Abstract
The high-resolution analysis of single-channel, seismic reflection data from Lake Erçek (Eastern Anatolia) revealed a wide range of shallow gas anomalies consisting of enhanced reflections, seismic chimneys, acoustic blanking/acoustic turbidity, strong reflectors, and pockmarks, including both surface and buried pockmarks. The enhanced reflections are represented by the higher amplitude reflection patterns resulting from high acoustic impedance variations. They are mostly clustered in the NW-corner of the lake. Seismic chimneys are represented by vertical and thinned columnar disturbances of amplitude blanking and mostly occurred in deep basinal and faulted sections in the West and East of the lake. Some seismic chimneys, occurring together with pockmarks, represent vertical vent activations. Acoustic gas masking was represented by chaotic and diffuse seismic reflection patterns, including acoustic blanking and acoustic turbidity. As diffuse acoustic turbidity indicates gas-charged sediments, columnar disturbances showing acoustic blanking indicate degassing of the sediments. These features extend from SE to NW, coinciding with the deep basin morphology of the lake. A very local strong reflector was identified in the W-section of the lake, simulating the lake floor. This reflector is due to extended enhanced reflections, suggesting shallow free gas. Pockmarks observed in the lake are structurally classified into the two distinct types; surface (active) pockmarks found in the SE-part of the lake and buried (passive) pockmarks found in the NW. The former enlarge through deeper gas reservoir feedback, as the layering is impermeable, while the latter have resulted from a cessation of the reservoir feedback mechanism and/or permeable layering. In the lake, shallow gas distribution is controlled by faults, that provide the faulting-driven depositional control and earthquakes, that provide the seismicity-driven overpressure control. The shallow gas is then vertically–horizontally distributed and shaped by asymmetric depositional–stratigraphic factors. This study of Lake Erçek presents complementary information about a possible tectono-thermal origin of observed shallow gas.

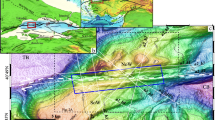
modified from Toker and Tur 2018). Inset map shows Lakes Van (blue) and Erçek (red) regions










modified from Toker and Tur 2018), including lacustrine shelf (Ls), sub-lacustrine slope (SLs), and deep basin (DB). The basinal pattern of gas anomalies correlates well with the water depth ≥ 25 m (DB) (see text for abbreviations). Surface pockmarks are only observed in the SE-part of the basin, where seismic chimneys are also seen and buried pockmarks detected are diffused in a few locations toward the NW. Seismic chimneys are densely observable in most of the surveyed area from SE (surface pockmark area) to NW (enhanced reflection area) and several seismic chimneys (triangles in orange) are diffusely isolated in a few locations toward the NW. Enhanced reflections dominantly clustered in the NW-corner of the basin are associated with the strong reflector, only identified in the W-end of the basin, where some chimneys and buried pockmark are also evident. Gas-charged sediments (GCS) associated with acoustic gas masking are distributed along-strike in an SE-to-NW pattern
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abegg F, Anderson AL (1997) The acoustic turbid layer in muddy sediments of Eckernfoerde Bay, Western Baltic: methane concentration, saturation and bubble characteristics. Mar Geol 137:137–147
