Abstract
Open dumping is one of the most common solid waste disposal methods in developing countries. As they lack planning and basic environmental protection engineering measures, dumpsites represent environmental and health risks that should be investigated. However, several dumpsites are abandoned without appropriate land-use management, difficulting their proper environmental assessment. The use of non-invasive methods for waste mass delimitation and preliminary screening of contamination plumes, such as geophysical methods, is an interesting alternative for the study of the environmental impacts caused by dumpsites. The aim of the present study is to apply electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) for the delimitation of the waste mass and the identification of anomalies related to the presence of alterations in the physical and chemical properties of soils and groundwater in an inactive dumpsite in the municipality of Miracatu, State of São Paulo, Brazil. The study was based on the use of the python software ResIPy, which uses an R family of ERT inversion codes. The 3D inversion of data showed a good correlation between the most electrically conductive anomalies and the delimitation of the waste mass. The behavior of these anomalies, associated with the presence of waste, was confirmed by the physical characterization of the geological materials obtained from drillings and installation of monitoring wells. The present study shows that the ERT inversion code for electrical data can be an interesting open-source alternative for data processing in complex scenarios: environments that present considerable anthropic interference, such as dumpsites.


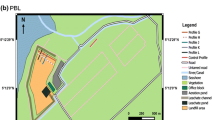
Source: Google Earth and personal file








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No applicable.
References
Abbaspour K, Matta V, Huggenberger P, Johnson CA (2000) A contaminated site investigation: comparison of information gained from geophysical measurements and hydrogeological modeling. J Contam Hydrol 40:4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-7722(99)00055-8
ABNT/NBR 15.495-1: 2007-Poços de monitoramento de águas subterrâneas em aquíferos granulares. Parte 1: Projeto e construção, Associação Brasileira de Normas Técnicas–ABNT, 25 pág
Abreu AES, Gandolfo OCB, Vilar O (2016) Characterizing a Brazilian sanitary landfill using geophysical seismic techniques. Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2016.03.048
Atekwana EA, Sauck WA, Werkema DD (2000) Investigations of geoelectrical signatures at a hydrocarbon contaminated site. J Appl Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9851(98)00033-0
Bharadwaj B, Rai RK, Nepal M (2020) Sustainable financing for municipal solid waste management in Nepal. PLoS ONE 15(8):e0231933
Binley A (2015) Tools and techniques: DC electrical methods. In: Schubert G (ed) Treatise on geophysics, vol 11, 2nd edn. Elsevier, pp 233–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53802-4.00192-5
Blake L (2005) Acid rain and soil acidification. Encyclopedia of soils in the environment. Elsevier, pp 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-12-348530-4/00083-7
Blanchy G, Saneiyan S, Boyd J, McLachlan P, Binley A (2020) ResIPy, an intuitive open source software for complex geoelectrical inversion/modeling. Comput Geosc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2020.104423
Boyd J, Blanchy G, Saneiyan S, McLachlan P, Binley A (2019) 3D geoelectrical problems with ResIPy, an open source graphical user interface for geoelectrical data processing. Fast times. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.35381.63205
Capozzoli CR, Pickbrenner K, Pinto EJ (2022) Atlas Pluviométrico do Brasil: equações Intensidade-Duração Frequência (Desagregação de Precipitações Diárias): estação pluviométrica Pedro Barros; código 02447043 (ANA), município Miracatu, SP-São Paulo:CPRM
Cardarelli E, Di Filippo G (2009) Electrical resistivity and induced polarization tomography in identifying the plume of chlorinated hydrocarbons in sedimentary formation: a case study in Rho (Milan–Italy). Waste Manag Res 27(6):595–602. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X09102524
Caterina D, Flores Orozco A, Nguyen F (2017) Long-term ERT monitoring of biogeochemical changes of an aged hydrocarbon contamination. J Contam Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2017.04.003
Companhia de Tecnologia de Saneamento Ambiental – CETESB (2001) “Relatório de Estabelecimento de Valores Orientadores para Solos e Águas Subterrâneas no Estado de São Paulo”- CETESB
Chaali N, Bravo D, Ouazaa S, Jaramillo Barrios C, Beltran J, Serralde D, Benavides-Erazo J (2022) New insights into arsenic and cadmium distribution and origin in paddy soils using electrical resistivity tomography. J Appl Geophys 202:104638. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2022.104638
Chambers JE, Kuras O, Meldrum PI, Ogilvy RD, Hollands J (2006) Electrical resistivity tomography applied to geologic, hydrogeologic, and engineering investigations at a former waste-disposal site. Geophysics 71:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2360184
Chiles J, Delfiner P (1999) Geostatistics: modeling spatial uncertainty. Wiley, New York, p 695. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470316993
