Abstract
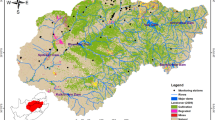
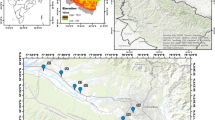
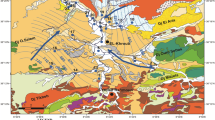
The chemical composition of groundwater from the Beberibe aquifer located in the Northeast of Brazil (NEB) was assessed using geostatistical, geoprocessing, and multivariate analysis techniques. The data collected came from 34 georeferenced mining and mineral water production units. From this, a Piper diagram was constructed and hydrogeological and hydrochemical spatial maps were generated. The data were submitted for analysis using descriptive statistics, kriging, and principal component analysis (PCA). The results showed that the artesian wells in porous sediments near the coast were of the mixed bicarbonate type and were generally suitable for human consumption. The coefficient of variation was medium too high for all hydrochemical variables. The variables showed a better fit to the Gaussian model, in the study of spatial dependence. In PCA, Cl was the one with the highest correlation with nitrate (NO3). The anthropogenic influence on water quality at the center of RMRE, mainly on NO3 concentrations, had a direct impact on water quality for human health.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
ABINAM (2020) Associação Brasileira Indústria Águas Minerais. <http://www.abinam.com.br/home.php>. Accessed 15 July 2020
APEVISA (2020) Agência Pernambucana de Vigilância Sanitária, Programa de Monitoramento e Fiscalização da Água Envasada (Pura). http://portal.saude.pe.gov.br/unidades-de-saude-e-servicos/secretaria-executiva-de-vigilancia-em-saude/apevisa. Accessed 11 Jan 2021
Anders R, Mendez GO, Futa K, Danskin WR (2014) A geochemical approach to determine sources and movement of saline groundwater in a coastal aquifer. Groundwater 52(5):756–768. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12108
Appleyard S, Cook T (2009) Reassessing the management of groundwater use from sandy aquifers: acidification and base cation depletion exacerbated by drought and groundwater withdrawal on the Gnangara Mound Western Australia. Hydrogeol J 17(3):579–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0410-2
Arshad S, Mobeen M, Bashir S, Aziz T, Rehman A (2019) Spatializing groundwater quality parameters and their impacts on land value in Khushab city, Punjab, Pakistan. Int J Econ Environ Geol 10(3):78–84. https://doi.org/10.46660/ijeeg.vol11.iss1.1919
Ayed B, Jmal I, Sahal S, Mokadem N, Saidi S, Boughariou E, Bouri S (2017) Hydrochemical characterization of groundwater using multivariate statistical analysis: the Maritime Djeffara shallow aquifer (Southeastern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 76(24):821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7168-6
Beck HE, Zimmermann NE, McVicar TR, Vergopolan N, Berg A, Wood EF (2018) Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci Data 5:180214. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.214
Bhuiyan MAH, Bodrud-Doza M, Islam AT, Rakib MA, Rahman MS, Ramanathan AL (2016) Assessment of groundwater quality of Lakshimpur district of Bangladesh using water quality indices, geostatistical methods, and multivariate analysis. Environ Earth Sci 75(12):1020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5823-y
Bodrud-Doza M, Bhuiyan MAH, Islam SDU, Rahman MS, Haque MM, Fatema KJ, Rahman MA (2019) Hydrogeochemical investigation of groundwater in Dhaka City of Bangladesh using GIS and multivariate statistical techniques. Groundw Sustain Dev 8:226–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.11.008
Bodrud-Doza M, Islam AT, Ahmed F, Das S, Saha N, Rahman MS (2016) Characterization of groundwater quality using water evaluation indices, multivariate statistics and geostatistics in central Bangladesh. Water Sci 30(1):19–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wsj.2016.05.001
Bulia IL, Enzweiler J (2018) The hydrogeochemistry of bottled mineral water in São Paulo state, Brazil. J Geochem Explor 188:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.01.007
Cambardella CA, Moorman TB, Novak JM, Parkin TB, Karlen DL, Turco RF, Konopka AE (1994) Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Sci Soc Amst J 58:1501–1511. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1994.03615995005800050033x
Cao F, Jaunat J, Vergnaud-Ayraud V, Devau N, Labasque T, Guillou A, Ollivier P (2020) Heterogeneous behaviour of unconfined Chalk aquifers infer from combination of groundwater residence time, hydrochemistry and hydrodynamic tools. J Hydrol 581:124433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124433
CETESB (2016) qualidade das águas subterrâneas no estado de são paulo. https://cetesb.sp.gov.br/aguas-subterraneas/wp-content/uploads/sites/13/2013/11/Cetesb_QualidadeAguasSubterraneas2015_Web_20-07.pdf. Accessed 29 July 2020.
CPRM (2007) Mapa de Domínios/Subdomínios Hidrogeológicos do Brasil 1:2.500.000. http://www.cprm.gov.br/publique/Hidrologia/Mapas-e-Publicacoes/Mapa-de-Dominios%7CSubdominios-Hidrogeologicos-do-Brasil-1%3A2.500.000-632.html. Accessed 1 July 2020.