Akkaya İ (2020) Availability of Seismic Vulnerability Index (Kg) in the Assessment of Building Damage in Van. Eastern Turkey, Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration 19(1):189–204
Altınok Y, Alpar B (2006) Marmara Island earthquakes, of 1265 and 1935; Turkey. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 6(6):999–1006. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-6-999-2006
Anderson AL, Bryant WR (1990) Gassy sediment occurrence and properties: Northern Gulf of Mexico. Geo-Mar Lett 10:209–220
Anderson AL, Hampton LD (1980) Acoustics of gas-bearing sediments II. J Acoustical Soc Am 67(6):1880–1903
Anderson AL, Abegg F, Hawkins JA, Duncan ME, Lyons AP (1998) Bubble populations and acoustic interaction with the gassy floor of Eckernförde Bay. Cont Shelf Res 18(14–15):1807–1838
Anka Z, Loegering MJ, di Primio R, Marchal D, Rodríguez JF, Vallejo E (2014) Distribution and origin of natural gas leakage in the Colorado Basin, offshore argentina Margin, South America: seismic interpretation and 3D basin modelling. Geol Acta 12(4):269–285
Artemieva I, Shulgin A (2019) Geodynamics of Anatolia: lithosphere thermal structure and thickness. Tectonics 38:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019TC005594
Baltzer A, Tessier B, Nouze H, Bates R, Moore C, Menier D (2005) Seistec seismic profiles: a tool to differentiate gas signatures. Marine Geophys Res 26:235–245
Baraza J, Ercilla G (1996) Gas-charged sediments and large pockmark-like features on the Gulf of Cadiz slope (SW Spain). Mar Petrol Geol 13:253–261
Berndt C, Bünz S, Mienert J (2003) Polygonal fault systems on the mid-Norwegian margin: a long term source for fluid flow. In: Van Rensbergen P, Hillis R, Maltman A, Morley C (eds) Subsurface sediment mobilization: geological society special publication, 216. Geological Society of London, pp 283–290
Bertin X, Chaumillon E (2005) New insights in shallow gas generation from very high resolution seismic and bathymetric surveys in the Marennes-Oléron Bay, France. Mar Geophys Res 26:225–233
Best AI, Tuffin MDJ, Dix JK, Bull JM (2004) Tidal height and frequency dependence of acoustic velocity and attenuation in shallow gassy marine sediments. J Geophys Res 109(B8):B08101. https://doi.org/10.1029/2003JB002748
Best AI, Richardson MD, Boudreau BP et al (2006) Shallow seabed methane gas could pose coastal hazard. Eos 87(22):213–215
Boudreau BP, Algar C, Johnson BD et al (2005) Bubble growth andrise in soft sediments. Geology 33(6):517–520. https://doi.org/10.1130/G21259.1
Chun JH, Ryu B-J, Lee CS, Kim YJ, Choi JY, Kang NK, Bahk JJ, Kim JH, Kim KJ, Yoo DG (2012) Factors determining the spatial distribution of gas-charged sediments in the continental shelf off southeastern Korea. Mar Geol 332–334:27–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2012.06.004
Çifçi G, Dondurur D (2003) Deep and shallow structures of large pockmarks in the Turkish shelf Eastern Black Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 23:311–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-003-0138-x
Clayton CJ, Hay SJ (1994) Gas migration mechanisms from accumulation to surface. Bull Geol Soc Den 41:12–23
Cole D, Stewart SA, Cartwright JA (2000) Giant irregular pockmark craters in the palaeogene of the outer moray firth Basin, UK North Sea. Mar Petrol Geol 17:563–577
Croker PF, Kozachenko M, Wheeler AJ (2005). Gas-related seabed structures in the Western Irish Sea (IRL-SEA6). Tech Rep Strategic Environ Assess SEA6.
