Abstract
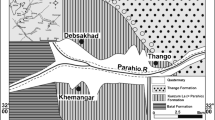
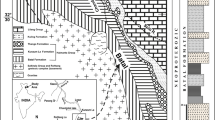
The geochemical characteristics of stream/slopewash sediments, modal composition and petrography of the clastic units from the Siwalik Group has been investigated to determine the provenance and tectonic setting of these rocks, as well as to appraise the influence of the weathering and recycling processes upon source rock signatures. The higher CIA index indicates that the source area underwent moderate to intense chemical weathering processes, possibly due to climatic and/or tectonic variations. Alternatively, modal analyses show that the source area of the Siwalik rocks may have been composed of recycled sedimentary materials. The La/Th ratios and Hf discriminant plot show that they originally come from a differentiated silicic source. This has been further supported by Hiscott Diagram (Cr/V vs. Y/Ni) and Th–Hf–Co discrimination diagram which supports a primitive silicic source for these rocks indicating a higher proportion of felsic material in their primitive source area. The Eu/Eu* versus (Gd/Yb)N diagram for the samples of the Siwalik sediments indicates that the source rocks are mainly influenced by post-Archean felsic rocks.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ajayi TR, Oyawale AA, Islander FY, Asubiojo OI, Klein DE, Adediran AI (2006) Trace and rare earth elements geochemistry of Oshosun sediments of Dahomey basin, Southwestern Nigeria. J Appl Sci 6:2067–2076
Auden JB (1935) Traverses Himalayas Ree Geolsurv India 692:125–132
Banerjee A, Banerjee DM (2010) Modal analysis and geochemistry of two sandstones of the Bhander group (late Neoproterozoic) in parts of the central Indian Vindhyan basin and their bearing on the provenance and tectonics. J Earth Syst Sci 119(6):825–839
Banerjee DM, Bhattacharya P (1989) Petrofacies analysis of the clastic rocks in the proterozoic Aravalli basin, Udaipur district. South Central Rajasthan Indian Minerals 43(3–4):194–225
Banerjee DM, Bhattacharya P (1994) Petrology and geochemistry of greywackes from the Aravalli Supergroup, Rajasthan, India and the tectonic evolution of a Proterozoic sedimentary basin. Precambr Res 67(1–2):11–35
Bera MK, Sarkar A, Chakraborty PP, Loyal RS, Sanyal P (2008) Marine to continental transition in Himalayan foreland Marine to continental transition in Himalayan foreland. GSA Bull 120(9–10):1214–1232
Bhatia MR (1983) Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones. J Geol 91(6):611–627
Bhatia MR (1985) Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywackes and mudrocks: provenance and tectonic control. Sed Geol 45(1–2):97–113
Bhatia MR, Crook KA (1986) Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins. Contrib Miner Petrol 92(2):181–193
Bhatia MR, Taylor SR (1981) Trace-element geochemistry and sedimentary provinces: a study from the Tasman Geosyncline. Australia Chem Geo 33(1–4):115–125
Boateng TK, Opoku F, Acquaah SO, Akoto O (2016) Groundwater quality assessment using statistical approach and water quality index in Ejisu-Juaben Municipality. Ghana Env Earth Sci 75(6):1–14
Brozovic N, Burbank DW (2000) Dynamic fluvial systems and gravel progradation in the Himalayan foreland. Geol Soc Am Bull 112(3):394–412
Chen J, Algeo TJ, Zhao L, Chen ZQ, Cao L, Zhang L, Li Y (2015) Diagenetic uptake of rare earth elements by bioapatite, with an example from lower triassic conodonts of South China. Earth Sci Rev 149:181–202
