Abstract
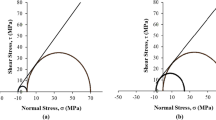
The stability of slopes of China’s Loess Plateau, where fissured loess is abundant, is affected by wet–dry cycles. Uniaxial compression tests and the PCAS system were used to analyze the development of visible cracks and mechanical behavior of fissured loess over wet–dry cycles. Results show that the wet–dry cycles and the fissure angle both influence the development of cracks in fissured loess samples. The failure of fissured loess samples manifests as four main modes such as fracture failure, slip-fracture failure, slip failure, and compression-shear failure. Wet–dry cycles had a negligible effect on the failure mode in samples with fissure angles of 0°, 15°, 45°, and 60°, but were more noticeable at fissure angles of 30° and 90°, ranging from compression-shear failure to fracture failure. The initial elastic modulus and uniaxial compressive strength of fissured loess both decline after wet–dry cycles. After various wet–dry cycles, the associations between uniaxial compressive strength and fissure angle all display a double-V shaped pattern, with abrupt shifts in 45°–90° and the minimum value at a fissure angle of 60°. After wet–dry cycles, the uniaxial compressive strength of fissured loess decreases, while the amplitude of change decreases.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Budhu M (2011) Earth fissure formation from the mechanics of ground water pumping. Int J Geomech 11(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000060
Cheng LH, Nie RS, Liu F (2017) An experimental study of the uniaxial compressive strength of fractured loess. Hydrogeology Eng Geo 44(5):80–87
Conway BD (2016) Land subsidence and earth fissures in south-central and southern Arizona, USA. Hydrogeol J 24(3):649–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-015-1329-z
Deng YH, Li L, Mu HD, Wang P, Li FX (2015) Experimental research on rheological properties of Q3 intact loess within ground fissures belt in Xi’an region. Rock Soil Mechanics 36(7):1847–1855
Fan W, Yu MH, Oda Y, Lin YL, Chen LW, Iwatate T (2004) Fracture mechanics analysis of ground fissure. Key eng materials 87(92):261–263
Fan W, Deng LS, Yuan WN (2017) Double parameter binary-medium model of fissured loess. Eng Geol 236:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.014
Hu CM, Yuan YL, Mei Y, Wang XY, Liu Z (2018) Comprehensive strength deterioration model of compacted loess exposed to drying-wetting cycles. Bull Eng Geol Env 79(1):383–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01561-8
Jia ZJ, Peng JB, Lu QZ, Meng LC, Meng ZJ, Qiao JW, Wang FY, Zhao JY (2020) Characteristics and genesis mechanism of ground fissures in Taiyuan Basin, northern China. Eng Geol 275:105783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105783
Lee CF, Zhang JM, Zhang YX (1996) Evolution and origin of the ground fissures in Xian. China Eng Geo 43(1):45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(95)00088-7
Li X, Wang SJ, Liu TY, Ma FS (2004) Engineering geology, ground surface movement and fissures induced by underground mining in the Jinchuan nickel mine. Eng Geol 76(1–2):93–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2004.06.008
Li L, Zhang K, Zhang QL, Mao YC, Li GY (2016) Experimental study on the loess strength degradation characteristics under the action of dry-wet and freeze-thaw cycles. J Glaciology Geocryology 38(4):1142–1149
Li GY, Wang F, Ma W, Fortier R, Mu YH, Mao YC, Hou X (2018) Variations in strength and deformation of compacted loess exposed to wetting-drying and freeze-thaw cycles. Cold Reg Sci Technol 151:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2018.03.021
Li YR, Shi WH, Aydin A, Beroya-Eitner MA, Gao GH (2020) Loess genesis and worldwide distribution. Earth Sci Rev 201(2020):102947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102947
Liu C, Tang CS, Shi B, Suo WB (2013) Automatic quantification of crack patterns by image processing. Comput Geosci 57:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2013.04.008
Liu NN, Feng XY, Huang QB, Fan W, Peng JB, Lu QZ, Liu WL (2019) Dynamic characteristics of a ground fissure site. Eng Geol 248:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.003
Liu ZH, Lu QZ, Qiao JW, Fan W (2021) In situ water immersion research on the formation mechanism of collapsible earth fissures. Eng Geol 280:105936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105936
Lu HJ, Li JX, Wang WW, Wang CH (2015) Cracking and water seepage of Xiashu loess used as landfill cover under wetting–drying cycles. Environmental Earth Sciences 74(11):7441–7450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4729-4
