Abstract
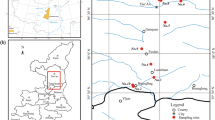
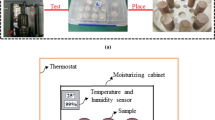
In this study, the influence of pH on the moisture-absorbing swelling cracks of red mudstone in southwest China was studied and its microscopic mechanism was revealed. A self-designed water absorption device combined with digital speckle correlation (DSCM), scanning electron microscope, XRD diffraction experiment, mercury injection experiment and other means were used. The results indicated that compared with an alkaline environment, an acidic environment resulted in the self-absorption and cracking of mudstone. The maximum water absorption rate of mudstone and crack rate in a pH of 3 were determined as 15.77 and 18.91%, respectively; whereas for pH = 11, they were 11.71 and 7.11%, respectively. In the acidic environment, the maximum combined displacement value and maximum principal strain value of mudstone self-priming and swelling evolution were both greater than in an alkaline environment. Simultaneously, in the former, the moisture absorption failure characteristics of mudstone exhibited increased swelling strain zones and swelling cores. The three possible mechanisms by which pH affects the expansion of mudstone hygroscopic cracks were proposed: hydration-expansion softening, adsorption-wedge failure, and humidity stress field. However, it was found that the solutions with different pH values may affect these three microscopic mechanisms through the following four physical or chemical processes: mineral dissolution, ion absorption and exchange, particle association, and pore change. The results of this study are expected to be of significance and aid in roadbed design, tunnel support, slope treatment, and other projects in the southwest region.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The experimental data used in our research may be available from the corresponding author by request.
References
Antamarina JC, Klein KA, Palomino A, Guimaraes, MS (2002) Micro-scale aspects of chemical-mechanical coupling. Interparticle forces and fabric. In: Maio, C.D.
Chen ZH (2014) On basic theories of unsaturated soils and special soils. Chin J Geotech Eng 36(2):201–272
Chen WW, Yuan PB, Liu XW (2009) Study on creep properties of red-bed soft rock under step load. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 28(S1):3076–3081
Chenevert ME (1970) Shale alteration by water adsorption. J Petrol Technol 22(9):1141–1148. https://doi.org/10.2118/2401-PA
Critelli T, Marini L, Schott J, Mavromatis V, Apollaro C, Rinder T, De Rosa R, Oelkers EH (2014) Dissolution rates of actinolite and chlorite from a whole-rock experimental study of metabasalt dissolution from 2 ≤ pH ≤ 12 at 25 degrees C. Chem Geol 390:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.10.013
Cuadros J, Diaz-Hernandez JL, Sanchez-Navas A, Garcia-Casco A (2015) Role of clay minerals in the formation of atmospheric aggregates of Saharan dust. Atmos Environ 120:160–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.08.077
Dai ZJ, Guo JH, Zhou Z, Chen SX, Yu F, Li J (2020) Inversion and prediction of long-term uplift deformation of high-speed railway subgrade in central Sichuan red-bed. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39(S2):3538–3548. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.1149
Dai ZJ, Guo JH, Yu F, Zhou Z, Li J, Chen SX (2021) Long-term uplift of high-speed railway subgrade caused by swelling effect of red-bed mudstone: case study in Southwest China. Bull Eng Geol Env 80:4855–4869. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02220-7
Fairhurst CE, Hudson JA (1999) International society for rock mechanics commission on testing methods. Int J Rock Mech Min 36:279–289
Fan YQ, Liang X, Han JS (2020) Experimental study on saturation and swelling-shrinkage characteristics of unsaturated expansive rocks. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 39(01):45–56. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0579
Feng X, Ding W, Cui Q (2010) Coupled chemical-stress effect on rock fracturing process. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Fereidooni D, Khajevand R (2018) Determining the geotechnical characteristics of some sedimentary rocks from Iran with an emphasis on the correlations between physical, index, and mechanical properties. Geotech Test J 41(3):555–573. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20170058
Fredlund DG, Hendry R (1993) Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils[M] [S. l.]. John Wiley and Sons, pp 64–66
Fukue M, Minato T, Horibe H, Taya N (1999) The micro-structures of clay given by resistivity measurements. Eng Geol 54(1–2):43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(99)00060-5
