Abstract
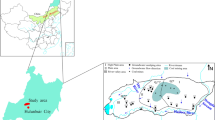
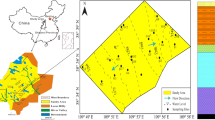
In mining areas, groundwater resources are crucial for providing drinking water, as well as water needed for plant growth and mining. The Yuhengbei mining area is situated in arid and semi-arid areas in Western China. As there are a number of large-scale mining fields in the area, their exploitation may affect both the quality and quantity of groundwater. The hydraulic connection between aquifers directly determines whether deep coal mining activities affect water quality in shallow aquifers. This study investigates the hydrogeochemical characteristics and the solute sources of groundwater (including surface water, Quaternary water, water from Cretaceous and Jurassic coal strata aquifer) in the Yuhengbei mining area. The study uses conventional, multivariate statistical analysis, and dissolved organic matter (DOM) analysis. The results suggest that all water samples were slightly alkaline, while the water from the shallow aquifers (surface water, Quaternary and Cretaceous aquifers) was predominantly of the HCO3-Ca type. Furthermore, the groundwater in the deep Jurassic aquifer was mostly of the SO4-Na type. Major ion and DOM concentrations appeared to decrease with increasing aquifer depth. Moreover, the groundwater circulation is regulated by natural processes. Namely, rock weathering was the main mechanism controlling the chemical constituents of groundwater in the shallow aquifers, while groundwater quality in deep aquifers was mainly governed by the dissolution of evaporation. Water–rock interaction and cation exchange were the main mechanisms controlling the chemical constituents of groundwater. The R-mode HCA revealed that natural processes controlled the chemical composition of groundwater, as well as that the evolution of groundwater is primarily controlled by the nature of the geological structures and the local hydrogeological conditions. The TOC and UV254 results suggest that the coal strata aquifer had a weak hydraulic connection with the overlying aquifers. The DOM was mainly derived from autogenous biological sources. Based on the indicator values, the hydraulic connection between the deep aquifers and the upper shallow aquifers was weak overall. These results show that in this area, although drinking water and irrigation water come predominantly from shallow groundwater, mining activities temporarily have little impact on the quality of shallow groundwater. Better understanding hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms will provide a technical basis for local groundwater management and support the sustainable use of water resources.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen L, Feng Q (2013) Geostatistical analysis of temporal and spatial variations in groundwater levels and quality in the Minqin oasis, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 70(3):1367–1378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2220-7
Chen J, Leboeuf EJ, Dai S, Gu B (2003a) Fluorescence spectroscopic studies of natural organic matter fractions. Chemosphere 50(5):639–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00616-1
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer JA, Booksh K (2003b) Fluorescence excitation−emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 37(24):5701–5710. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034354c
Delgado-Outeiriño I, Araujo-Nespereira P, Cid-Fernández JA, Mejuto JC, Martínez-Carballo E, Simal-Gándara J (2009) Behaviour of thermal waters through granite rocks based on residence time and inorganic pattern. J Hydrol 373(3–4):329–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.04.028
Fulazzaky MA, Seong T, Masirin M (2010) Assessment of water quality status for the Selangor River in Malaysia. Water Air Soil Pollut 205:63–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0056-2
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:795–840. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Hambly ACE, Arvin LF, Pedersen PB, Seredyńska-Sobecka PB, Stedmon CA (2015) Charactering organic matter in recirculating aquaculture systems with fluorescence EEM spectroscopy. Water Resour 83:112–120
Huang XJ, Wang GC, Liang XY et al (2017) Hydrochemical and stableisotope (δD and δ18O) characteristics of Groundwater and hydrogeochemical processes in the Ningtiaota coalfield, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(1):119–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0477-x
Hutchins MG, Smith B, Rawlins BG, Lister TR (1999) Temporal and spatial variability of stream waters in wales, the welsh borders and part of the west midlands, UK.1. major ion concentrations. Water Res 33(16):3479–3491. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00057-3
Jaffe R, Boyer JN, Lu X, Maie N, Yang C, Scully NM, Mock S (2004) Source characterization of dissolved organic matter in a subtropical mangrove-dominated estuary by fluorescence analysis. Mar Chem 84(3/4):195–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2003.08.001
Jain CK, Sharma SK, Singh S (2018) Physico-chemical characteristics and hydrogeological mechanisms in groundwater with special reference to arsenic contamination in Barpeta District, Assam (India). Environ Monit Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6781-5
Javadinejad S, Ostad-Ali-Askari K, Jafari F (2019) Using simulation model to determine the regulation and to optimize the quantity of chlorine injection in water distribution networks. Model Earth Syst Environ 5(3):1015–1023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-019-00587-x1
Javadinejad S, Eslamian S, Askari K (2021) The analysis of the most important climatic parameters affecting performance of crop variability in a changing climate. Int J Hydrol Sci Technol 11(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJHST.2021.112651
Kurunc A, Uz BY, Aslan GE et al (2016) Seasonal changes of spatial variation of some groundwater quality variables in a large irrigated coastal Mediterranean region of Turkey. Sci Total Environ 554–555:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.158
Li P (2018) Mine water problems and solutions in China. Mine Water Environ 3–4:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-0543-z
