Abstract
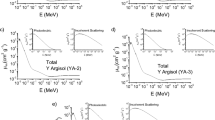
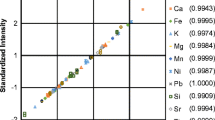
The objective of this paper was to study the radiation interaction parameters and the degree of weathering of horizons of a Cambisol located in a conservation unit using the percentages of oxides. The oxide contents of the horizons were obtained by employing ED (energy dispersive) and WD (wavelength dispersive) X-ray fluorescence (XRF) techniques, considering that their interpretation of the weathering indices differs according to their resolution. The radiation interaction parameters were calculated using the XCOM computational code, which allowed us to obtain the following parameters: µ/ρ (mass attenuation coefficient), σA and σE (atomic and electronic cross section), Zeff (effective atomic number) and Nel (electronic density). The results indicated that although both techniques proved to be efficient in detecting the levels of oxides, WDXRF was more sensitive. Fe2O3 showed great influence on the parameters µ/ρ, σA and σE, while Zeff and Nel presented no correlations. However, the curves of Zeff and Nel, in the studied energy range (1–100 keV), showed a better distinction between them when compared to the other parameters. The studied Cambisol presented a preserved structure, since it belongs to a conservation unit. Therefore, our findings should be considered a reference result for soils in the region with the same classification and origin, but which were subjected to anthropic action.

Source: Renata Santos Momoli, 2020






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Available upon request.
Code availability
Available upon request.
References
Appoloni CR, Rios EA (1994) Mass attenuation coefficients of Brazilian soils in the range 10–1450 keV. Appl Radiat Isot 45:287–291
Camargo MA, Kodum KS, Pires LF (2021) How does the soil chemical composition affect the mass attenuation coefficient? A study using computer simulation to understand the radiation-soil interaction processes. Braz J Phys 51:1775–1783
Conner AL, Atwater HF, Plassmann EH, Mccrary JH (1970) Gamma-ray attenuation coefficient measurements. Phys Rev A 1:539–544
Crestana S, Cesareo R, Mascarenhas S (1986) Using a computed tomography miniscanner in soil science. Soil Sci 142:56–61
Demir D, Turṣucu A (2013) Measurement of the effective atomic number of FexCr1-x and FexNix alloys using scattering of gamma rays. J Alloy Comp 581:213–216
EMBRAPA (1997) Manual de Métodos de Análise de Solo. 2ª edição, Centro Nacional de Pesquisa de Solos.
Ferreira TR, Pires LF, Brinatti AM, Auler AC (2018) Surface liming effects on soil radiation attenuation properties. J Soils Sediment 18:1641–1653
Hillel D (1998) Introduction to environmental soil physics. Elsevier Science, USA
Hubbell JH, Seltzer SM (1995) Tables of X-ray mass attenuation coefficients and mass energy-absorption coefficients 1 keV to 20 MeV for elements Z=1 to 92 and 48 additional substances of dosimetric interest. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg
Kaplan I (1997) Nuclear physics. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Boston
Ker J C, Curi N, Schaefer C E G, Torrado-Vidal J (2012) Pedologia fundamentos. Sociedade Brasileira de Ciência do solo.
Knoll GF (2010) Radiation and detection measurements. John Wiley & Sons Inc, Hoboken
Kucuk N, Tumsavas Z, Carkir M (2013) Determining photon energy absorption parameters for different soils samples. J Radiat Res 54:578–586
Lepsch IF (2010) Formação e Conservação dos Solos. Oficina de Textos, São Paulo
Marques FA, Ribeiro MR, Bittar SMB, Neto LAL, Lima JFWF (2007) Caracterização e classificação de Cambissolos do arquipélago de Fernando de Noronha, Pernambuco. R Bras Ci Solo 31:1023–1034
Medhat ME (2011) Studies on effective atomic numbers and electron densities in different solid state track detectors in the energy range 1 keV-100 GeV. Ann Nucl Energy 38:1252–1263
Medhat ME (2012) Study of the mass attenuation coefficients and effective atomic numbers in some gemstones. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 293:555–564
Medhat ME (2015) Comprehensive study of photon attenuation through different construction matters by Monte Carlo Simulation. Radiat Phys and Chem 107:65–74
Medhat ME, Pires LF (2016) Importance of atomic cross section for studying physical properties of different types of soils. X-Ray Spectrom 45:202–206
Medhat ME, Pires LF, Arthur RCJ (2014) Analysis of photon interaction parameters as function of soil composition. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 300:1105–1112
Momoli RS, Correchel V, Faria KMS, Pinto AB (2021) Conservação dos solos e ecoturismo no Parque Estadual de Serra Dourada, Goiás. Geografia 46:1–21
Moreira HL, Oliveira VA (2008) Evolução e gênese de um plintossolo pétrico concrecionário êutrico argissólico no município de Ouro Verde de Goiás. R Bras Ci Solo 32:1683–1690