Gautam TP, Shakoor A (2013) Slaking behavior of clay-bearing rocks during a one-year exposure to natural climatic conditions. Eng Geol 166:17–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.08.003
Ghobadi MH, Momeni AA (2011) Assessment of granitic rocks degradability susceptive to acid solutions in urban area. Environ Earth Sci 64(3):753–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0895-6
Guo YC, Xie Q, Wen JQ (2007) Red beds distribution and engineering geological problem in China. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 6:67–71
Gupta V, Ahmed I (2007) The effect of pH of water and mineralogical properties on the slake durability (degradability) of different rocks from the Lesser Himalaya, India. Eng Geol 95(3–4):79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.09.004
He MC, Zhou L, Li DJ, Wang CG, Lie W (2008) Experimental research on hydrophilic characteristics of mudstone in deep well. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 27(6):1113–1120 (in Chinese)
Huang SB, Cheng Q, Hu HT (2005) A study on distribution of Sichuan red beds and engineering environment characteristics. Highway 5:81–85 (in Chinese)
Ji M (2009) Study on mechanical properties evolution and creep characteristics of calay-mudstone under humidity field. China University of Mining and Technology
Konrad JM, Ayad R (1997) Desiccation of a sensitive clay: field experimental observations. Can Geotech J 34(6):929–942. https://doi.org/10.1139/t97-063
Kozaki T, Fujishima A, Saito N, Sato S, Ohashi H (2005) Effects of dry density and exchangeable cations on the diffusion process of sodium ions in compacted montmorillonite. Eng Geol 81(3):246–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.06.010
Li XN (2016) Macro and meso damage characteristics of silty mudstone under acidic environment. Southwest Jiaotong University
Li L, Tang DZ, Xu H, Meng YJ, Fang N, Tang SL (2015) Pore and fissure structure characteristics of medium rank coal under the control of coal petrology: taking Liulin mining area as the example. China Sci Paper 10(9):1058–1065
Li CD, Fu ZY, Wang Y, Tang HM, Yan JF, Gong WP, Yao WM, Criss RE (2019) Susceptibility of reservoir-induced landslides and strategies for increasing the slope stability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area: Zigui Basin as an example. Eng Geol 261:105279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105279
Li CD, Criss RE, Fu ZY, Long JJ, Tan QW (2021) Evolution characteristics and displacement forecasting model of landslides with stair-step sliding surface along the Xiangxi River, three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Eng Geol 283:105961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105961
Li XJ, Zhang QJ, Liu P, Li T, Liu GF, Liu ZK, Zhao HF (2022) Investigation on the microscopic damage mechanism of fracturing fluids to low-permeability sandstone oil reservoir by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Pet Sci Eng 209:109821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109821
Liu XM, Song YF, Xia Z, Chen RP (2020) Assessing the slake durability of red stratum sandstone in different solution environments by a novel dual rotation test. Eng Geol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105503
Liu JD, Tang CS, Zeng H, Shi B (2021) Evolution of desiccation cracking behavior of clays under drying-wetting cycles. Rock Soil Mech 42(10):2763–2772. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2021.0459
Lu ZH, Chen ZH, Pu YB (2002) A CT study on the crake evolution of expansive soil during drying and wetting cycles. Rock Soil Mech 23(4):417–422 (in Chinese)
Ma LN (2016) Research on low clay mineral mudstone expansion mechanism and influence for high-speed railway subgrade. Lanzhou Jiaotong University
Ma J, Chen SX, Yu F, Feng MG (2007) Experimental research on crack evolution process in fissured clay. Rock Soil Mech 28(10):2203–2208. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2007.10.021
Mao X, Xin SJ, Cheng MS, Chen ZH, Wang XQ (2018) Mechanical behavior of expansive soil under initial damage and wetting-drying cycles. Rock Soil Mech 39(2):571–579. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2017.1136
Mawlood YI, Hummadi RA (2019) Reversible and irreversible deformations of expansive clays. Proc Inst Civ Eng 172(5):442–452. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeen.18.00236
Mi H (2013) Rock mechanical behaviors testing by digital speckle correlation method. J Appl Opt 34(1):123–127. https://doi.org/10.5768/JAO201334.0103006
Miller SE, Low PF (1990) Characterization of the electrical double-layer of montmorillonite. Langmuir 6(3):572–578. https://doi.org/10.1021/la00093a010
Miu XX (1995) Coupling equations of humidity stress field theory. Mech Eng 6:22–24