Lu QZ, Liu Y, Peng JB, Li L, Fan W, Liu N, Sun K, Liu RD (2020) Immersion test of loess in ground fissures in Shuanghuaishu, Shaanxi Province, China. Bull Eng Geol Env 79(5):2229–2312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01718-5
Hamdia K, Silani M, Zhuang XY, He PF, Rabczuk T (2017) Stochastic analysis of the fracture toughness of polymeric nanoparticle composites using polynomial chaos expansions, International Journal of Fracture 206,215-227, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-017-0210-6
Ni WK, Yuan KZ, Lu XF, Yuan ZH (2020) Comparison and quantitative analysis of microstructure parameters between original loess and remolded loess under different wetting-drying cycles. Sci Rep 10:5547. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62571-1
Pan ZX, Yang GS, Ye WJ, Tian JF, Liang B (2020) Study on mechanical properties and microscopic damage of undisturbed loess under dry and wet cycles. J Eng Geol 28(6):1186–1192
Peng JB, Qiao JW, Leng YQ, Wang FY, Xue SZ (2016) Distribution and mechanism of the ground fissures in Wei River Basin, the origin of the silk road. Environ Earth Science 75:718–730
Rabczuk T, Zi G, Bordas S, Nguyern-Xuan H (2010) A simple and robust three-dimensional cracking-particle method without enrichment. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(37–40):2437–2455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2010.03.031
Ren HL, Zhuang XY, Rabczuk T (2017) Dual-horizon peridynamics: a stable solution to varying horizons. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 318:762–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2016.12.031
Rojas E, Arzate J, Arroyo M (2002) A method to predict the group fissuring and faulting caused by regional groundwater decline. Eng Geol 65(4):245–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00135-1
Wang F, Li GY, Mu YH, Zhang P, Wu YH, Fan SZ (2016) Experimental study of deformation characteristics of compacted loess subjected to drying-wetting cycle. Rock Soil Mech 37(8):2306–2312
Wang F, Li GY, Ma W, Mu YH, Zhou ZW, Zhang J, Chen D, Zhao JS (2020a) Effect of Repeated Wetting-drying-freezing-thawing cycles on the mechanic properties and pore characteristics of compacted loess. Advances in Civil Engineering 2020:8839347. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8839347
Wang TX, Hao YZ, Wang Z, Cheng L, Li JL (2020b) Experimental study on dynamic strength properties of compacted loess under wetting-drying cycles. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39(6):1242–1251
Yan FR, Fan W, He TY (2012) Study on binary-medium model of fissured loess. applied mechanics and materials 256–259:240–244, DOI: https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.256-259.240
Ye WJ, Li CQ, Ma WC (2016) Mechanism fractured loess expansion joints under the effect of wet-dry cycle. Sci Tech Eng 16(30):122–127
Ye WJ, Bai Y, Cui CY, Duan Y (2020) Deterioration of the internal structure of loess under dry-wet cycles. Adv Civil Eng 2020:8881423. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8881423
Yuan ZH, Ni WK, Tang C, Hu SM (2017) Experimental study of structure strength and strength attenuation of loess under wetting-drying cycle. Rock Soil Mech 38(7):1894–1902
Zhang YY, Ye WJ (2018) Effect of dry-wet cycle on the formation of loess slope spalling hazards. Civil Eng J 4(4):785–795. https://doi.org/10.28991/cej-0309133
Zhou B, Wu YG, Chan JW, Wang SC, Qiao ZX, Hu SH (2019) Wetting–drying cycles enhance the release and transport of autochthonous colloidal particles in Chinese loess. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 25(1):335–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1571402
Zhu PS, Helm DC, Jiang L (2003) Mechanisms of earth fissuring caused by groundwater withdrawal. Environ Eng Geosci 9(4):351–362. https://doi.org/10.2113/9.4.351
Funding
The research described in this paper was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51878551 and 51778528), and the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (Program No.2019JLM-56). These supports are greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: JX; methodology: JX, SW; formal analysis and investigation: KH, LZ; writing-original draft preparation: KH; writing-review and editing: KH, LZ; data curation: YL, LZ, WY, KH; funding acquisition: JX; resources: JX, SW; supervision: JX, SW.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Hu, K., Zhou, L. et al. Influence of wet–dry cycles on uniaxial compression behavior of fissured loess. Environ Earth Sci 82, 5 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10684-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10684-3