. A., Crespi, C. M., & Bower, J. E. (2017). Improvements in emotion regulation following mindfulness meditation: Effects on depressive symptoms and perceived stress in younger breast cancer survivors. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 85(4), 397–402. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000186
Bränström, R., Duncan, L. G., & Moskowitz, J. T. (2011). The association between dispositional mindfulness, psychological well-being, and perceived health in a Swedish population-based sample. British Journal of Health Psychology, 16(2), 300–316. https://doi.org/10.1348/135910710x501683
Brown, K. W., & Ryan, R. M. (2003). The benefits of being present: Mindfulness and its role in psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 84(4), 822–848. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.84.4.822
Buchheld, N., Grossman, P., & Walach, H. (2001). Measuring mindfulness in insight meditation (Vipassana) and meditation-based psychotherapy: The development of the Freiburg Mindfulness Inventory (FMI). Journal for Meditation and Meditation Research, 1(1), 11–34.
Calvete, E., Morea, A., & Orue, I. (2019). The role of dispositional mindfulness in the longitudinal associations between stressors, maladaptive schemas, and depressive symptoms in adolescents. Mindfulness, 10(3), 547-558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-018-1000-6
Calvete, E., Orue, I., & Sampedro, A. (2017). Does the acting with awareness trait of mindfulness buffer the predictive association between stressors and psychological symptoms in adolescents? Personality and Individual Differences, 105, 158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2016.09.055
Carpenter, J. K., Conroy, K., Gomez, A. F., Curren, L. C., & Hofmann, S. G. (2019). The relationship between trait mindfulness and affective symptoms: A meta-analysis of the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire (FFMQ). Clinical Psychology Review, 74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2019.101785
Cash, M., & Whittingham, K. (2010). What facets of mindfulness contribute to psychological well-being and depressive, anxious, and stress-related symptomatology? Mindfulness, 1(3), 177–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-010-0023-4
Chadwick, P., Hember, M., Symes, J., Peters, E., Kuipers, E., & Dagnan, D. (2008). Responding mindfully to unpleasant thoughts and images: Reliability and validity of the Southampton Mindfulness Questionnaire (SMQ). British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 47(4), 451–455. https://doi.org/10.1348/014466508x314891
Cheung, M. W. L. (2015). metaSEM: An R package for meta-analysis using structural equation modeling. Frontiers in Psychology, 5, 1521. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01521
Ciarrochi, J., Kashdan, T. B., Leeson, P., Heaven, P., & Jordan, C. (2011). On being aware and accepting: A one-year longitudinal study into adolescent well-being. Journal of Adolescence, 34(4), 695–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2010.09.003
Ciesla, J. A., Reilly, L. C., Dickson, K. S., Emanuel, A. S., & Updegraff, J. A. (2012). Dispositional mindfulness moderates the effects of stress among adolescents: Rumination as a mediator. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 41(6), 760–770. https://doi.org/10.1080/15374416.2012.698724
Crescentini, C., Chittaro, L., Capurso, V., Sioni, R., & Fabbro, F. (2016). Psychological and physiological responses to stressful situations in immersive virtual reality: Differences between users who practice mindfulness meditation and controls. Computers in Human Behavior, 59, 304–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.02.031
Demarzo, M., Montero-Marin, J., Puebla-Guedea, M., Navarro-Gil, M., Herrera-Mercadal, P., Moreno-González, S., Calvo-Carrión, S., Bafaluy-Franch, L., & Garcia-Campayo, J. (2017). Efficacy of 8- and 4-session mindfulness-based interventions in a non-clinical population: A controlled study. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1343. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01343
Dixon, H. C., & Overall, N. C. (2016). Dispositional mindfulness attenuates the link between daily stress and depressed mood. Journal of Social and Clinical Psychology, 35(3), 255-268. https://doi.org/10.1521/jscp.2016.35.3.255
Droutman, V., Golub, I., Oganesyan, A., & Read, S. (2018). Development and initial validation of the Adolescent and Adult Mindfulness Scale (AAMS). Personality and Individual Differences, 123, 34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.10.037