Miu XX, Yang CY, Chen ZD (1993) Theory of humidity stress field in expansive rock mass. Rock Soil Mech 14(4):49–55. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.1993.04.009
Moon VG (1993) Geotechnical characteristics of ignimbrite—a soft pyroclastic-rock type. Eng Geol 35(1–2):33–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(93)90068-N
Olphen V (1977) Clay colloid chemistry, 2nd edn. Krieger Publishing Company, Malabar, p 318
Salimi M, Asghari-Kaljahi E, Hajialilue-Bonab M (2018) Expansive soils characterizations and their destructive effects on Tabriz northern highway Iran. In: Zhou A, Tao J, Gu X, Hu L (eds) Proceedings of GeoShanghai 2018 international conference: fundamentals of soil behaviours GSIC 2018. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-0125-4_85
Shen PW, Tang HM, Wang DJ, Su XX, Huang L (2020) Weakening of mudstone fragments due to disintegration: an experimental investigation. Bull Eng Geol Env 79(10):5477–5497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01874-z
Song YM, Ma SP, Yang XB, Wang X (2011) Experimental investigation on failure of rock by digital speckle correlation method. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 30(01):170–175
Spagnoli G, Rubinos D, Stanjek H, Fernandez-Steeger T, Feinendegen M, Azzam R (2012) Undrained shear strength of clays as modified by pH variations. Bull Eng Geol Env 71(1):135–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-011-0372-9
Su XX, Tang HM, Huang L, Shen PW, Xia D (2020) The role of pH in red-stratum mudstone disintegration in the Three Gorges reservoir area, China, and the associated micromechanisms. Eng Geol 279:5873–5873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105873
Sun Q, Cai C, Zhang SK, Tian S, Li B, Xia YJ, Sun QW (2019) Study of localized deformation in geopolymer cemented coal gangue-fly ash backfill based on the digital speckle correlation method. Constr Build Mater 215:321–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.04.208
Tandon RS, Gupta V, Venkateshwarlu B (2021) Geological, geotechnical, and GPR investigations along the Mansa Devi hill-bypass (MDHB) Road, Uttarakhand, India. Landslides 18:849–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01546-9
Tang CS, Cui YJ, Tang AM, Shi B (2012a) Shrinkage and desiccation cracking process of expansive soil and its temperature-dependent behaviour. Chin J Geo-Tech Eng 4(12):2181–2187 (in Chinese)
Tang CS, Shi B, Cui YJ, Liu C, Gu K (2012b) Desiccation cracking behavior of polypropylene fiber-reinforced clayey soil. Can Geotech J 49(9):1088–1101. https://doi.org/10.1139/T2012-067
Tang CS, Shi B, Cui YJ (2018) Behaviors and mechanisms of desiccation cracking of soils. Chin J Geotech Eng 40(8):1415–1423. https://doi.org/10.11779/CJGE201808006
Terzaghi K, Peck RB (1967) Soil mechanics in engineering practice, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
Townsend RP (1984) Thermodynamics of ion exchang in clays. Philos Trans R Soc 311:301–314. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.1984.0030
Vanolphen H (1951) Rheological phenomena of clay sols in connection with the charge distribution on the micelles. Discuss Faraday Soc 11:82–84. https://doi.org/10.1039/DF9511100082
Wang J, Gong BW, Zhang JJ, Zhou XW, Tan FY (2010) Field observation and description method of cracks development on expansive rock. J Yangtze River Sci Res Inst 27(9):74–75
Wang L, Liu HQ, Xie GX, Yuan QP, Chen LP (2021) Detailed characterization of the pore and fracture structure and strength degradation mechanism of gas-containing coal. Rock Soil Mech 42(12):1–15. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2021.1039
Wei BX, Liu B, Liu X (2015) Research on the quantitative basic index of expansive soil cracks. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 42(5):84–89. https://doi.org/10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2015.05.14
Wen T, Tang HM, Huang L, Wang YK, Ma JW (2020) Energy evolution: a new perspective on the failure mechanism of purplish-red mudstones from the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Eng Geol 264:105350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105350
Wu JH, Yuan JP, Ng CWW (2012) Theoretical and experimental study of initial cracking mechanism of an expansive soil due to moisture-change. J Central South Univ 19(5):1437–1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-012-1160-9
Xin J, Liu L, Xu LH, Wang JY, Yang P, Qu HS (2022) A preliminary study of aeolian sand-cement-modified gasification slag-paste backfill: fluidity, microstructure, and leaching risks. Sci Total Environ 830:154766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154766
