Abstract
An interpretation approach for analysis of electrical resistivity and chargeability inverse models generated at two upgraded semi-aerobic landfill sites was developed. The inverse models produced from a 2D inversion program (RES2DINV) were used to set up a grid of electrical resistivity and chargeability imaging at the landfill sites. The investigations confirmed a high chargeability unit (>70 ms) depicting waste deposits and a saturated clayey layer, while the leachate plume showed low resistivity (<10 Ωm) and weak chargeability zone (<20 ms). Moreover, the IP responses of a diffused leachate plume downstream of a separate semi-aerobic landfill site in a similar geological setting were evaluated, obtaining an analogous result. The ion-dominated plume that exhibited a weak chargeability promoted membrane polarization rather than electrode polarization in its IP responses. However, the high concentration of ions in the diffused leachate restrained the ionic polarization, diminishing the IP effects in host sediments. The interpretation of the resistivity and chargeability profiles at the characterization sites allowed delineating the different zones of the subsurface strata. In particular, comparison of the leachate zones at the two locations revealed that the active landfill with a lesser proportion of waste deposits contained a greater accumulation of leachate than the closed site. The results in this study support the effectiveness of contaminant plume monitoring through the joint application of resistivity and IP methods. These non-invasive, rapid and cost-effective, geophysical techniques could lead to a promising reconnaissance tool for remediation or reclamation of solid waste disposal sites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrahman A, Nawawi MNM, Saad R, Adiat KAN (2013) Volumetric assessment of leachate from solid waste using 2D and 3D electrical resistivity imaging. Adv Mater Res 726:3014–3022. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.726-731.3014
Abu-Zeid N, Bianchini G, Santarato G, Vaccaro C (2004) Geochemical characterisation and geophysical mapping of landfill leachates: the Marozzo canal case study (NE Italy). Environ Geol 45(4):439–447. doi:10.1007/s00254-003-0895-x
Aluko OO, Sridhar M (2005) Application of constructed wetlands to the treatment of leachates from a municipal solid waste landfill in Ibadan, Nigeria. J Environ Health 67(10):58–62
Archie GE (1942) The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans AIMe 146(99):54–62
Aristodemou E, Thomas-Betts A (2000) DC resistivity and induced polarisation investigations at a waste disposal site and its environments. J Appl Geophys 44(2):275–302. doi:10.1016/S0926-9851(99)00022-1
Aziz HA, Adlan MN, Amilin K, Yusoff MS, Ramly NH, Umar M (2012) Quantification of leachate generation rate from a semi-aerobic landfill in Malaysia. Environ Eng Manage J 11(9):1581–1585
Aziz HA, Yusoff MS, Adlan MN, Adnan NH, Alias S (2004) Physico-chemical removal of iron from semi-aerobic landfill leachate by limestone filter. Waste Manage 24(4):353–358. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2003.10.006
Bashir MJ, Aziz HA, Yusoff MS, Aziz SQ, Mohajeri S (2010) Stabilized sanitary landfill leachate treatment using anionic resin: treatment optimization by response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater 182(1):115–122
Bernstone C, Dahlin T (1999) Assessment of two automated electrical resistivity data acquisition systems for landfill location surveys: two case studies. J Environ Eng Geophys 4(2):113–121. doi:10.4133/JEEG4.2.113
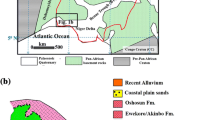
Bosch JHA (1988) The Quaternary Deposits in the Coastal Plains of Peninsular Malaysia Geological Survey Malaysia. Report No. QG/1 of 1988
Breede K, Kemna A (2012) Spectral induced polarization measurements on variably saturated sand-clay mixtures. Near Surf Geophys 10(6):479–489. doi:10.3997/1873-0604.2012048
Carlson NR, Hare JL, Zonge KL (2001) Buried landfill delineation with induced polarization: progress and problems. Paper presented at the Proceedings 14th meeting Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems (SAGEEP), Denver
Chambers JE, Kuras O, Meldrum PI, Ogilvy RD, Hollands J (2006) Electrical resistivity tomography applied to geologic, hydrogeologic, and engineering investigations at a former waste-disposal site. Geophysics 71(6):B231–B239. doi:10.1190/1.2360184
Dahlin T (1996) 2D Resistivity surveying for environmental and engineering applications. First Break. doi:10.3997/1365-2397.1996014