Motta PEF, Filho AC, Ker JC, Pereira NR, Junior WC, Blancaneaux P (2002) Soil-geomorphic surface relationships and landscape evolution in the area of the Brazilian Central Plateau. Pesq Agropec Bras 37:869–878
Mudahar SG, Sahota HS (1988) Effective atomic number studies in different soils for total photon interaction in the energy region 10–5000 keV. Appl Radiat Isot 39:1251–1254
Ondrasek G, Begíc HB, Zovko M, Filipovíc L, Gergichevich CM, Savíc R, Rengel Z (2019) Biogeochemistry of soil organic matter in agroecosystems and environmental implications. Sci Total Enviro 658:1559–1573
Pires LF (2018) Soil analysis using nuclear techniques: a literature review of the gamma ray attenuation method. Soil till Res 184:216–234
Pires LF, Pereira AB (2014) Gamma-ray attenuation to evaluate soil porosity: an analysis of methods. Sci World J 2014:1–10
Pires LF, Costa JC, Borges JAR, Arthur RCJ, Bacchi OOS (2014a) Soil mass attenuation coefficient: analysis and evaluation. Ann Nucl Energy 64:206–211
Pires LF, Prandel LV, Saab SC (2014b) The effect of wetting and drying cycles on soil chemical composition and the impact on bulk density evaluation: Na analysis by using XCOM data and gamma-ray computed tomography. Geoderma 213:512–520
Pires LF, Brinatti AM, Prandel LV, Saab SC (2015) Mineralogical composition of hardsetting soils and its effect on the radiation attenuation characteristics. J Soils Sediment 16:197–210
Pires LF, Leite WC, Brinatti AM, Saab SC (2019) Radiation attenuation properties based on the qualification of soil components using Rietveld method. Results Phys 12:2009–2011
Pires LF, Auler AC, Roque WL, Mooney SJ (2020) X-ray microtomography analysis of pore soil structure dynamics under wetting and drying cycles. Geoderma 362:103–114
Prandel LV (2014) Integração de Métodos de Caracterização Mineralógica de Solos Cauliníticos. Universidade Estadual de Ponta Grossa, Dissertação
Prandel LV, Saab SC, Brinatti AM, Giarola NFB, Leite WC, Cassaro FAM (2014) Mineralogical analysis of clays in hardsetting soils horizons, by X-ray fluorescence and X-ray diffraction using Rietveld method. Radiat Phys Chem 95:65–68
Prandel LV, Saab SC, Tonial LMS, Brinatti AM, Pires LF (2021) Can the granulometric soil fractions attenuate the radiation differently from the whole soil? Braz Arch Biol Technol 64:1–10
R Core Team (2020) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Rocha WW, Junior MSD, Lima JM, Miranda EEV, Silva AR (2002) Resistência ao cisalhamento e grau de intemperismo de cinco solos na região de Lavras (MG). R Bras Ci Solo 26:297–303
Sandhu BS, Singh MP, Singh B (2007) Measurement of effective atomic number of composite materials using scattering of γ-rays. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A 580:50–53
Santos AC, Pereira MG, Anjos LHC, Bernini TA, Cooper M, Nummer A, Francelino MR (2010) Gênese e classificação de solos numa topossequência no ambiente de mar de morros de médio vale do Paraíba do Sul, RJ. R Bras Ci Solo 34:1297–1314
Santos H D, Jacomine P K T, Anjos L H C, Oliveira V A, Lumbreras J F, Coelho M R, Almeida J A, Araújo Filho J C, Oliveira J B, Cunha T J F (2018) Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos. 5ª edição EMBRAPA.
Simões LSA (1984) Geologia do Grupo Araxá na Região de Mossâmedes-Goiás, e as ocorrências minerais associadas. Universidade de Brasília, Dissertação
Susoy G, Tekin HO, Kaçal MR, Issa SAM, Polat H, Akman F, Kiligoglu O, Gillette VH (2020) Sodium dodecatungsphosphate hydrate-filled polymer composites for nuclear radiation shielding. Mater Chem Phys 256:123667
Tekin HO, Elazaka AI, Hesham MH, Zakaly MH, Issa SAM, Rashad M, Saudi HA, Gillette VH, Erguzel TT, Mostafa AG (2021) New approach to removal of hazardous bypass cement dust (BCD) from the environment: 20Na2O-20BaCl2-(60–x)B2O3-(x)BCD glass system and Optical, mechanical, structural and nuclear radiation shielding competences. J Hazard Mater 403:123738
Acknowledgements
LT would like to thank the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for the PhD grant (Code 001). LFP would like to acknowledge the financial support provided by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) through Grant 304925/2019-5 (Productivity in Research).
Funding
Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq)—Grant 304925/2019-5 (Productivity in Research).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. All co-authors have seen and agreed with the contents of the manuscript and there is no financial interest to report. We certify that the submission is original work and is not under review at any other publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tech, L., Pires, L.F., Brinatti, A.M. et al. Elemental and radiation attenuation parameter analyses to characterize a Cambisol from the Serra Dourada State Park, Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 81, 63 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10198-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-022-10198-y