Cingolani CA, Manassero M, Abre P (2003) Composition, provenance, and tectonic setting of ordovician siliciclastic rocks in the san rafael block: Southern extension of the Precordillera crustal fragment, Argentina. J S Am Earth Sci 16(1):91–106
Condie KC (1993) Chemical composition and evolution of the upper continental crust: contrasting results from surface samples and shales. Chem Geol 04(1–4):1–37
Cullers RL, Basu A, Suttner LJ (1988) Geochemical signature of provenance in sand-size material in soils and stream sediments near the tobacco root batholith, montana, USA. Chem Geol 70(4):335–348
Das A, Krishnaswami S, Sarin MM, Pande K (2005) Chemical weathering in theKrishna basin and Western Ghats of the deccan traps, India: rates of basalt weathering and their controls. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(8):2067–2084
Das BK, Al-Mikhlafi AS, Kaur P (2006) Geochemistry of mansar lake sediments, Jammu, India: implication for source-area weathering, provenance, and tectonic setting. J Asian Earth Sci 26(6):649–668
Deepthi K, Natesan U, Muthulakshmi AL, Ferrer VA, Venugopalan VP, Narasimhan SV (2013) Geochemical characteristics and depositional environment of Kalpakkam, southeast coast of India. Env Earth Sci 69(7):2357–2364
Dhital MR (2015) Introduction to Siwaliks. In Geology of the Nepal Himalaya. Springer Cham 371–384
Dickinson WR (1985) Interpreting provenance relations from detrital modes of sandstones. Provenance of arenites. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 333–361
Dickinson WR, Beard LS, Brakenridge GR, Erjavec JL, Ferguson RC, Inman KF, Knepp RA, Lindberg FA, Ryberg PT (1983) Provenance of North American Phanerozoic sandstones in relation to tectonic setting. Geol Soc Am Bull 94(2):222–235
Dinelli E, Lucchini F, Mordenti A, Paganelli L (1999) Geochemistry of Oligocene-Miocene sandstones of the northern apennines (Italy) and evolution of chemical features in relation to provenance changes. Sed Geol 127(3–4):193–207
Floyd PA, Leveridge BE (1987) Tectonic environment of the devonian Gramscatho basin, south cornwall: framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones. J Geol Soc 144(4):531–542
Friend PF, Raza SM, Geehan G, Sheikh KA (2001) Intermediate-scale architectural features of the fluvial Chinji Formation (Miocene), Siwalik Group, northern Pakistan. J Geol Soc 158(1):163–177
Gansser A (1964) Geology of the Himalayas. Wiley, New York, p 289
Garrett R, Reimann C, Smith D, Xie, X (2008). From geochemical prospecting to international geochemical mapping: A historical overview. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis 8(3): 205– 217
Ghazi S, Mountney NP (2011) Petrography and provenance of the early permian fluvial warchha sandstone, salt range. Pakistan Sedimentary Geo 233(1–4):88–110
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170(3962):1088–1090
Goswami PK, Deopa T (2018) Lithofacies characters and depositional processes of a middle miocene lower Siwalik fluvial system of the Himalayan foreland basin, India. J Asian Earth Sci 162:41–53
Guleria SS, Kishore N, Madhuri SR (2014) Morphometry and Geomorphological Investigations of the Neugal Watershed, beas river basin, Kangra District, Himachal Pradesh Using GIS Tools. J Environ Earth Sci 4(2):78–86
Hammer Ø, Harper DA, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontologia Electronic 4(1):9
Herron MM (1988) Geochemical classification of terrigenous sands and shales from core or log data. J Sediment Res 58(5):820–829
Hiscott RN (1984) Ophiolitic source rocks for Taconic-age flysch: trace-element evidence. Geol Soc Am Bull 95(11):1261–1267