Çukur D, Krastel S, Schmincke HU, Sumita M, Tomonaga Y, Çagatay MN (2014) Water level changes in Lake Van, Turkey, during the past ca. 600 ka: climatic, volcanic and tectonic controls. J Paleolimnol 52:201–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-014-9788-0
Çukur, D., Krastel, S., Schlüter, F.D., Demirbag, E., Imren, C., Niessen, F., Toker, M., PaleoVan-Working Group (2013a) Sedimentary evolution of Lake Van (Eastern Turkey) reconstructed from high resolution seismic investigations. Int J Earth Sci 102(2):571–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-012-0816-x
Çukur, D., Krastel, S., Tomonaga, Y., Çagatay, M.N., Meydan, A.F., and the PaleoVan Science Team (2013b) Seismic evidence of shallow gas from Lake Van, eastern Turkey. Mar and Pet Geo 48:341–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.08.017
Curzi PV, Veggiani A (1985) I pockmarks nel mare Adriatico centrale. Acta Nat Ateneo Parmense 21:9–90
Davis AM (1992) Shallow gas: an overview. Cont Shelf Res 12:1077–1079
Davy B (1992) Seismic reflection profiling on southern Lake Rotorua–evidence for gas-charged lake floor sediments. Geothermics 21:97–108
Delph JR, Zandt G, Beck SL (2015) A new approach to obtaining a 3D shear wave velocity model of the crust and upper mantle: an application to eastern Turkey. Tectonophysics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.09.031
Dicle S, Üner S (2017) New active faults on Eurasian-Arabian collision zone: tectonic activity of Özyurt and Gülsünler faults (eastern Anatolian Plateau, Van-Turkey). Geol Acta 15(2):107–120. https://doi.org/10.1344/GeologicaActa2017.15.2.3
Domżalski J, Górecki W, Mazurek A, Myśko A, Strzetelski W, Szamałek K (2004) The prospects for petroleum exploration in the eastern sector of Southern Baltic as revealed by sea bottom geochemical survey correlated with seismic data. Przegląd Geologiczny 52(8/2):792–799
Duarte H, Pinheiro LM, Teixeira FC, Monteiro JH (2007) High-resolution seismic imaging of gas accumulations and seepage in the sediments of the Ria de Aveiro barrier lagoon (Portugal). Geo-Mar Lett 27:115–126
Emeis KC, Bruchert V, Currie B, Endler R, Ferdelman T, Kiessling A, Leipe T, Noli-Peard K, Struck U, Vogt T (2004) Shallow gas in shelf sediments of the Namibian coastal upwelling ecosystem. Cont Shelf Res 24(6):627–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2004.01.007
Emery KO, Hoggan D (1958) Gases in marine sediments. AAPG Bull 42:2174–2188
Fleischer P, Orsi TH, Richardson MD, Anderson AL (2001) Distribution of free gas in marine sediments: a global overview. Geo-Mar Lett 21(2):103–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003670100072
Fleischer P, Orsi TH, Richardson MD, Anderson AL (2001) Distribution of free gas in marine sediments: a global overview. Geo-Mar Lett 21:103–122
Garcia-Gil S, Vilas F, Garcia-Garcia A (2002) Shallow gas features in incised-valley fills (Ria de Vigo, NW Spain): a case study. Cont Shelf Res 22:2303–2315
Gay A, Lopez M, Berndt C, Séranne M (2007) Geological controls on focused fluid flow associated with seafloor seeps in the Lower Congo Basin. Mar Geol 244:68–92
Hage S, Hubert-Ferrari A, Lamair L, Avşar U, El Ouahabi M, Van Daele M et al (2017) Flow dynamics at the origin of thin clayey sand lacustrine turbidites: examples from Lake Hazar. Turkey Sedimentol 64(7):1929–1956
Hartwig A, Anka Z, di Primio R (2012) Evidence of a widespread paleo-pockmarked field in the Orange Basin: An indication of an early Eocene massive fluid escape event off-shore South Africa. Mar Geol 332–334:222–234
Hovland M (1981a) A classification of pockmarks related features in the Norwegian Trench. Continental Shelf Institute (IKU), p 28
Hovland M (1981b) Characteristics of pockmarks in the Norwegian Trench. Mar Geol 39:103–117
Hovland M (1982) Pockmarks and the recent geology of the central section of the Norwegian Trench. Mar Geol 47:283–301
Hovland M (1984) Gas-induced erosion features in the North Sea. Earth Surf Proc Landforms 9:209–228
Hovland M (1989) The formation of pockmarks and their potential influence on offshore construction. Quart J Eng Geol 22:131–138
Hovland M (1992) The effects of shallow gas in the skagerrak surficial sediments. Geol Föreningens Stockholm Förhandlingar 114:235–251
Hovland M (2008) Deep-water coral reefs: unique biodiversity hotspots. Praxis Publishing (Springer), p 278
Hovland M, Judd AG (1988) Seabed pockmarks and seepages. Impact on geology, biology and the marine environment. Graham & Trotman Ltd, p 293
Hovland M, Judd AG, Burke RA Jr (1993) The global flux of methane from shallow submarine sediments. Chemosphere 26(1–4):559–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(93)90442-8
Hustoft S, Bünz S, Mienert J (2010) Three-dimensional seismic analysis of the morphology and spatial distribution of chimneys beneath the Nyegga pockmark field, offshore mid-Norway. Basin Res 22:465–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2117.2010.00486.x
Jackson DR, Richardson M (2007) High-frequency seafloor acoustics. Springer-Verlag
Jakobsson M, Bjorck S, O’Regan M, Floden T, Greenwood SL, Sward H et al (2014) Major earthquake at the Pleistocene-Holocene transition in Lake Vattern, southern Sweden. Geology 42(5):379–382
Jaśniewicz D, Klusek Z, Brodecka-Goluch A, Bolałek J (2019) Acoustic investigations of shallow gas in the southern Baltic Sea (Polish Exclusive Economic Zone): a review. Geo-Mar Lett 2019(39):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00367-018-0555-5
Jobe ZR, Lowe DR (2009) Pockmarks on the modern seafloor as indicators of submarine Canyon abandonment, offshore equatorial. In: AAPG Search and Discovery Article, Pacific Section Meeting, Ventura, California.