Dahlin T (2014) Factors affecting time domain IP quality. 3rd International Workshop on Induced Polarization. Oléron Island, France
Dahlin T, Leroux V, Nissen J (2002) Measuring techniques in induced polarisation imaging. J Appl Geophys 50(3):279–298. doi:10.1016/S0926-9851(02)00148-9
Dahlin T, Rosqvist H, Leroux V (2010) Resistivity-IP for landfill applications. First Break 28(8):101–105 (id: 2344519)
Domenico PA, Schwartz FW (1998) Physical and chemical hydrogeology, 2nd edn. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York
Farquhar G (1989) Leachate: production and characterization. Can J Civ Eng 16(3):317–325. doi:10.1139/l89-057
Frohlich RK, Urish DW, Fuller J, O’Reilly M (1994) Use of geoelectrical methods in groundwater pollution surveys in a coastal environment. J Appl Geophys 32(2):139–154. doi:10.1016/0926-9851(94)90016-7
Gallas JDF, Taioli F, Malagutti Filho W (2011) Induced polarization, resistivity, and self-potential: a case history of contamination evaluation due to landfill leakage. Environ Earth Sci 63(2):251–261. doi:10.1007/s12665-010-0696-y
Gazoty A, Fiandaca G, Pedersen J, Auken E, Christiansen A (2012a) Mapping landfills with Time Domain IP: the Eskelund case study. Near Surf Geophys 10:563–574. doi:10.3997/1873-0604.2012046
Gazoty A, Fiandaca G, Pedersen J, Auken E, Christiansen A, Pedersen J (2012b) Application of time-domain induced polarization to the mapping of lithotypes in a landfill site. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16(6):1793–1804. doi:10.5194/hess-16-1793-2012
Griffiths D, Turnbull J, Olayinka A (1990) Two-dimensional resistivity mapping with a computer-controlled array. First Break. doi:10.3997/1365-2397.1990008
Guérin R, Munoz ML, Aran C, Laperrelle C, Hidra M, Drouart E, Grellier S (2004) Leachate recirculation: moisture content assessment by means of a geophysical technique. Waste Manage 24(8):785–794. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2004.03.010
Iliceto V, Santarato G, Veronese S (1982) An approach to the identification of fine sediments by induced polarization laboratory measurements. Geophys Prospect 30(3):331–347. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1982.tb01310.x
Inanc B, Idris A, Terazono A, Sakai SI (2004) Development of a database of landfills and dump sites in Asian countries. J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 6(2):97–103. doi:10.1007/s10163-004-0116-z
Ishola KS, Nawawi MNM, Abdullah K (2014) Combining multiple electrode arrays for two-dimensional electrical resistivity imaging using the unsupervised classification technique. Pure Appl Geophys. doi:10.1007/s00024-014-1007-4
Kamaludin B (1990) A summary of the quaternary geology investigations in Seberang Perai, Pulau Pinang, and Kuala Kurau. Geol Soc Malaysia Bull 26:47–54
Kaya MA, Özürlan G, Şengül E (2007) Delineation of soil and groundwater contamination using geophysical methods at a waste disposal site in Çanakkale, Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 135(1–3):441–446. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9662-x
Kelly WE (1976) Geoelectric sounding for delineating ground-water contamination. Groundwater 14(1):6–10. doi:10.1111/j.1745-6584.1976.tb03626.x
Legaz A, Christiansen AV, Auken E, Pedersen J, Fiandaca G (2010) Evaluation of landfill disposal boundaries by means of induced polarization and electrical resistivity imaging. Nordrocs, Copenhagen
Leroux V, Dahlin T, Svensson M (2007) Dense resistivity and induced polarization profiling for a landfill restoration project at Härlöv. Southern Sweden. Waste Manage Res 25(1):49–60. doi:10.1177/0734242X07073668
Loke MH, Acworth I, Dahlin T (2003) A comparison of smooth and blocky inversion methods in 2D electrical imaging surveys. Explor Geophys 34(3):182–187. doi:10.1071/EG03182
Loke MH, Barker RD (1996a) Rapid least-squares inversion of apparent resistivity pseudosections by a quasi-Newton method. Geophys Prospect 44(1):131–152. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1996.tb00142.x
Loke MH, Barker RD (1996b) Practical techniques for 3D resistivity surveys and data inversion. Geophys Prospect 44(3):499–523. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2478.1996.tb00162.x
Martinho E, Almeida F (2006) 3D behaviour of contamination in landfill sites using 2D resistivity/IP imaging: case studies in Portugal. Environ Geol 49(7):1071–1078. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0151-7
