Abstract
Vulnerability assessment of an urban area to earthquake hazards is the requirement to attaining sustainable urban resilience. Quetta city is the capital of the province of Balochistan surrounded by mountains with the existence of many active faults. The main objective of the current study was to assess the earthquake vulnerability in Quetta valley. A total of 400 households were selected for the primary household survey. A simple random sampling technique is employed using proportionate allocation method because of the heterogeneity of the area in terms of population. Secondary data was taken from the Geological Survey of Pakistan (GSP), the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics (PBS), and the United States Geological Survey (USGS). Analytical Hierarchal Process (AHP) & Weighted Linear Combination (WLC) methods are used to identify earthquake vulnerability. The results of the study reveal that the Northwestern and Southeastern parts of Quetta are seismically vulnerable to earthquake hazard; its geology coupled with the human dimension indicates a more disastrous future events. Results of the composite earthquake vulnerability show that seven out of thirteen Zones of Quetta city are highly vulnerable to all four components of vulnerability. Four Zones have a medium level of vulnerability and only two Zones are considered low earthquake vulnerable Zones in the study area. The topmost influential factors that make Quetta city highly earthquake-vulnerable are the soil type (0.45), peak ground acceleration (0.34), proximity to the hospitals and fire service stations (0.22, 0.21), elderly population (0.22) and fault lines (0.21) as shown in Fig. 12. This research study has significant implications for urban planners and provides a risk reduction platform in order to reduce future earthquake losses and make Quetta city more resilient and sustainable.

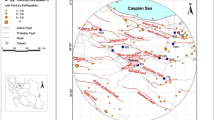
(Source: National Seismic Monitoring Centre, Islamabad)











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Ahasan R, Alam MS, Chakraborty T, Hossain MM (2020) Applications of GIS and geospatial analyses in COVID-19 research: a systematic review. F1000Res 9:1379. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.27544.1
Ainuddin S, Routray JK (2012) Community resilience framework for an earthquake prone area in Baluchistan. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 2(1):25–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2012.07.003
Ainuddin S, Routray JK, Ainuddin S (2015) Operational indicators for assessing vulnerability and resilience in the context of natural hazards and disasters. Int J Risk Assess Manag 18(1):66–88. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJRAM.2015.068135
Alam MS, Haque SM (2018) Assessment of urban physical seismic vulnerability using the combination of AHP and TOPSIS models: a case study of residential neighborhoods of Mymensingh City, Bangladesh. J Geosci Environ Prot 06(02):165–183. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2018.62011
Alam MS, Mondal M (2019) Assessment of sanitation service quality in urban slums of Khulna city based on SERVQUAL and AHP model: A case study of railway slum, Khulna, Bangladesh. J Urban Manag 8(1):20–27
Alam MS, Haque SM (2021) Multi-dimensional earthquake vulnerability assessment of residential neighborhoods of Mymensingh City, Bangladesh: a spatial multi-criteria analysis based approach. J Urban Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jum.2021.09.001
Alizadeh M, Hashim M, Alizadeh E, Shahabi H, Karami MR, Pour AB, Pradhan B, Zabihi H (2018) Multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) model for seismic vulnerability assessment (SVA) of urban residential buildings. ISPRS Int J Geo-Inform. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7110444
Arkin H, Colton RR (1963) Tables for statisticians, 2nd edn. Barnes and Noble Books, New York, contributed by National Library of Australia
Armaş I (2012) Multi-criteria vulnerability analysis to earthquake hazard of Bucharest, Romania. Nat Hazards 63(2):1129–1156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0209-2
Armaş I, Toma-Danila D, Ionescu R, Gavriş A (2017) Vulnerability to earthquake hazard: Bucharest case study, Romania. Int J Disaster Risk Sci 8(2):182–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13753-017-0132-y
Bendito A, Rozelle J, Bausch D (2014) Assessing potential earthquake loss in Mérida State, Venezuela using Hazus. Int J Disaster Risk Sci 5(3):176–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13753-014-0027-0