Howladar MF, Al Numanbakth MA, Faruque MO (2018) An application of water quality Index (WQI) and multivariate statistics to evaluate the water quality around Maddhapara Granite Mining Industrial Area, Dinajpur. Bangladesh Envir Sys Res 6(1):1–18
Jalal P, Ghosh SK (2012) Provenance of the Late Neogene Siwalik sandstone, Kumaun Himalayan foreland basin: Constraints from the metamorphic rank and index of detrital rock fragments. J Earth Syst Sci 121(3):781–792
Jalal P, Ghosh SK, Sundriyal YP (2011) Detrital modes of Late Neogene Siwalik Sandstone of the Ramganga Sub-basin, Kumaun Sub-Himalaya: Implication for the source area tectonic history. Him Geol 32(2):123–135
Jaswal AK, Kumar N, Khare P (2014) Climate variability in Dharamsala-a hill station in western Himalayas. J Indian Geophysical Union 18(3):336–355
Kasanzu C, Maboko MA, Manya S (2008) Geochemistry of fine-grained clastic sedimentary rocks of the Neoproterozoic Ikorongo group, NE Tanzania: implications for provenance and source rock weathering. Precambr Res 164(3–4):201–213
Kayastha SL (1958) Precipitation characteristics of the Himalayan beas basin. J Scientific Res Banaras Hindu University 8(2):183–189
Kettanah YA, Armstrong-Altrin JS, Mohammad FA (2021) Petrography and geochemistry of siliciclastic rocks of the middle eocene Gercus formation, Northern Iraq: implications for provenance and tectonic setting. Geol J 56(5):2528–2549
Khan ZA, Tewari RC (2011) Paleochannel and paleohydrology of a Middle Siwalik (Pliocene) fluvial system, Northern India. J Earth Syst Sci 120(3):531
Kotlia BS, Goswami PK, Joshi LM, Singh AK, Sharma AK (2018) Sedimentary environment and geomorphic development of the uppermost Siwalik molasses in Kumaun Himalayan foreland basin. North India Geological Journal 53(1):159–177
Kumar R, Tandon SK (1985) Sedimentology of Plio-Pleistocene late orogenic deposits associated with intraplate subduction—the Upper Siwalik subgroup of a part of Panjab Sub-Himalaya. India Sedimentary Geology 42(1–2):105–158
Kumar R, Ghosh SK, Sangode SJ (2003) Mio– Pliocene sedimentation history in the northwestern part of the Himalayan foreland basin. India; Curr Sci 84(8):1006–1113
Kumar SK, Babu SH, Rao PE, Selvakumar S, Thivya C, Muralidharan S, Jeyabal G (2017) Evaluation of water quality and hydrogeochemistry of surface and groundwater, Tiruvallur District, Tamil Nadu. India Applied Water Science 7(5):2533–2544
Kundu A, Matin A, Mukul M, Eriksson PG (2011) Sedimentary facies and soft-sediment deformation structures in the late Miocene-Pliocene Middle Siwalik subgroup, Eastern Himalaya, Darjiling District, India. J Geol Soc India 78(4):321
Mandal SK, Scherler D, Romer RL, Burg J, Guillong M, Schleicher AM (2019) Multiproxy isotopic and geochemical analysis of the Siwalik sediments in NW India: Implication for the Late Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalaya. Tectonics 38(1):120–143
Maxwell JA (1968) Rock and mineral analysis. Wiley, Newyork
Mclennan SM (1989) Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: influence of provenance and sedimentary processes. Rev Mineral 21:169–200
McLennan SM, Taylor SR (1991) Sedimentary rocks and crustal evolution: tectonic setting and secular trends. J Geol 99(1):1–21
McLennan SM, Hemming S, McDaniel DK, Hanson GN (1993) Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance and tectonics. In: Johnsson, M.J., Basu, A. (Eds.), Processes controlling the composition of clastic sediments, Geological Society of America, Special Papers 285:21–40.