CPRH (2020) recursos hídricos subterrâneos.http://www.cprh.pe.gov.br/downloads/25_Recursos_Hidricos_Subterraneos.pdf. Accessed 22 July 2020.
Deutsch CV, Journel AG (1998) GSLIB Geostatistical Software Library and User’s Guide, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York, p 369
Dias P, Bernardes AM (2016) Carbon emissions and embodied energy as tools for evaluating environmental aspects of tap water and bottled water in Brazil. Desalin Water Treat 57(28):13020–13029. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1055815
DNPM (2016) Estudo Diagnóstico das Águas Minerais e Potáveis de Mesa do Brasil. http://www.dnpm.gov.br/dnpm/documentos/estudo-diagnostico/estudo-diagnostico-das-aguas-minerias-e-potaveis-de-mesa-do-brasil.pdf/view. Accessed 15 July 2020.
England EJ, Sparks A, Robinson MD (1989) Geo—EAS (Geostatistical Environmental Assessment Software). Environ Softw 4(2):70–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0266-9838(89)90033-6
Gilabert-Alarcón C, Daesslé LW, Salgado-Méndez SO, Pérez-Flores MA, Knöller K, Kretzschmar TG, Stumpp C (2018) Effects of reclaimed water discharge in the Maneadero coastal aquifer, Baja California, Mexico. Appl Geochem 92:121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.03.006
Gois G, Delgado RC, de Oliveira Júnior JF (2015) Modelos teóricos transitivos aplicados na interpolação espacial do Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) para os episódios de El Niño forte no Estado do Tocantins Brasil. Irriga 20(2):371–387. https://doi.org/10.1589/irriga.2015v20n2p371
Golden Software (2010) Golden software. Surfer® 9 for windows. Golden, Colorado. Available online http://www.goldensoftware.com/products/surfer/surfer.shtml
Gu X, Xiao Y, Yin S, Pan X, Niu Y, Shao J, Hao Q (2017) Natural and anthropogenic factors affecting the shallow groundwater quality in a typical irrigation area with reclaimed water, North China Plain. Environ Monit Assess 189(10):514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6229-3
Guadayol M, Cortina M, Guadayol JM, Caixach J (2016) Determination of dimethyl selenide and dimethyl sulphide compounds causing off-flavours in bottled mineral waters. Water Res 92:149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.016
Hossain M, Patra PK (2020) Contamination zoning and health risk assessment of trace elements in groundwater through geostatistical modelling. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 189:110038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110038
Hu K, Awange JL, Forootan E, Goncalves RM, Fleming K (2017) Hydrogeological characterisation of groundwater over Brazil using remotely sensed and model products. Sci Total Environ 599:372–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.188
Huang L, Liu Y (2017) Health information and consumer learning in the bottled water market. Int J Ind Organ 55:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijindorg.2017.08.002
IBGE (2018) Levantamento hidrogeologico. http://geoftp.ibge.gov.br/informacoes_ambientais/geologia/levantamento_hidrogeologico_e_hidroquimico/vetores/regionais/?fbclid=IwAR2TbZ0MFLJEUHKjVWv6IbgPkqReC2vN7H6tMg3R_3AI01ndqVTgh3mr000. Accessed 5 July 2020.
IBGE (2020) Hidroquímica subterrânea. https://www.ibge.gov.br/geociencias/informacoes-ambientais/geologia/15824-hidrogeologia.html?=&t=downloads. Accessed 5 July 2020.
Iqbal J, Nazzal Y, Howari F, Xavier C, Yousef A (2018) Hydrochemical processes determining the groundwater quality for irrigation use in an arid environment: the case of Liwa Aquifer, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Groundw Sustain Dev 7:212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.06.004
Jang CS (2015) Geostatistical analysis for spatially characterizing hydrochemical features of springs in Taiwan. Environ Earth Sci 73(11):7517–7531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3924-z
Kaiser HF (1958) The varimax criterion for analytic rotation in factor analysis. Psychometrika 23(3):187–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02289233
Kunrath CCN, Patrocínio DC, Rodrigues MAS, Benvenuti T, Amado FDR (2020) Electrodialysis reversal as an alternative treatment for producing drinking water from brackish river water: a case study in the dry season, northeastern Brazil. J Environ Chem Eng 8(2):103719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.103719
Liu J, Gao Z, Wang M, Li Y, Ma Y, Shi M, Zhang H (2018) Study on the dynamic characteristics of groundwater in the valley plain of Lhasa City. Environ Earth Sci 77(18):646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7833-4
Ministério da Saúde (1999) PORTARIA Nº 26, DE 15 DE JANEIRO DE 1999. http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/anvisa/1999/prt0026_15_01_1999.html. Accessed 29 July 2020.
Ministério da Saúde (2006) VIGILÂNCIA E CONTROLE DA QUALIDADE DA ÁGUA PARA CONSUMO HUMANO. <https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/vigilancia_controle_qualidade_agua.pdf>. Accessed 29 July 2020.