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2012) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li P, Qian H, Zhou W (2017) Finding harmony between the environment and humanity: an introduction to the thematic issue of the Silk Road. Environ Earth Sciences 76(3):105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6428-9
Liu J, Wang H, Jin D et al (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of karst groundwater in Carboniferous Taiyuan formation in the Pingdingshan coalfield. Environ Earth Sci 79(6):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8898-4
Mahato MK, Singh PK, Singh AK, Tiwari AK (2018) Assessment of hydrogeochemical processes and mine water suitability for domestic, irrigation, and industrial purposes in east bokaro coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ 37(3):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0508-7
Nieto-Cid M, Álvarez-Salgado XA, PÉrez FF (2006) Microbial and photochemical reactivity of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in a coastal upwelling system. Limnol Oceanogr 51(3):1391–1400. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2006.51.3.1391
Ostad-Ali-Askari K et al (2017) Artificial neural network for modeling nitrate pollution of groundwater in marginal area of Zayandeh-Rood River, Isfahan, Iran. KSCE J Civil Eng Korean Soc Civil Eng 21(1):134–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-016-0572-8
Patel P, Raju NJ, Reddy BCSR et al (2016) Geochemical processes and multivariate statistical analysis for the assessment of groundwater quality in the Swarnamukhi River basin, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 75(7):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5108-x
Piper AM (1944) A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Am Geophys Union Trans 25:914–928
Qian J, Wang L, Ma L, Lu YH, Zhao W, Zhang Y (2016) Multivariate statistical analysis of water chemistry in evaluating groundwater geochemical evolution and aquifer connectivity near a large coal mine, Anhui, China. Environ Earth Sci 75:747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5541-5
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Research, Series-33. UNESCO, Delft, pp 54–83
Singh AK, Mahato MK, Neogi B, Singh KK (2010) Quality assessment of mine water in the Raniganj coalfield area, India. Mine Water Environ 29(4):248–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-010-0108-2
Singh AK, Mahato MK, Neogi B, Tewary BK, Sinha A (2012) Environmental geochemistry and quality assessment of mine water of Jharia coalfield, India. Environ Earth Sci 65(1):49–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1064-2
Subba Rao N, Marghade D, Dinakar A, Chandana I, Sunitha B, Ravindra B, Balaji T (2017) Geochemical characteristics and controlling factors of chemical composition of groundwater in a part of Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Environ Earth Sci 76(21):747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7093-8
Tiwari AK, Singh PK, Mahato MK (2016) Environmental geochemistry and a quality assessment of mine water of the West Bokaro coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ 35(4):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-015-0382-0
Wang XY, Wang TT, Wang Q, Li RZ (2016) Evaluation of floor water inrush based on fractal theory and an improved analytic hierarchy process. Mine Water Environ 36:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-016-0407-3
Utom AU, Odoh BI, Egboka BCE (2013) Assessment of hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater quality in the vicinity of Okpara coal and Obwetti fireclay mines, near Enugu town, Nigeria. Appl Water Sci 3(1):271–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0080-7
Wang Y, Li J, Ma T, Xie X, Deng Y, Gan Y (2020) Genesis of geogenic contaminated groundwater: as, F and I. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1807452
WHO (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. World Health Organization, Geneva, p p631
Wu J, Li P, Hui Q et al (2014) Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: a case study in Laoheba phosphorene mine in Sichuan, China. Arab J Geosci 7(10):3973–3982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1057-4
Yang J, Jin DW (2015) Variation characteristics of dissolved organic matter in underground mine water with combined water treatment process at surface and underground mine. J Chin Coal Soc 40(2):439–444. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2014.0191
Yang Y, Shen Z, Zhao Z, Wen D, Hou G, Zhao Z, Wang D (2008) Hydrochemical characteristics and sources of sulfate in groundwater of the ordos cretaceous groundwater basin. Acta Geoscientica Sinica 29(5):553–562. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.05.003
Zhang YD (2009) Harmony of large-scale underground mining and surface ecological environment protection in desert district-a case study in Shendong mining area, northwest of China. Procedia Earth Planet Sci 1(1):1114–1120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2009.09.171
Zhang Y, Zhang E, Yin Y, van Dijk MA, Feng L, Shi Z, Qina B (2010) Characteristics and sources of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in lakes of the Yungui Plateau, China, differing in trophic state and altitude. Limnol Oceanogr 55(6):2645–2659. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.6.2645
Zsolnay A, Baigar E, Jimenez M, Steinweg B, Saccomandi F (1999) Differentiating with fluorescence spectroscopy the sources of dissolved organic matter in soils subjected to drying. Chemosphere 38(1):45–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(98)00166-0
Acknowledgements
The study was jointly supported by the following projects: The Technological Innovation Program of the Tiandi Science and Technology Company (2018-TD-MS072, 2019-TD-ZD003, 2020-TD-ZD002) and the National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFC0804103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to infuence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, L., Jianyuan, C., Ji, L. et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and solute sources of groundwater in the Yuhengbei mining area, Shaanxi Province, China. Environ Earth Sci 81, 516 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10551-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10551-1