Judd AG, Hovland M (1992) The evidence of shallow gas in marine sediments. Cont Shelf Res 12(10):1081–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-4343(92)90070-Z
Judd AG, Hovland M (2007) Seabed fluid flow, the impact on geology biology and marine environment. Cambridge University Press, p 475
Judd AG, Hovland M, Dimitrov LI, Garcia-Gill S, Jukes V (2002) The geological methane budget at continental margins and its influence on climate change. Geofluids 2:109–126
Judd AG, Curzi PV (2002) The rising influence of shallow gas: an introduction to the bologna conference on ‘Gas in Marine Sediments’. Cont. Shelf Res. 22: 2267–2271.
Kaden H, Peeters F, Lorke A, Kipfer R, Tomonaga Y, Karabiyikoglu M (2010) Impact of lake level change on deep-water renewal and oxic conditions in deep saline Lake Van. Turkey Water Resour Res 46:W11508
Kamar G (2021) Holocene palynology and pollen-based palaeoclimate reconstruction of Lake Erçek (Eastern Anatolia); short-term climatic fluctuations and their relation with global palaeoclimatic change; results of cores E1 and E10. Geol Bull Turkey 64:253–266. https://doi.org/10.25288/tjb.927117
Kelley JT, Dickson SM, Belknap DF, Barnhardt WA, Henderson M (1994) Giant sea-bed pockmarks: evidence for gas escape from Belfast Bay. Mar Geol 22:59–62
King LH, MacLean B (1970) Pockmarks on the Scotian Shelf. Geol Soc Am Bull 81:3141–3148
Kipfer R, Aeschbach-Hertig W, Baur H, Hofer M, Imboden DM, Signer P (1994) Injection of mantle type helium into Lake Van (Turkey): the clue for quantifying deep water renewal. Earth Planet Sci Lett 125:357–370
Koyama T (1953) Measurement and analysis of gases in lake muds. J Earth Sci (nagoya University) 1:107–118
Kuhlmann G, Adams S, Campher C, Van Der Spuy D, di Primio R, Horsfield B (2010) Passive margin evolution and its controls on natural gas leakage in the southern Orange Basin, blocks 3/4, offshore South Africa. Mar Pet Geol 27:973–992
Kurtman F, Akkus MF, Gedik A (1978) The geology and oil potential of Mus-Van region. In: Degens ET, Kurtman F (eds) Geology of Lake Van, 169. M.T.A. Press, pp 124–133
Kwiecien O, Stockhecke M, Pickarski N, Heumann G, Litt T, Sturm M, Anselmetti F, Kipfer R, Haug GH (2014) Dynamics of the last four glacial terminations recorded in Lake Van. Turkey, Quat Sci Rev 104:42–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.07.001
Laier T, Jensen JB (2007) Shallow gas depth-contour map of the Skagerrak, western Baltic Sea region. Geo-Mar Lett 27:127–141
Lee GH, Kim DC, Ki HJ, Jou HT, Lee YJ (2005) Shallow gas in the central part of the Korea Strait shelf mud off the southeastern coast of Korea. Cont Shelf Res 25:2036–2052
Leroy SA, Schwab MJ, Costa PJ (2010) Seismic influence on the last 1500-year infill history of Lake Sapanca (North Anatolian Fault, NW Turkey). Tectonophysics 486(1–4):15–27
Litt T, Krastel S, Sturm M, Kipfer R, Orcen S, Heumann G, Franz SO, Ulgen UB, Niessen F (2009) PALEOVAN, international continental scientific drilling program (ICDP): site survey results and perspectives. Quat Sci Rev 28(15–16):1555–1567