Bilham R (2019) Himalayan earthquakes: a review of historical seismicity and early 21st century slip potential. Geol Soc Lon Spec Publ. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp483.16
Bollinger L et al (2004) Thermal structure and exhumation history of the Lesser Himalaya in central Nepal. Tectonics 23(5)
Cutter SL, Finch C (2008) Temporal and spatial changes in social vulnerability to natural hazards. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(7):2301–2306. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0710375105
Cutter SL, Boruff BJ, Shirley WL (2003) Social vulnerability to environmental hazards. Soc Sci Q 84(2):242–261. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-6237.8402002
Cutter social vulnerability index paper (2003)
D’Ayala D, Speranza E (2003) Definition of collapse mechanisms and seismic vulnerability of historic masonry buildings. Earthq Spectra 19(3):479–509. https://doi.org/10.1193/1.1599896
Daniell JE (2011) Open source procedure for assessment of loss using global earthquake modelling software (OPAL). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 11(7):1885–1899. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-11-1885-2011
Dewi R, Budhiana J, Permana I, Mariam I, Frans Unmehopa Y, Novianty L, Novianti Utami R, Sanjaya W, Rahman La Ede A, Rahmanishati W (2020) Factors affecting nurse preparedness in disaster management in the emergency room of the pelabuhan ratu hospital in sukabumi regency. Sys Rev Pharm 11(12):1218–1225
Flores KL, Escudero CR, Zamora-Camacho A (2021) Multicriteria seismic hazard assessment in Puerto Vallarta metropolitan area, Mexico. Nat Hazards 105(1):253–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04308-x
Ghajari YE, Alesheikh AA, Modiri M, Hosnavi R, Abbasi M (2017) Spatial modelling of urban physical vulnerability to explosion hazards using GIS and fuzzy MCDA. Sustainability (switzerland) 9(7):1–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9071274
Gupta AK, Smith KG, Shalley CE (2006) The interplay between exploration and exploitation. Acad Manag J 49(4):693–706
Hajibabaee M, Hosseini KA, Ghayamghamian MR (2012) A new method for assessing the seismic risk index of urban fabrics. 15th WCEE
Hajibabaee M, Amini-hosseini K, Reza M (2014) Assessing the risk of earthquake in urban areas (Case study : Tehran City ). Second Europian Conference on Earthquake ENGINEERING 3
Jena R, Pradhan B (2020) Integrated ANN-cross-validation and AHP-TOPSIS model to improve earthquake risk assessment. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 50:101723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101723
Ji H, Lee D (2021) Disaster risk reduction, community resilience, and policy effectiveness: the case of the Hazard Mitigation Grant Program in the United States. Disasters 45(2):378–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/disa.12424
Kamranzad F, Memarian H, Zare M (2020) کامران زاد. Pdf. 1
Khan A, Connolly JAD, Maclennan J, Mosegaard K (2007) Joint inversion of seismic and gravity data for lunar composition and thermal state. Geophys J Int 168(1):243–258
Kheirizadeh Arouq M, Esmaeilpour M, Sarvar H (2020) Vulnerability assessment of cities to earthquake based on the catastrophe theory: a case study of Tabriz city, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 79(14):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09103-2
Lantada N, Irizarry J, Barbat AH, Goula X, Roca A, Susagna T, Pujades LG (2010) Seismic hazard and risk scenarios for Barcelona, Spain, using the Risk-UE vulnerability index method. Bull Earthq Eng 8(2):201–229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-009-9148-z
Lee S, Oh S (2022) A comprehensive seismic risk assessment map of South Korea based on seismic, geotechnical, and social vulnerability. Environ Earth Sci 81(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10153-3
Martins L (2018) Earthquake damage and loss assessment of reinforced concrete buildings. PhD Dissertation, University of Porto
Manyena SB (2006) The concept of resilience revisited. Disasters 30(4):434–450
Meghdad M, Sharif Bakhtiar M (2014) Minimum Power Miller-Compensated CMOS Operational Ampli ers. Sci Iran 21(6):2243–2249
Molnar P, Tapponnier P (1975) Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: effects of a continental collision: features of recent continental tectonics in Asia can be interpreted as results of the India-Eurasia collision. Science 189(4201):419–426