Montenegro SMGL, Cabral JJDSP, Paiva AD, Montenegro ADA, Demetrio JGA, Cavalcanti GL (2009) Águas subterrâneas na zona costeira da planície do Recife (PE): evolução da salinização e perspectivas de gerenciamento. Revista Brasileira De Recursos Hídricos 14(3):81–93. https://doi.org/10.21168/rbrh.v14n3.p81-93
Nunes LGDP, Oliveira MDV, de Souza AA, Lopes LDF, Dias PCES, Nogueira GB, Souza MAAD (2018) Water quality comparison between a supply network and household reservoirs in one of the oldest cities in Brazil. Int J Environ Health Res 29(2):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2018.1531114
Pacheco MH, Esmerino EA, Capobiango CS, Cruz AG, Leddomado LS, Pimentel TC, de Freitas MQ (2018) Bottled mineral water: classic and temporal descriptive sensory analysis associated with liking. Br Food J 120(7):1547–1560. https://doi.org/10.1108/BFJ-11-2017-0655
Pazand K, Khosravi D, Ghaderi MR, Rezvanianzadeh MR (2018) Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of groundwater in a semi-arid region using major ion chemistry: a case study of Ardestan basin in Central Iran. Groundw Sustain Dev 6:245–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.01.008
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. EOS Trans Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928. https://doi.org/10.1029/TR025i006p00914
R Core Team (2019) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Sargazi S, Mokhtari M, Ehrampoush MH, Almodaresi SA, Sargazi H, Sarhadi M (2020) The application of geographical information system (GIS) approach for assessment of groundwater quality of Zahedan city, Sistan and Baluchestan Province Iran. Groundw Sustain Dev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100509
Schwanz TG, Llorca M, Farré M, Barceló D (2016) Perfluoroalkyl substances assessment in drinking waters from Brazil, France and Spain. Sci Total Environ 539:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.034
Shruti VC, Pérez-Guevara F, Kutralam-Muniasamy G (2020) Metro station free drinking water fountain-A potential “microplastics hotspot” for human consumption. Environ Pollut 261:114227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114227
Silva TA, Rosário FF, Silva Júnior GC (2020) Environmental isotopes and hydrochemical tracers applied to hydrogeological conceptual modeling of the southwest portion of the Amazon Aquifer System (Acre, Brazil). Appl Geochem 120:104670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104670
Teramoto EH, Gonçalves RD, Chang HK (2020) Hydrochemistry of the Guarani aquifer system modulated by mixing with underlying and overlying hydrostratigraphic units. J Hydrol: Reg Stud 30:100713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2020.100713
Tiwari K, Goyal R, Sarkar A (2017) GIS-based spatial distribution of groundwater quality and regional suitability evaluation for drinking water. Environ Process 4(3):645–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-017-0257-4
Tlili-Zrelli B, Gueddari M, Bouhlila R, Mohamed Naceur O (2015) Groundwater hydrogeochemistry of Mateur alluvial aquifer (Northern Tunisia). J Hydrogeol Hydrol Eng. https://doi.org/10.4172/2325-9647.1000128
Tundisi JG (2008) Water resources in the future: problems and solutions. Estudos Avançados 22(63):7–16. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-40142008000200002
Vauclin M, Vieira SR, Vachaud G, Nielsen DR (1983) The use of cokriging with limited field soil observations 1. Soil Sci Soc Am J 47(2):175–184. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1983.03615995004700020001x
Warrick AW, Nielsen DR (1980) Spatial variability of soil physical properties in the field. In: Hillel D (ed) 2. Applications of Soil Physics, New York: Academic, pp 319–344
Yang Q, Li Z, Ma H, Wang L, Martín JD (2016) Identification of the hydrogeochemical processes and assessment of groundwater quality using classic integrated geochemical methods in the Southeastern part of Ordos basin, China. Environ Pollut 218:879–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.08.017
Yang Q, Li Z, Xie C, Liang J, Ma H (2020) Risk assessment of groundwater hydrochemistry for irrigation suitability in Ordos Basin, China. Nat Hazards 101:309–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3451-4
Yin S, Xiao Y, Gu X, Hao Q, Liu H, Hao Z, Pei Q (2019) Geostatistical analysis of hydrochemical variations and nitrate pollution causes of groundwater in an alluvial fan plain. Acta Geophys 67(4):1191–1203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-019-00302-5
Funding
To the Programa de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia Agrícola (PGEA), Programa de Pós-graduação em Química (PPGQ), and the Grupo de Pesquisa em Ambiência (GPESA) of the Federal Rural University of Pernambuco (UFRPE) for supporting the development of this research. The Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES-Finance Code 001) and the Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco (FACEPE), for the financing of scholarships. The third and fourth authors are grateful for the Research Productivity grant from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) level 2 under process number 304060/2016-0 and 309681/2019-7, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva, M.V., Moraes, A.S., Pandorfi, H. et al. A geostatistical assessment of the natural and anthropogenic factors that influence groundwater quality in the Beberibe aquifer in northeastern Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 81, 450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10577-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10577-5