Xu XL (2018) Study on mechanical properties evolution and microscopic mechanism of granites under temperature loading. China University of Mining and Technology
Yagiz S (2010) Geomechanical properties of construction stones quarried in South-western Turkey. Sci Res Essays 5(8):750–757. https://doi.org/10.5897/SRE.9000526
Yang ZC, Zhang JY, Zhou DP (2006) Study on rapid weathering characteristics of red mudstone slope. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 25(2):275–283
Yao HL, Zheng SH, Ge XR, Yi SX (2002) Assessment on slope stability in cracking expansive soils. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 21(S2):2331–2335
Yi SM, Li ZH, Zhang YZ (1999) The fractal characteristics of fractures in expansion soil and its significance. Chin J Geotech Eng 3:294–298 (in Chinese)
Yin ZZ, Yuan JP, Wei J, Cao XS, Liu HQ, Xu B (2012) Influences offissures on slope stability of expansive soil. Chin J Geotech Eng 34(12):2155–2161
Yong RN, Sethi AJ, Booy E, Dascal O (1979) Basic characterization and effect of some chemicals on a clay from outardes 2. Eng Geol 14(2–3):83–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(79)90079-6
Yuan W, Liu XR, Fu Y (2019a) Chemical thermodynamics and chemical kinetics analysis of sandstone dissolution under the action of dry-wet cycles in acid and alkaline environments. Bull Eng Geol Env 78(2):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1162-9
Yuan W, Liu XR, Fu Y (2019b) Chemical thermodynamics and chemical kinetics analysis of sandstone dissolution under the action of dry-wet cycles in acid and alkaline environments. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78(2):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1162-9
Zeng L, Yao XF, Zhang JH, Gao QF, Chen JC, Gui YT (2020) Ponded infiltration and spatial–temporal prediction of the water content of silty mudstone. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:5371–5383. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01880-1
Zhang Y, Hu ZQ, Li L, Xue ZJ (2018a) Improving the structure and mechanical properties of loess by acid solutions—an experimental study. Eng Geol 244:132–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.023
Zhang ZH, Liu W, Cui Q, Han L, Yao HY (2018b) Disintegration characteristics of moderately weathered mudstone in drawdown area of Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Arab J Geosci 11:405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3751-8
Zhang SH, Zhang DS, Zhao Q, Chi MB, Zhang W, Yu W (2019) DEM investigation of the influence of minerals on crack patterns and mechanical properties of red mudstone. Processes 7(3):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7030162
Zhang YA, Liu CJ, Deng HW, Lin Y, Li JL, Gao F (2022) Peridynamic simulation of heterogeneous rock based on digital image processing and low-field nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Int J Geomech 22(6):04022083. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0002406
Zhao JX, Lu CH, Deng LM, Liu GC (2018) Impacts of simulated acid solution on the disintegration and cation release of purple rock (mudstone) in Southwest China. Geomorphology 316:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.05.009
Zhong ZB, Li AH, Deng RG, Wu PP, Xu J (2019) Experimental study on the time-dependent swelling characteristics of red-bed mudstone in Central Sichuan. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 38(1):76–86. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2018.0861
Zhou CY, Tan XS, Deng YM, Zhang LM, Wang JH (2005) Research on softening micro-mechanism of special soft rocks. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 24(3):394–400
Zhou QJ, Ma DC, Deng RG, Kang JW, Zhu QB (2020) Experimental study on mechanical properties of red-layer soft rock in geothermal systems. Rock Soil Mech 41(10):3333–3342. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2020.0035
Zhou Z, Chen SX, Wang YH, Dai ZJ (2021) Crack evolution characteristics and cracking mechanism of red beds in central sichuan during seepage and swelling. Geofluids 2021:81046–81046. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/9981046
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42172308) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2022331). The authors also want to frankly acknowledge Yang WZ for their technical help during the digital image correlation data processing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, K., Yu, F., Zhou, Z. et al. Influence of pH on moisture-absorbing swelling cracks of red layer in central Sichuan and its micro-mechanism. Environ Earth Sci 81, 441 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10570-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10570-y