Nath SK, Adhikari MD, Devaraj N, Maiti SK (2015) Seismic vulnerability and risk assessment of Kolkata City, India. Nat Hazard 15(6):1103–1121. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-15-1103-2015
Ozmen HB, Inel M, Meral E (2014) Evaluation of the main parameters affecting seismic performance of the RC buildings. Sadhana 39(2):437–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-014-0235-8
Peter F (2000) A nonlinear analysis method for performance-based seismic design. Earthq Spectra 16:573–592
Rafi Z, Ahmed N, Ur-Rehman S, Azeem T, Abd el-aal AEAK (2013) Analysis of Quetta-Ziarat earthquake of 29 October 2008 in Pakistan. Arabian J Geosci 6(6):1731–1737
Rahman N, Ansary MA, Islam I (2015) GIS based mapping of vulnerability to earthquake and fire hazard in Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 13:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2015.07.003
Rehman A, Song J, Haq F, Ahamad M, Sajid M, Zahid Z (2021) Geo-physical hazards microzonation and suitable site selection through multicriteria analysis using geographical information system. Appl Geogr 135:102550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2021.102550
Rehman A, Song J, Haq F, Mahmood S, Ahamad MI, Basharat M, Sajid M, Mehmood MS (2022) Multi-hazard susceptibility assessment using the analytical hierarchy process and frequency ratio techniques in the Northwest Himalayas, Pakistan. Remote Sens 14(3):1–31. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030554
Rendall M (2020) Household structure and social vulnerability: lessons from Hurricane Katrina. Household Structure and Social Vulnerability: Lessons from Hurricane Katrina 2–4. https://doi.org/10.7249/rb9597
Rezaie F, Panahi M (2015) GIS modeling of seismic vulnerability of residential fabrics considering geotechnical, structural, social and physical distance indicators in Tehran using multi-criteria decision-making techniques. Nat Hazard 15(3):461–474. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-15-461-2015
Tunner HG, Heppich S (1981) Premeiotic genome exclusion during oogenesis in the common edible frog, Rana esculenta. Die Naturwissenschaften 68(4):207–208
UNDESA (2020) World Social Report; INEQUALITY IN A RAPIDLY CHANGING WORLD. ST/ESA/372 United Nations publication Sales No. E.20.IV.1
UNDRR and CRED (2020) Human cost of disasters: an overview of the last 20 years. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 21(4):324–343
UNDRR (2021) United nations office for disaster risk reduction: 2020 annual report. 107. https://www.unisdr.org/files/64454_unisdrannualreport2018eversionlight.pdf
Vicente R, Ferreira T, Maio R (2014) Seismic risk at the urban scale: assessment, mapping and planning. Procedia Econom Finance 18:71–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2212-5671(14)00915-0
Walker BB, Schuurman N, Swanlund D, Clague JJ (2021) GIS-based multicriteria evaluation for earthquake response: a case study of expert opinion in Vancouver, Canada. Nat Hazards 105(2):2075–2091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-020-04390-1
Wind Y, Saaty TL (1980) Marketing applications of the analytic hierarchy process. Manag Sci 26(7):641–658
World Social Report 2020 (2020) In World Social Report 2020. https://doi.org/10.18356/7f5d0efc-en
Wood NJ, Burton CG, Cutter SL (2010) Community variations in social vulnerability to Cascadia-related tsunamis in the US Pacific Northwest. Nat Hazards 52:369–389
Yariyan P, Zabihi H, Wolf ID, Karami M, Amiriyan S (2020) Earthquake risk assessment using an integrated Fuzzy analytic Hierarchy process with artificial neural networks based on GIS: a case study of Sanandaj in Iran. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct 50:101705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101705
Zebardast E (2013) Constructing a social vulnerability index to earthquake hazards using a hybrid factor analysis and analytic network process (F’ANP) model. Nat Hazards 65(3):1331–1359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-012-0412-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SA and J conceived of the presented idea. J and SK developed the theory and performed the computations. GM and SF verified the analytical methods. All authors discussed the results and contributed.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jamal-ud-din, Ainuddin, S., Murtaza, G. et al. Earthquake vulnerability assessment through spatial multi-criteria analysis: a case study of Quetta city, Pakistan. Environ Earth Sci 82, 262 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10967-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10967-3