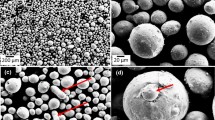
Abstract
The effect of liquid phase sintering on the densification, shrinkage and microstructural characteristics of Cu–Sn–Pb alloyed powder was studied by powder metallurgy processing. Experiments were conducted to evaluate the effects of temperature on phase transformation and liquid phase sintering of the leaded tin bronze compact. Microstructures of sintered samples were analyzed and were used to determine the gravity effect on liquid phase settling and microstructural heterogeneity that caused distortion and graded structure. Also, fragmentation and rearrangement of the particles were detected. A capillary force caused the breakdown of weak solid–solid bonds that were formed by heating. It was concluded that persistent liquid phase sintering inside the Cu–Sn–Pb partially alloyed powder and supersolidus liquid phase sintering were responsible for all described events.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kolesnichenko L, Fushchich O, Ignatenko L, Talochka A Y, and Chernyauskas S, Powder Metall Metal Ceram 25 (1986) 377.
Aksoy M, Kuzucu V, and Turhan H, J Mater Process Technol 124 (2002) 113.
Neikov O D, Naboychenko S, Gopienko V G, and Frishberg I V, Handbook of Non-ferrous Metal Powders: Technologies and Applications, Elsevier, Amsterdam (2009).
Lee P W, Trudel Y, German R M, Ferguson B L, Eisen W B, Mover K, Madan D, Sanderow H, Lampman S R, and Davidson G M, ASM Handb 7 (1998) 1146.
Davis J R, Copper and Copper Alloys, ASM International, Almere (2001).
German R M, Liquid Phase Sintering, Plenum Press, New York (1985).
Azadbeh M, Danninger H, and Gierl-Mayer C, Powder Metall 56 (2013) 342.
Sethi G, Upadhyaya A, and Agrawal D, Sci Sinter 35 (2003) 49.
German R M, Int J Powder Metall 26 (1990) 23.
German R M, Int J Powder Metall 26 (1990) 35.
Upadhyaya A, Sethi G, Kim H, Agrawal D, and Roy R, Adv Powder Metall Part Mater 13 (2002) 362.
German R M, Metall Mater Trans A 28 (1997) 1553.
Upadhyaya A, and Sethi G, Scr Mater 56 (2007) 469.
Mohammadzadeh A, Sabahi Namini A, and Azadbeh M, Iran J Mater Sci Eng 11 (2014) 67.
Mohammadzadeh A, Azadbeh M, and Sabahi Namini A, Sci Sinter 46 (2014) 23.
Mohammadzadeh A, Azadbeh M, and Danninger H, Powder Metall 58 (2015) 123.
Azadbeh M, Danninger H, Mohammadzadeh A, and Gierl-Mayer C, Powder Metall 58 (2015) 91.
Mohammadzadeh A, Azadbeh M, and Danninger H, Powder Metall (2015) 1743290115Y.0000000013 (in press).
Kohara S, and Tatsuzawa K, J Jpn Soc Powder Powder Metall 33 (1986) 139.
Upadhyaya A, and German R M, Mater Chem Phys 67 (2001) 25.
Lu K, and German R M, J Mater Sci 45 (2010) 4454.
Heaney D F, German R M, and Ahn I S, J Mater Sci 30 (1995) 5808.
Liu Y, Heaney D F, and German R M, Acta metallurgica et materialia 43 (1995) 1587.
Raman R, and German R M, Metall Mater Trans A 26 (1995) 653.
Tewari A, Gokhale A M, and German R M, Acta Mater 47 (1999) 3721.
Liu J, Lal A, and German R M, Acta Mater 47 (1999) 4615.
Baker H, and Okamoto H, ASM Handbook. Vol. 3. Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio 44073-0002, USA (1992) p 501.
Phase Diagrams & Computational Thermodynamics, Cu-Sn-Pb system, The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). http://www.metallurgy.nist.gov.
Sabahi Namini A, Azadbeh M, and Mohammadzadeh A, Sci Sinter 45 (2013) 351.
Acknowledgments
All authors of this article would like to appreciate Dr. Tabatabaie, Head manager of Tabriz Powder Metallurgy Company, for supplying the starting powder.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabahi Namini, A., Azadbeh, M., Mohammadzadeh, A. et al. Liquid Phase Sintering of Leaded Tin Bronze Alloyed Powder. Trans Indian Inst Met 69, 1377–1388 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0683-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-015-0683-9