Meju MA (2000) Geoelectrical investigation of old/abandoned, covered landfill sites in urban areas: model development with a genetic diagnosis approach. J Appl Geophys 44(2):115–150. doi:10.1016/S0926-9851(00)00011-2
Morris JW, Barlaz MA (2011) A performance-based system for the long-term management of municipal waste landfills. Waste Manage 31(4):649–662. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2010.11.018
Mota R, Monteiro Santos F, Mateus A, Marques F, Gonçalves M, Figueiras J, Amaral H (2004) Granite fracturing and incipient pollution beneath a recent landfill facility as detected by geoelectrical surveys. J Appl Geophys 57(1):11–22. doi:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2004.08.007
Muhammad NS, Hambali S, Romali NHM, Shani NM (2008) The effectiveness of leachate treatment in Pulau Burung sanitary landfill, Pulau Pinang. ESTEEM 4:35–44
Naudet V, Revil A, Rizzo E, Bottero JY, Bégassat P (2004) Groundwater redox conditions and conductivity in a contaminant plume from geoelectrical investigations. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 8(1):8–22 (HAL Id: hal-00330848)
Schön JH (1996) Physical properties of rocks—fundamentals and principles of petrophysics. Pergamon Press, Oxford, p 583
Sharma PV (1997) Environmental and engineering geophysics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Singh RP, Singh P, Araujo ASF, Ibrahim MH, Sulaiman O (2011) Management of urban solid waste: vermicomposting a sustainable option. Resour Conserv Recycl 55(7):719–729. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2011.02.005
Slater LD, Lesmes D (2002) IP interpretation in environmental investigations. Geophysics 1:77–88. doi:10.1190/1.1451353
Slater L, Ntarlagiannis D, Wishart D (2006) On the relationship between induced polarization and surface area in metal-sand and clay-sand mixtures. Geophysics 71(2):A1–A5. doi:10.1190/1.2187707
Soupios P, Papadopoulos N, Papadopoulos I, Kouli M, Vallianatos F, Sarris A, Manios T (2007) Application of integrated methods in mapping waste disposal areas. Environ Geol 53(3):661–675. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-0681-2
Syafalni S, Zawawi MH, Abustan I (2014) Isotopic and hydrochemistry fingerprinting of leachate migration in shallow groundwater at controlled and uncontrolled landfill sites. World Appl Sci J 31(6):1198–1206. doi:10.5829/idosi.wasj.2014.31.06.217
Turesson A, Lind G (2005) Evaluation of electrical methods, seismic refraction and ground-penetrating radar to identify clays below sands—two case studies in SW Sweden. Near Surf Geophys 3(2):59–70. doi:10.3997/1873-0604.2005001
Umar M, Aziz HA, Yusoff MS (2010) Variability of parameters involved in leachate pollution index and determination of LPI from four landfills in Malaysia. Int J Chem Eng. doi:10.1155/2010/747953
Ustra AT, Elis VR, Mondelli G, Zuquette LV, Giacheti HL (2012) Case study: a 3D resistivity and induced polarization imaging from downstream a waste disposal site in Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 66(3):763–772. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1284-5
Wynn J, Grosz A (2000) Induced polarization—a tool for mapping titanium-bearing placers, hidden metallic objects, and urban waste on and beneath the seafloor. J Environ Eng Geophys 5(3):27–35. doi:10.4133/JEEG5.3.27
Yoon J, Lee K, Kwon B, Han W (2003) Geoelectrical surveys of the Nanjido waste landfill in Seoul, Korea. Environ Geol 43(6):654–666. doi:10.1007/s00254-002-0670-4
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Idaman Bersih Sendirian Berhad and Majlis Daerah Kerian Bangai Sarai for granting permission for use of the landfills selected for characterization and the leachate assessment site, respectively. This work was funded by an Incentive Grant from the Universiti Sains Malaysia (Graduate Student Account Number 1001/PFIZIK/821060). The authors are grateful to Dr. Hassan Baioumy for his comments during data interpretation. The constructive criticism from the anonymous reviewers which improved the quality of this manuscript is greatly acknowledged. The field support from Mydin Bin Jamal, Low Weng Leng and other members of the technical staff of the Geophysics Programme, Universiti Sains Malaysia, is highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdulrahman, A., Nawawi, M., Saad, R. et al. Characterization of active and closed landfill sites using 2D resistivity/IP imaging: case studies in Penang, Malaysia. Environ Earth Sci 75, 347 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5003-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5003-5