McLennan SM (2001) Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 2 (4) N/A
Medlicott HB (1864) On the geological structure and relations of the southern portion of the Himalayan ranges between the rivers Ganges and the Ravee. Geol Surv India Memoir 3(2):1–212
Meigs AJ, Burbank DW, Beck RA (1995) Middle-late Miocene (>10 Ma) formation of the main boundary thrust in the Western Himalaya. Geology 23(5):423–426. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1995)0232.3.CO;2
Miall AD (2016) Facies models. Stratigraphy: a modern synthesis. Springer, Cham, pp 161–214
Mir IA, Mir RA (2019) Geochemistry of surface sediments in parts of Bandipora-Ganderbal areas, Kashmir valley, western Himalaya: implications for provenance and weathering. J Earth Syst Sci 128(8):1–16
Mishra PK, Ankit Y, Gautam PK, Lakshmidevi CG, Singh P, Anoop A (2019a) Inverse relationship between south-west and north-east monsoon during the late Holocene: Geochemical and sedimentological record from Ennamangalam Lake, southern India. CATENA 182:104117
Mishra PK, Parth S, Ankit Y, Kumar S, Ambili V, Kumar VV, Singh S, Anoop A (2019b) Geochemical and sedimentological characteristics of surface sediments from Ashtamudi Estuary, Southern India: implications for provenance and modern sedimentary dynamics. Env Earth Sci 78(14):1–11
Moghaddam AA, Fijani E (2008) Distribution of fluoride in groundwater of Maku area, Northwest of Iran. Environ Geol 56(2):281–287
Najman Y, Bickle M, Chapman H (2000) Early himalayan exhumation: Isotopic constraints from the Indian foreland basin. Terra Nova 12(1):28–34
Najman Y, Bickle M, Garzanti E, Pringle M, Barfod D, Brozovic N, Burbank D, Ando S (2009) Reconstructing the exhumation history of the Lesser Himalaya, NW India, from a multitechnique provenance study of the foreland basin Siwalik Group. Tectonics 28.
Nakayama K, Ulak PD (1999) Evolution of fluvial style in the Siwalik Group in the foothills of the Nepal Himalaya. Sedim Geol 125:205–224
Nesbitt H, Young GM (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299(5885):715–717
Nesbitt HW, Young GM, McLennan SM, Keays RR (1996) Effects of chemical weathering and sorting on the petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments, with implications for provenance studies. J Geol 104(5):525–542
Parkash B, Sharma RP, Roy AK (1980) The Siwalik Group (molasse)—sediments shed by collision of continental plates. Sed Geol 25(1–2):127–159
Pettijohn FJ, Potter PE, Siever R (1987) Sand and Sandstone, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, p 553
Pilgrim GE (1913) Correlation of the Siwaliks with mammal Horizons of Europe. Rec Geol SUIV India 43(4):264–326
Piper AM (1944) A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–928
Powers PM, Lillie RJ, Yeats RS (1998) Structure and shortening of the Kangra and Dehra Dun reentrants, sub-Himalaya. India Geo Soc America Bulletin 110(8):1010–1027
Prakash S, Sharma MC, Kumar R, Dhinwa PS, Sastry KLN, Rajawat AS (2016) Mapping and assessing land degradation vulnerability in Kangra district using physical and socio-economic indicators. Spat Inf Res 24(6):733–744
Prasad KN (2001) An introduction to the mammalian fauna of the Siwalik System (Chennai: Prasad Publications) 295
Ranjan N, Banerjee DM (2009) Central himalayan crystallines as the primary source for the sandstone–mudstone suites of the Siwalik group: new geochemical evidence. Gondwana Res 16(3–4):687–696
Rao VS, Sreenivas B, Balaram V, Govil PK, Srinivasan R (1999) The nature of the Archean upper crust as revealed by the geochemistry of the proterozoic shales of the Kaladgi basin, Karnataka, southern India. Precambr Res 98(1–2):53–65
Reátegui K, Martínez M, Esteves I, Gutiérrez JV, Martínez A, Meléndez W, Urbani F (2005) Geochemistry of the mirador formation (Late Eocene-Early Oligocene), southwestern Venezuela: Chemostratigraphic constraints on provenance and the influence of the sea level. Geochem J 39(3):213–226