Litt T, Pickarski N, Heumann G, Stockhecke M, Tzedakis PC (2014) A 600,000-year long continental pollen record from Lake Van, eastern Anatolia (Turkey). Quatern Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.03.017
Litt T, Anselmetti FS, Cagatay MN, Kipfer R, Krastel S, Schmincke HU, Paleo Van Working Team (2011) A 500,000 year-long sedimentary archive drilled in Eastern Anatolia (Turkey), The Paleo Van Drilling Project. EOS, 453–164.
Lodolo E, Baradello L, Darbo A, Caffau M, Tassone A, Lippai H, Lodolo A, De Zorzi G, Grossi M (2012) Occurrence of shallow gas in the easternmost Lago Fagnano (Tierra del Fuego). Near Surf Geophys 10:161–169. https://doi.org/10.3997/1873-0604.2011040
Lowe JJ, Walker MJC (1997) Reconstructing quaternary environments. Longman Publ, p 446
Mahatsente R, Önal G, Çemen I (2018) Lithospheric structure and the isostatic state of Eastern Anatolia: insight from gravity data modelling. Lithosphere 10:279–290
Mathys M, Thiessen O, Theilen F, Schmidt M (2005) Seismic characterization of gas-rich near surface sediments in the Arkona Basin, Baltic Sea. Marine Geophys Res 26:207–224
Mazumdar A, Peketi A, Dewangan P, Badesab F, Ramprasad T, Ramana MV, Patil DJ, Dayal A (2009) Shallow gas charged sediments off the Indian west coast: Genesis and distribution. Mar Geol 267(1–2):71–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2009.09.005
Missiaen T, Murphy S, Loncke L, Henriet J-P (2002) Very high-resolution seismic mapping of shallow gas in the Belgian coastal zone. Cont Shelf Res 22:2291–2301
Naudts L, De Batist M, Greinert J, Artemov Y (2009) Geo- and hydro-acoustic manifestations of shallow gas and gas seeps in the Dnepr paleo-delta, northwestern Black Sea. Lead Edge 28:1030–1040
Nelson H, Tor DR, Sandstrom MW, Kvenvolden KA (1979) Modern biogenic gas-related craters (sea-floor _pockmarks_) on the Bering Shelf, Alaska. Geol Soc Am Bull 90:1144–1152
Orange D, Garcia-Garcia A, Lorenson T, Nittrouer C, Milligan T, Miserocchi S et al (2005) Shallow gas and flood deposition on the Po Delta. Mar Geol 222–223:159–177
Ostanin I, Anka Z, di Primio R, Bernal A (2012) Identification of a large upper cretaceous polygonal fault network in the hammerfest basin: implications on the reactivation of regional faults and gas leakage dynamics, SW Barents Sea. Mar Geol 332–334:109–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2012.03.005
Pickrill RA (1993) Shallow seismic stratigraphy and pockmarks of a hydrothermally influenced lake, Lake Rotoiti, New Zealand. Sedimentology 40:813–828
Pig-Pib (2008) Petrobaltic Kronos Geos Geosfera (consortium). Strefy perspektywnczne dla występowania złóż węglowodorów (in Polish). In: Anolik P, Karczewska A, (eds) Badania geochemiczne południowego Bałtyku pod kątem analizy skażeń geogenicznych I poszukiwań naftowych (in Polish). Polish Geological Institute, Warsaw part II.