Duan, W., & Li, J. (2016). Distinguishing dispositional and cultivated forms of mindfulness: Item-level factor analysis of Five-Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire and construction of short inventory of mindfulness capability. Frontiers in Psychology, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01348
Duijndam, S., Denollet, J., Nyklíček, I., & Kupper, N. (2017). Perceived cognition after percutaneous coronary intervention: Association with quality of life, mood and fatigue in the THORESCI study. International Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 24(4), 552–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12529-016-9624-1
El Morr, C., Ritvo, P., Ahmad, F., Moineddin, R., & MVC Team. (2020). Effectiveness of an 8-week web-based mindfulness virtual community intervention for university students on symptoms of stress, anxiety, and depression: Randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mental Health, 7(7), e18595. https://doi.org/10.2196/18595
Eisenlohr-Moul, T. A., Walsh, E. C., Charnigo, R. J., Jr., Lynam, D. R., & Baer, R. A. (2012). The “what” and the “how” of dispositional mindfulness: Using interactions among subscales of the Five-Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire to understand its relation to substance use. Assessment, 19(3), 276–286. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073191112446658
Elhai, J. D., Levine, J. C., O’Brien, K. D., & Armour, C. (2018). Distress tolerance and mindfulness mediate relations between depression and anxiety sensitivity with problematic smartphone use. Computers in Human Behavior, 84, 477-484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.03.026
Feldman, G., Hayes, A., Kumar, S., Greeson, J., & Laurenceau, J. P. (2007). Mindfulness and emotion regulation: The development and initial validation of the Cognitive and Affective Mindfulness Scale-Revised (CAMS-R). Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 29(3), 177–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-006-9035-8
Galla, B. M. (2017). “Safe in my own mind”: Supporting healthy adolescent development through meditation retreats. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 53, 96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2017.09.006
Gambrel, L. E., & Piercy, F. P. (2015). Mindfulness‐based relationship education for couples expecting their first child—Part 1: A randomized mixed‐methods program evaluation. Journal of Marital and Family Therapy, 41(1), 5-24. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmft.12066
Gómez-Odriozola, J., & Calvete, E. (2020). Longitudinal bidirectional associations between dispositional mindfulness, maladaptive schemas, and depressive symptoms in adolescents. Mindfulness, 11, 1943-1955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01402-w
Gu, J., Strauss, C., Bond, R., & Cavanagh, K. (2015). How do mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction improve mental health and wellbeing? A systematic review and meta-analysis of mediation studies. Clinical Psychology Review, 37, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2016.09.011
Groth, N., Schnyder, N., Kaess, M., Markovic, A., Rietschel, L., Moser, S., Michel, C., Schultze-Lutter, F., & Schmidt, S. J. (2019). Coping as a mediator between locus of control, competence beliefs, and mental health: A systematic review and structural equation modelling meta-analysis. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 121, 103442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brat.2019.103442
Hair, J.F., Hult, G.T.M., Ringle, C.M., & Sarstedt, M. (2017). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM). 2nd Ed. Sage.
Henrich, J. F., Gjelsvik, B., Surawy, C., Evans, E., & Martin, M. (2020). A randomized clinical trial of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for women with irritable bowel syndrome—Effects and mechanisms. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 88(4), 295-310. https://doi.org/10.1037/ccp0000483
Jak, S., & Cheung, M. W. L. (2020). Meta-analytic structural equation modeling with moderating effects on SEM parameters. Psychological Methods, 25(4), 430–455. https://doi.org/10.1037/met0000245
Johnson, C., & Wade, T. (2019). Which aspects of mindfulness are important to include in adolescent interventions? Early Intervention in Psychiatry, 13(3), 387-397. https://doi.org/10.1111/eip.12490
Jury, T. K., & Jose, P. E. (2019). Does rumination function as a longitudinal mediator between mindfulness and depression? Mindfulness, 10(6), 1091–1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-018-1031-z
Kabat-Zinn, J. (1994). Wherever you go, there you are: Mindfulness meditation in everyday life. Hyperion.