Ciampi P, Esposito C, Cassiani G, Deidda GP, Flores-Orozco A, Rizzetto P, Chiappa A, Bernabei M, Gardon A, Petrangeli Papini M (2022) Contamination presence and dynamics at a polluted site: spatial analysis of integrated data and joint conceptual modeling approach. J Contam Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2022.104026
Corwin DL, Lesch SM (2003) Application of soil electrical conductivity to precision agriculture: theory, principles, and guidelines. Agron J 95:455–471. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.4550
Das S, Lee SH, Kumar P, Kim KH, Lee SS, Bhattacharya SS (2019) Solid waste management: scope and the challenge of sustainability. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.323
Doyoro YG, Chang PY, Puntu JM, Lin DJ, Huu TV, Rahmalia DA, Shie MS (2022) A review of open software resources in python for electrical resistivity modelling. Geosci Lett 9:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40562-022-00214-1
Eludoyin AO (2020) Precipitation–soil water chemistry relationship: case study of an intensively managed grassland ecosystem in southwest England. Appl Water Sci 10:125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01209-z
Furman A, Ferre TPA, Warrick AW (2003) A sensitivity analysis of electrical resistivity tomography array types using analytical element modeling. Vadose Zone J 2:416–423. https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2003.4160
Gandolfo OCB (2007) Um estudo do imageamento geoelétrico na investigação rasa. Tese (Doutorado)—Universidade de São Paulo- Instituto de Geociências
Garpelli LN, Gastmans D (2020) Potencial hidromineral dos aquíferos do estado de São Paulo. Pesquisas Em Geociências 47(3):e100458. https://doi.org/10.22456/1807-9806.109987
Gimenez Filho A, Albuquerque Filho JL, Dantas ASL, Fernandes LA, Nagata N, Teixeira AL (1987) Geologia da Folha Miracatu, sul-sudeste do estado de São Paulo. In: Simp Reg Geol, 6. Rio Claro, vol 1, pp 225–241
Glover PW (2015) Geophysical properties of the near surface earth: electrical properties. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53802-4.00189-5
Gomaa MM (2020) Salinity and water effect on electrical properties of fragile clayey sandstone. Appl Water Sci 10:116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01189-0
Guimarães CC, Barbosa AM, Gandolfo OCB (2019) Visual interpretation of satellite and aerial images to identify and study the evolution of inadequate waste disposal sites. Detritus 6:85–95. https://doi.org/10.31025/2611-4135/2019.13821
Guinea A, Bicknell J, Cox N, Swan H, Simmons N (2022) Characterization of legacy landfills with electrical resistivity tomography; a comparative study. J Appl Geophys 203:104716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2022.104716
Guireli Netto L, Barbosa AM, Galli VL, Silva Pereira JP, Gandolfo OCB, Birelli CA (2020) Application of invasive and non-invasive methods of geo-environmental investigation for determination of the contamination behavior by organic compounds. J Appl Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2020.104049
Guireli Netto L, Malagutti Filho W, Moreira CA, di Donato FT, Helene LPI (2021) Delineation of necroleachate pathways using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT): case study on a cemetery in Brazil. Environ Chall 5:100344. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100344
Helene LPI, Moreira CA (2021) Analysis of leachate generation dynamics in a closed municipal solid waste landfill by means of geophysical data (DC resistivity and self-potential methods). Pure Appl Geophys 178:1355–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-021-02700-7
Helene LPI, Moreira CA, Bovi RC (2020) Identification of leachate infiltration and its flow pathway in landfill by means of electrical resistivity tomography (ERT). Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-8206-5
International Solid Waste Association–ISWA (2015) Wasted health: the tragic case of dumpsites. ISWA, Vienna
International Solid Waste Association–ISWA (2016) A roadmap for closing waste dumpsites: the world’s most polluted places. ISWA, Vienna
Issaoui W, Nasr IH, Khaskhoussi S, Inoubli MH (2023) Monitoring of soil contamination from olive mill wastewater (OMW) using physico-chemical, geotechnical analysis and electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) investigation. Environ Earth Sci 82:331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11020-z
Jefayinfa SM, Oladunjoye M, Doro K (2023) Imaging the distribution of bitumen contaminants in shallow coastal plain sands in southwestern Nigeria using electrical resistivity. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10718-w
Kaya M, Özürlan G, Şengül E (2007) Delineation of soil and groundwater contamination using geophysical methods at a waste disposal site in Çanakkale, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 135:441–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-9662-x
Kaza S, Yao L, Bhada-Tata P, Van Woerden F (2018) What a waste 2.0: a global snapshot of solid waste management to 2050. World Bank Publications
Khatri N, Tyagi S (2015) Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front Life Sci 8:23–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/21553769.2014.933716
Koda E, Osiński P, Podlasek A, Vaverková MD (2020) Geoenvironmental investigation methods used for landfills and contaminated sites management. In: Reddy KR, Agnihotri AK, Yukselen-Aksoy Y, Dubey BK, Bansal A (eds) Sustainable environmental geotechnics. Lecture notes in civil engineering, vol 89. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51350-4_8