Pilcher R, Argent J (2007) Mega-pockmarks and linear pockmark trains on the West African continental margin. Mar Geol 244:15–32
Prior DB, Coleman JB (1984) Submarine slope instability. In: Brunsden D, Prior DB (eds) Slope instability. Wiley, pp 419–455
Randlett M-E, Bechtel A, van der Meer MTJ, Peterse F, Litt T, Pickarski N, Kwiecien O, Stockhecke M, Wehrli B, Schubert CJ (2017) Biomarkers in Lake Van sediments reveal dry conditions in eastern Anatolia during 110.000–10.000 years B.P. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 18:571–583. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GC006621
Sammartini, M., Moernaut, J., Anselmetti, F.S., Hilbe, M., Lindhorst, K., Praet, N., and Strasser, M (2020) An Atlas of Mass‐Transport Deposits in Lakes in Submarine Landslides: Subaqueous Mass Transport Deposits from Outcrops to Seismic Profiles, Geophysical Monograph 246. In: Kei O, Andrea F, Gian AP (2020) American Geophysical Union. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Schroot BM, Schuttenhelm RTE (2003) Expressions of shallow gas in the Netherlands North Sea. Neth J Geosci 82:91–105
Schubel JR (1974) Gas bubbles and the acoustically impenetrable, or turbid, character of some estuarine sediments. In: Kaplan IR (ed) Natural Gases in Marine Sediments. Plenum Press, pp 275–298
Schüler F (1952) Untersuchungen uber die Machtigkeiten von Schlickschichten mit Hilfe des Echographen (In Deutsch). Deutsche Hydrographische Zeitschrift 5:220–231
Shiki T, Kumon F, Inouchi Y, Kontani Y, Sakamoto T, Tateishi M et al (2000) Sedimentary features of the seismo-turbidites, Lake Biwa. Japn Sediment Geol 135(1–4):37–50
Solheim A, Elverhoi A (1993) Gas-related sea floor craters in the Barents Sea. Geo-Mar Lett 13:235–243
Solovyeva MA, Starovoytov AV, Akhmanov GG, Khlystov OM, Khabuev AV, Tokarev MY, Chensky DA (2016) The evolution of slump-induced destruction of Kukuy Griva slope (Lake Baikal) revealed on the base of the data of seismic and acoustic surveys. Mosc Univ Geol Bull 71(6):416–428
Stockhecke M, Kwiecien O, Vigliotti L, Anselmetti FS, Beer J, Cagatay MN, Channell JET, Kipfer R, Lachner J, Litt T, Pickarski N, Sturm M (2014a) Chronostratigraphy of the 600,000 year old continental record of Lake Van (Turkey). Quat Sci Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.04.008
Stockhecke M, Sturm M, Brunner I, Schmincke HU, Sumita M, Kipfer R, Cukur D, Kwiecien O, Anselmetti FS (2014b) Sedimentary evolution and environmental history of Lake Van (Turkey) over the past 600,000 years. Sedimentology. https://doi.org/10.1111/sed.12118
Taylor DI (1992) Near shore shallow gas around the U.K. coast. Cont Shelf Res 12:1135–1144
Toker M (2013) Time-dependent analysis of aftershock events and structural impacts on intraplate crustal seismicity of the Van earthquake (Mw 71, 23 October 2011) E-Anatolia. Cent Eur J Geosci 5(3):423–434
Toker M (2014) Discrete characteristics of the aftershock sequence of the 2011 Van earthquake. J Asian Earth Sci 92:168–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.06.015
Toker M (2017) The b value analysis of aftershocks 170 days after the 23 October 2011 Van earthquake (Mw, 71) of the Lake Van basin, Eastern Anatolia: a new perspective on the seismic radiation and deformation characteristics. In: Zouaghi T (ed) Earthquakes tectonics. Hazard and Risk Mitigation
Toker M, Şahin Ş (2019) Crustal Poisson’s ratio tomography and velocity modeling across tectono-magmatic lake regions of Eastern Anatolia (Turkey): new geophysical constraints for crustal tectonics. J Geodyn 131(101651):1–28
Toker M, Şengör AMC (2011) Van Gölü havzasının temel yapısal unsurları, tektonik ve sedimanter evrimi, Doğu Türkiye (Structural elements of Lake Van basin, its tectonic and sedimentary evolution, Eastern Turkey). ITU J Ser D: Eng 10:119–130