Kabat-Zinn, J. (2003). Mindfulness-based interventions in context: Past, present, and future. Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice, 10(2), 144–156. https://doi.org/10.1093/clipsy/bpg016
Keng, S. L., Lee, C. S. L., & Eisenlohr-Moul, T. A. (2019). Effects of brief daily mindfulness practice on affective outcomes and correlates in a high BPD trait sample. Psychiatry Research, 280, 112485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112485
Kessler, R. C., Chiu, W. T., Demler, O., & Walters, E. E. (2005). Prevalence, severity, and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62(6), 617–627. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.62.6.617
Khan, F., & Laurent, H. K. (2019). Assessing the impact of mindfulness and life stress on maternal well-being. Mindfulness, 10(1), 26–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-018-0943-y
*Kiken, L. G., Lundberg, K. B., & Fredrickson, B. L. (2017). Being present and enjoying it: Dispositional mindfulness and savoring the moment are distinct, interactive predictors of positive emotions and psychological health. Mindfulness, 8(5), 1280–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0704-3
Lin, L., & Chu, H. (2018). Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics, 74(3), 785–794. https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.12817
Ma, Y., She, Z., Siu, A. F.-Y., Zeng, X., & Liu, X. (2018). Effectiveness of online mindfulness-based interventions on psychological distress and the mediating role of emotion regulation. Frontiers in Psychology, 9, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02090
Mattes, J. (2019). Systematic review and meta-analysis of correlates of FFMQ mindfulness facets. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 02684. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02684
Nassif, T. H., Start, A. R., Toblin, R. L., & Adler, A. B. (2019). Self-reported mindfulness and soldier health following a combat deployment. Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy, 11(4), 466–474. https://doi.org/10.1037/tra0000413
Petrocchi, N., & Ottaviani, C. (2016). Mindfulness facets distinctively predict depressive symptoms after two years: The mediating role of rumination. Personality and Individual Differences, 93, 92–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.08.017
Pots, W. T., Fledderus, M., Meulenbeek, P. A., Peter, M., Schreurs, K. M., & Bohlmeijer, E. T. (2016). Acceptance and commitment therapy as a web-based intervention for depressive symptoms: Randomised controlled trial. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 208(1), 69-77. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.114.146068
Rhodes, R. E., Boudreau, P., Josefsson, K. W., & Ivarsson, A. (2020). Mediators of physical activity behaviour change interventions among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Psychology Review, 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1080/17437199.2019.1706614
Rodríguez-Vega, B., Melero-Llorente, J., Bayón-Pérez, C., Cebolla, S., Mira, J., Valverde, C., & Fernández-Liria, A. (2014). Impact of mindfulness training on attentional control and anger regulation processes for psychotherapists in training. Psychotherapy Research, 24(2), 202-213. https://doi.org/10.1080/10503307.2013.838651
Rosenthal, R. (1978). Combining results of independent studies. Psychological Bulletin, 85, 185–193. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.85.1.185
Royuela-Colomer, E., & Calvete, E. (2016). Mindfulness facets and depression in adolescents: Rumination as a mediator. Mindfulness, 7(5), 1092-1102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-016-0547-3
Sairanen, E., Lappalainen, R., Lappalainen, P., Kaipainen, K., Carlstedt, F., Anclair, M., & Hiltunen, A. (2019). Effectiveness of a web-based acceptance and commitment therapy intervention for wellbeing of parents whose children have chronic conditions: A randomized controlled trial. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 13, 94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2019.07.004
Sauer, S., Walach, H., Schmidt, S., Hinterberger, T., Lynch, S., Büssing, A., & Kohls, N. (2013). Assessment of mindfulness: Review on state of the art. Mindfulness, 4(1), 3–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-012-0122-5