Roser BP, Korsch RJ (1986) Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone mudstone suites using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio. J Geol 94:635–650
Sahoo HB, Gandre DK, Das PK, Karim MA, Bhuyan GC (2018) Geochemical mapping of heavy metals around Sukinda-Bhuban area in Jajpur and Dhenkanal districts of Odisha. India Env Earth Sci 77(2):1–17
Sanyal P, Sinha R (2010) Evolution of the Indian summer monsoon: synthesis of continental records. Geol Soc, London, Special Pub 342(1):153–183
Schelling D (1992) The tectonostratigraphy and structure of the eastern Nepal Himalaya. Tectonics 11(5):925–943
Shao L, Stattegger K, Garbe-Schoenberg CD (2001) Sandstone petrology and geochemistry of the Turpan basin (NW China): implications for the tectonic evolution of a continental basin. J Sediment Res 71(1):37–49
Singh RL (1971) India: A regional geography. National geographical society of India p, Varanasi, p 992
Singh T (2008a) Hypsometric analysis of watersheds developed on actively deforming Mohand anticlinal ridge, NW Himalaya. Geocarto Int 23:417–427
Singh T (2008b) Tectonic implications of geomorphometric characterization of watersheds using spatial correlation: Mohand Ridge, NW Himalaya, India. Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie 52:489–501
Singh T, Jain V (2009) Tectonic constraints on watershed development on frontal ridges: Mohand Ridge, NW Himalaya, India. Geomorphology 106:231–241
Sinha S, Islam R, Ghosh SK, Kumar R, Sangode, SJ (2007) Geochemistry of Neogene Siwalik mudstones along Punjab re-entrant India: Implications for source-area weathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Current Science 1103-1113
Sreenivas B, Srinivasan R, Roy AB (1999) Geochemical changes across the Archean-Proterozoic Boundary -- A study from the Udaipur area of aravalli mountain belt, Rajasthan, India; In proceedings of the seminar on geology of Rajasthan - Status and Perspective (ed) P Kataria (Geology Dept. M L Sukhadia Univ. Udaipur, India) 57–86
Sreenivas B, Srinivasan R (1994) Identification of paleosols in the Precambrian metapelitic assemblages of peninsular India–a major element geochemical approach. Curr Sci 67:89–94
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. Geo Soc, London, Spe Pub 42(1):313–345
Syangbo DK, Tamrakar NK (2013) Lithofacies and depositional environment of the Siwalik group in Samari-Sukaura River area, Central Nepal. Bulletin of the Department of Geology 16:53–64.
Tandon SK (1976) Siwalik sedimentation in a part of the Kumaun Himalaya. India Sedimentary Geo 16(2):131–154
Thakur VC, Pandey AK, Suresh N (2007) Late Quaternary-Holocene evolution of dun structure and the Himalayan frontal fault zone of the Garhwal sub-Himalaya, NW India. J Asian Earth Sci 29(2–3):305–319
Valdiya KS (2010) The making of India Geodynamic Evolution.
VonEynatten H, Gaupp R (1999) Provenance of Cretaceous synorogenic sandstones in the Eastern alps: constraints from framework petrography, heavy mineral analysis and mineral chemistry. Sed Geol 124(1–4):81–111
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr. G.S. Tiwari, DDG, Geological Survey of India, Chandigarh for his constant support and encouragement. The geochemical Division, GSI, NR Lucknow is acknowledged for the geochemical and hydrochemical analyses. The authors thank anonymous reviewers for their constructive and valuable comments on the earlier version of this manuscript.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Interpretation, Writing – original draft. RK: Data curation, Investigation, Formal analysis and Methodology. SD: Formal analysis, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rimjhim, S., Kanwal, R. & Dhillon, S. Provenance and source area weathering of Siwalik foreland basin rocks in NW Himalayas: insights from hydrochemistry, petrography and geochemical signature. Environ Earth Sci 82, 14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10714-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10714-0