Toker M, Tur H (2018) Structural patterns of the Lake Erçek Basin, eastern Anatolia (Turkey): evidence from single-channel seismic interpretation. Mar Geophys Res 39:567–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-017-9333-4
Toker M, Pınar A, Tur H (2017) Source mechanisms and faulting analysis of the aftershocks in the Lake Erçek area (Eastern Anatolia, Turkey) during the 2011 Van event (Mw 7.1): implications for the regional stress field and ongoing deformation processes. J Asian Earth Sci 150:73–86
Toker M, Pınar A, Hoşkan N (2021) An integrated critical approach to off-fault strike-slip motion triggered by the 2011 Van mainshock (Mw 71), Eastern Anatolia (Turkey): new stress field constraints on subcrustal deformation. J Geodyn 147(101861):1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jog.2021.101861
Toker M (2015) Preliminary results of Lake Erçek Seismic Survey (LESS, in: 2015). Project Report in Scientific Research Projects-Coordination Unit, 2015-MİM-B119. Yuzuncu Yil University, Van.
Toker M, Sengör AMC, Demirel-Schluter F, Demirbağ E, Çukur D, Imren C, Niessen F, Group P-W (2017) The structural elements and tectonics of the Lake Van basin (Eastern Anatolia) from multi-channel seismic reflection profiles. J Afr Earth Sci 129:165–178
Toker M (2021) The Structural Coupling to Rupture Complexity of the Aftershock Sequence of the 2011 Earthquakes in Lake Van Area (Eastern Anatolia, Turkey). J Eng Sci Design. https://doi.org/10.21923/jesd.861520.
Tomonaga Y, Brennwald MS, Kipfer R (2011) Spatial distribution and flux of terrigenic He dissolved in the sediment pore water of Lake Van (Turkey). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75(10):2848–2864
Tomonaga Y, Brennwald MS, Livingstone DM, Kwiecien O, Randlett M-È, Stockhecke M, Unwin K, Anselmetti FS, Beer J, Haug GH, Schubert CJ, Sturm M, Kipfer R (2017) Porewater salinity reveals past lake-level changes in Lake Van, the Earth’s largest soda lake. Sci Rep 7:313. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00371-w
Tóth Zs, Spiess V, Jensen J (2014) Seismo-acoustic signatures of shallow free gas in the Bornholm Basin, Baltic Sea. Cont Shelf Res 88:228–239
Tóth Zs, Spiess V, Keil H (2015) Frequency dependence in seismoacoustic imaging of shallow free gas due to gas bubble resonance. J Geophys Res Solid Earth 120:8056–8072. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015JB012523
Türkoğlu E, Unsworth MJ, Cağlar I, Tuncer V, Avsar U (2008) Lithospheric structure of the Arabia-Eurasia collision zone in eastern Anatolia: magnetotelluric evidence for widespread weakening by fluids? Geology 36:619–622
Üner S (2017) Evolution of Çolpan barrier and lagoon complex (Lake Van-Turkey): sedimentological and hydrological approach. Quatern Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2017.05.019
Van Daele M, Moernaut J, Doom L, Boes E, Fontijn K, Heirman K et al (2015) A comparison of the sedimentary records of the 1960 and 2010 great Chilean earthquakes in 17 lakes: Implications for quantitative lacustrine palaeoseismology. Sedimentology 62(5):1466–1496
Vardar D, Alpar B (2016) High-resolution seismic characterization of shallow gas accumulations in the southern shelf of marmara sea, Turkey. Acta Geophys 64(3):589–609. https://doi.org/10.1515/acgeo-2015-0059
Vardar D, Ozturk K, Yaltırak C, Alpar B, Tur H (2014) Late Pleistocene-Holocene evolution of the southern Marmara shelf and sub-basins: middle strand of the North Anatolian fault, southern Marmara Sea, Turkey. Mar Geophys Res 35(1):69–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11001-013-9210-8
