Abstract
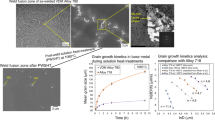
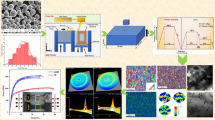
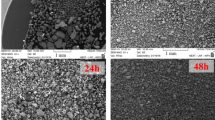
In the present study, Ti-6Al-4V alloy was fabricated by Selective Laser Manufacturing (SLM) technique and subsequently subjected to an annealing treatment at, above and below the β transition temperature. We emphasized the influence of porosity, oxygen and phase morphology on the strength, ductility and elongation of SLM-manufactured Ti-6Al-4V and compared the alloy's properties with conventionally manufactured Ti-6Al-4V from the literature. The as-built Ti-6Al-4V sample showed a very high strength due to acicular martensite, and the growth of α+β lamellae on heat treatment improved ductility. Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), Optical and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) were used to identify the chemical composition, calculate lamellar width and analyze the fracture mechanisms. The grain size and the average thickness of α lamellae, inter-granular β and prior β grain boundary increased with annealing temperature. The porosity and oxygen content of the samples were found to have a consequential effect on the strength, especially in as-built and high-temperature annealing conditions and optimum mechanical properties were observed in SLM Ti-6Al-4V annealed at 800 °C.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neikter M, Åkerfeldt P, Pederson R, and Antti M-L, IOP Conf Series: Mater Sci Eng 258, (2017) 012007
Hong S Y, Ding Y, and Jeong W, Int J Mach Tools Manuf 41 (15), (2001) 2271–2285.
Jerold B D, and Kumar M P, ASME J Manuf Sci Eng 135 (3), (2013) 031005
Sivalingam V, Sun J, Yang B, Liu K, and Raju R, J Manuf Process 36, (2018) 188–196.
Chetan Ghosh S, and Venkateswara Rao P, J Cleaner Prod 100, (2015) 17–34.
Singaravel B, Shekar K C, Reddy G G, et al., Ain Shams Eng J 11 (1), (2019) 143–147.
Liu S, and Shin Y C, Mater Design 164, (2019) 107552
Ngo T D, Kashani A, Imbalzano G, Nguyen K T Q, and Hui D, Compos Part B: Eng 143, (2019) 172–196.
Li N, Huang S, Zhang G, Qin R, Liu W, Xiong H, and Blackburn J, J Mater Sci Technol 35 (2), (2018) 242–269.
Xu Y, Zhang D, Guo Y, Hu S, Wu X, and Jiang Y, J Alloys Compd 816, (2020) 152536
Xu W, Brandt M, Sun S, Elambasseril J, Liu Q, Latham K, and Qian M, Acta Mater 85, (2015) 74–84.
Simonelli M, Tse Y Y, and Tuck C, J Mater Res 29 (17), (2014) 2028–2035.
Malý M, Höller C, Skalon M, Meier B, Koutný D, Pichler R, and Paloušek D, Materials 12 (6), (2019) 930.
Al-Rubaie K S, Melotti S, Rabelo A, Paiva J M, Elbestawi M A, and Veldhuis S C, J Manuf Processes 57, (2020) 768–786.
Simonelli M, Tse Y Y, and Tuck C, Mater Sci Eng: A 616, (2014) 1–11.
Zhou B, Zhou J, Li H, and Lin F, Mater Sci Eng: A 724, (2018) 1–10.
Liu L, Chen C, Zhao R, Wang X, Tao H, Shuai S, and Ren Z, Addit Manuf 46, (2021) 102142
Yang J, Yu H, Yin J, Gao M, Wang Z, and Zeng X, Mater Design 108, (2016) 308–318.
Do D K, and Li P, Virt Phys Protot 11 (1), (2016) 41–47.
Liu J, Sun Q, Zhou C, Wang X, Li H, Guo K, and Sun J, Mater Sci Eng A 766, (2019) 138319
Song B, Dong S, Liao H, and Coddet C, Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61 (9–12), (2011) 967–974.
Manvatkar V, De A, and DebRoy T, Mater Sci Technol 31 (8), (2014) 924–930.
Sun J, Yang Y, and Wang D, Optics Laser Technol 49, (2013) 118–124.
Shi X, Ma S, Liu C, Chen C, Wu Q, Chen X, and Lu J, Materials 9 (12), (2016) 975.
Shao M, Vijayan S, and Jinschek J, Microsc Microanal 27 (S1), (2021) 2682–2684.
Gong H, Rafi K, Gu H, Janaki-Ram G D, Starr T, and Stucker B, Mater Des 86, (2015) 545–554.
Zhang X-Y, Fang G, Leeflang S, Böttger A J, Zadpoor A, and Zhou J, J Alloys Compd 735, (2018) 1562–1575.
Khorasani A M, Gibson I, Awan U S, and Ghaderi A, Addit Manuf 2019 (25), (2019) 176–186.
Leuders S, Thöne M, Riemer A, Niendorf T, Tröster T, Richard H A, and Maier H J, Int J Fatigue 48, (2013) 300–307.
Tammas-Williams S, Withers P J, Todd I, and Prangnell P B, Scripta Materialia 122, (2016) 72–76.
Vrancken B, Thijs L, Kruth J-P, and Van Humbeeck J, J Alloys Compd 541, (2012) 177–185.
Vilaro T, Colin C, and Bartout J D, Metall Mater Trans A 42 (10), (2011) 3190–3199.
Liang Z, Sun Z, Zhang W, Wu S, and Chang H, J Alloys Compd 782, (2019) 1041–1048.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Science and Engineering Research Board, Department of Science and Technology (SERB-DST; File No. CRG/2018/002483, GAP 03/19), India, for offering financial support to carry out the research work. The support staff of the Central Instrumentation Facility and Additive Manufacturing Facility of CSIR-CECRI, Karaikudi, for the characterization and 3D printing work, respectively, is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sai Deepak Kumar, A., Pattanayak, D.K., Fayaz Anwar, M. et al. The Effect of Porosity, Oxygen and Phase Morphology on the Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V with Respect to Annealing Temperature. Trans Indian Inst Met 76, 1789–1798 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-02886-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-023-02886-5