Krook J, Svensson N, Eklund M (2012) Landfill mining: a critical review of two decades of research. Waste Manag 32:513–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2011.10.015
Lesmes DP, Friedman SP (2005) Relationships between the electrical and hydrogeological properties of rocks and soils. In: Rubin Y, Hubbard SS (eds) Hydrogeophysics water science and technology library, vol 50. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3102-5_4
Li Y, Yang Z, Yang K, Wei J, Li Z, Ma C, Yang X, Wang T, Zeng G, Yu G, Zhigang Y, Zhang C (2022) Removal of chloride from water and wastewater: removal mechanisms and recent trends. Sci Total Environ 821:153174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153174
Massoud MA, Khoury R, Ghanem R, Ghoussainy R, Merhbi F (2022) Development of a pragmatic methodology for the environmental assessment of uncontroled dumpsites in developing countries. Environ Earth Sci 81(296):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10417-6
Minasny B, McBratney AB (2018) Limited effect of organic matter on soil available water capacity. Eur J Soil Sci 69(1):39–47. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12475
Ministério do Meio Ambiente–MMA (2020) Plano Nacional de Resíduos Sólidos (Planares). MMA, Brasília, DF. https://www.gov.br/mma/pt-br/assuntos/agendaambientalurbana/lixao-zero/plano_nacional_de_residuos_solidos-1.pdf
Mohammed Nazifi H, Gulen L, Gürbüz E, Peksen E (2022) Time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) monitoring of used engine oil contamination in laboratory setting. J Appl Geophys 197:104531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2022.104531
Moreira CA, Lapola MM, Carrara A (2016) Comparative analyzes among electrical resistivity tomography arrangements in the characterization of flow structure in free aquifer. Geofís Int 55(2):119–129
Moreira CA, dos Santos EG, Ilha LM, Paes RAS (2019) Recognition of sulfides zones in marble mine through comparative analysis of electrical tomography arrangements. Pure Appl Geophys 176:4907–4920. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-019-02243-y
Morita A, Pelinson NS, Elis VR, Wendland E (2020) Long-term geophysical monitoring of an abandoned dumpsite area in a Guarani Aquifer recharge zone. J Contam Hydrol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103623
Morita AKM, Ibelli-Bianco C, Anache JAA, Coutinho JV, Pelinson NS, Nobrega J, Rosalem LMP, Leite CMC, Niviadonski LM, Manastella C, Wendland E (2021) Pollution threat to water and soil quality by dumpsites and non-sanitary landfills in Brazil: a review. Waste Manag 131:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2021.06.004
Ojo AO, Olurin OT, Ganiyu SA, Badmus BS, Idowu OA (2022) Electrical imaging characterization of a dumpsite on an abandoned quarry site in Abeokuta, South West, Nigeria. Sci Afr 17:e01330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2022.e01330
Parasnis DS (1997) Principles of applied geophysics, 5th edn. Chapman and Hall, New York, p 429
Passarelli CR, Basei MAS, Wemmer K, Siga O Jr, Oyhantçabal P (2010) Major shear zones of southern Brazil and Uruguay: escape tectonics in the eastern border of Rio de La plata and Paranapanema cratons during the Western Gondwana amalgamation. Int J Earth Sci (geol Rundsch) 100:391–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-010-0594-2
Ross JLS, Moroz IC (2011) Mapa Geomorfológico Do Estado De São Paulo. Revista Do Departamento De Geografia 10:41–58. https://doi.org/10.7154/RDG.1996.0010.0004
Schaefer C, Fabris JD, Ker J (2008) Minerals in the clay fraction of Brazilian Latosols (Oxisols): a review. Clay Miner 43:137–154. https://doi.org/10.1180/claymin.2008.043.1.11
Shubo T, Fernandes L, Montenegro SG (2020) An overview of managed aquifer recharge in Brazil. Water 12(4):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12041072
SNIS-Sistema Nacional de Informações Sobre Saneamento (2022) Diagnóstico do manejo de resíduos sólidos urbanos – 2021. SNS/MDR, Brasília, DF
United Nations Environmental Programme–UNEP (2021) Roadmap for the progressive closure of dumpsites in Latin America and the Caribbean. UNEP Coalition for the closure of dumpsites Latin America and Caribbean
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2017) Water Quality Standards Handbook: Chapter 3: Water Quality Criteria. EPA-823-B-17-001. EPA Office of Water, Office of Science and Technology, Washington, DC
Zhan LT, Xu H, Jiang XM, Lan JW, Chen YM, Zhang ZY (2019) Use of electrical resistivity tomography for detecting the distribution of leachate and gas in a large-scale MSW landfill cell. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:20325–20343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05308-6
Funding
No funding was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LGN and CCG wrote the main manuscript text. AMB performed hydrochemical data analysis. OCBG carried out the geophysical acquisitions. LGN processing of geophysical data. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Netto, L.G., Guimarães, C.C., Barbosa, A.M. et al. Characterization of an inactive dumpsite using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data: a case study in Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 82, 529 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11233-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-11233-2