Schut, D. M., & Boelen, P. A. (2017). The relative importance of rumination, experiential avoidance and mindfulness as predictors of depressive symptoms. Journal of Contextual Behavioral Science, 6(1), 8–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcbs.2016.11.008
Shahar, B., Britton, W. B., Sbarra, D. A., Figueredo, A. J., & Bootzin, R. R. (2010). Mechanisms of change in mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for depression: Preliminary evidence from a randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Cognitive Therapy, 3(4), 402–418. https://doi.org/10.1521/ijct.2010.3.4.402
Shearer, A., Hunt, M., Chowdhury, M., & Nicol, L. (2016). Effects of a brief mindfulness meditation intervention on student stress and heart rate variability. International Journal of Stress Management, 23(2), 232–254. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0039814
Thomas, J., Raynor, M., & Bahussain, E. (2016). Stress reactivity, depressive symptoms, and mindfulness: A Gulf Arab perspective. International Perspectives in Psychology: Research, Practice, Consultation, 5(3), 156–166. https://doi.org/10.1037/ipp0000055
Tomlinson, E. R., Yousaf, O., Vittersø, A. D., & Jones, L. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness and psychological health: A systematic review. Mindfulness, 9(1), 23–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-017-0762-6
Van Son, J., Nyklíček, I., Nefs, G., Speight, J., Pop, V. J., & Pouwer, F. (2015). The association between mindfulness and emotional distress in adults with diabetes: Could mindfulness serve as a buffer? Results from diabetes MILES: The Netherlands. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 38, 251–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-014-9592-3
Walach, H., Buchheld, N., Buttenmüller, V., Kleinknecht, N., & Schmidt, S. (2006). Measuring mindfulness-the Freiburg Mindfulness Inventory (FMI). Personality and Individual Differences, 40(8), 1543–1555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2005.11.025
Walsh, J. J., Balint, M. G. S. J. D. R. S., L. K., Fredericksen, S., & Madsen. (2009). Predicting individual differences in mindfulness: The role of trait anxiety, attachment anxiety and attentional control. Personality and Individual Differences, 46(2), 94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2008.09.008
Williams, V., Ciarrochi, J., & Deane, F. P. (2010). On being mindful, emotionally aware, and more resilient: Longitudinal pilot study of police recruits. Australian Psychologist, 45(4), 274–282. https://doi.org/10.1080/00050060903573197
World Health Organization. (2017). Depression and other common mental disorders: Global health estimates. https://www.who.int/mental_health/management/depression/prevalence_global_health_estimates/en
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Basque Country (Ref. IT982-16 and Ref. PI_2016_1_0023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.P. collaborated with the design of the study, analyzed the data, wrote part of the paper, prepared the tables, and conducted literature search. J.G. developed the theoretical framework, wrote part of the paper, prepared the tables, and revised the references. E.R. collaborated with the design of the study and conducted literature search. I.O. collaborated with the design of the study and contributed to the final version of the manuscript. L.F. collaborated with the design of the study and revised the references. L.O. contributed to the development of the theoretical framework. N.C. contributed to the final version of the manuscript, contributed to the development of the theoretical framework, and reviewed the tables. I.I. collaborated with the design of the study and verified the analytical methods. E.C. collaborated with the design of the study, supervised the project, and conceived the original idea. All the authors except I.I. collaborated in the selection process of the articles. All authors discussed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Standards
The procedures of this study have been approved by the institutional research committee of the University of Deusto and have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prieto-Fidalgo, Á., Gómez-Odriozola, J., Royuela-Colomer, E. et al. Predictive Associations of Dispositional Mindfulness Facets with Anxiety and Depression: a Meta-analytic Structural Equation Modeling Approach. Mindfulness 13, 37–53 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-021-01756-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-021-01756-9