Vigliotti L, Channell JET, Stockhecke M (2014) Paleomagnetism of Lake Van sediments: chronology and paleoenvironment since 350 ka. Quat Sci Rev 104:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.09.028
Visnovitz F, Bodnar T, Toth Zs, Spiess V, Kudo I, Timar G, Horvath F (2015) Seismic expressions of shallow gas in the lacustrine deposits of Lake Balaton, Hungary. Near Surf Geophys 2015(13):433–446. https://doi.org/10.3997/1873-0604.2015026
Wagner B, Francke A, Sulpizio R, Zanchetta G, Lindhorst K, Krastel S et al (2012) Possible earthquake trigger for 6th century mass wasting deposit at Lake Ohrid (Macedonia/Albania). Climate past 8(6):2069–2078
Wallner J (2008) Holozane Landschaftsentwicklung am Lago Budi, Chile (38, 9°C): Palaolimnologisch/palaoseismische Untersuchungen an Lagunensedimenten (Doctoral dissertation). University of Jena
Whiticar MJ (2002) Diagenetic relationships of methanogenesis, nutrients, acoustic turbidity, pockmarks and freshwater seepages in Eckernforde Bay. Mar Geol 182(1–2):29–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-3227(01)00227-4
Wick L, Lemcke G, Sturm M (2003) Evidence of Late-glacial and Holocene climatic change and human impact in eastern Anatolia: high resolution pollen, charcoal, isotopic and geochemical records from the laminated sediments of Lake Van Turkey. J. Paleolimnol Holocene 13:665–675
Wilkens RH, Richardson MD (1998) The influence of gas bubbles on sediment acoustic properties: in situ, laboratory, and theoretical results from Eckernförde Bay. Baltic Sea Cont Shelf Res 18(14):1859–1892. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0278-4343(98)00061-2
Wood W, Ruppel C (2000) Seismic and thermal investigations of hydrate bearing sediments on the Blake Ridge Crest: a synthesis of ODP Leg 164 results. Proc Ocean Drill Progr Final Rep 164:253–264
Yeşilova Ç, Gülyüz E, Ci-Rong H, Chuan-Chou S (2019) Giant tufas of Lake Van record lake-level fluctuations and climatic changes in eastern Anatolia, Turkey. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 533:1–9
Yeşilova Ç, Güngör Yeşilova P, Açlan M, Yu T-L, Shen C-C (2021) U-Th ages and facies properties of Edremit travertines and tufas, Van, Eastern Anatolia: implications for the neotectonics of the region. Geological Quarterly 65:28. https://doi.org/10.7306/gq.1597
Yun JW, Orange DL, Field ME (1999) Subsurface gas offshore of northern California and its link to submarine geomorphology. Mar Geol 154:357–368
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Yuzuncu Yıl University, Scientific Research Projects-Coordination Unit (SRP-CU), Van, Turkey for supporting the Lake Erçek Seismic Survey project, 2015 (Toker, 2015) and the research vessel scientific crew during the survey. This research was undertaken as part of a multidisciplinary LESS-2015 project of Istanbul University Cerrahpaşa (IU), Department of Geophysical Engineering, Istanbul and Yuzuncu Yıl University (YYU), Division of Earth Physics, Van (Turkey). The LESS-2015 project was supported by Research Fund of the Yuzuncu Yıl University (under Scientific Research Project Number: 2015-MİM-B119), and was partly supported by the University of Oulu (Oulu, Finland) post-doctoral research grant. The authors offer their greatest thanks to the editors and the two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions, which helped to improve the manuscript. The maps in this paper were generated using public domain generics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toker, M., Tur, H. Shallow seismic characteristics and distribution of gas in lacustrine sediments at Lake Erçek, Eastern Anatolia, Turkey, from high-resolution seismic data. Environ Earth Sci 80, 727 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10039-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-10039-4