Abstract
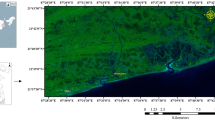
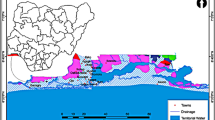
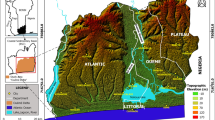
An analysis of borehole logs with hydrophysical data from the Lagos coastal belt, Southwestern Nigeria, was carried out to evaluate the subsurface lithological units and geo-environmental impact of seawater intrusion into coastal freshwater. Forty-five (45) borehole logs, consisting of natural gamma, electrical resistivity log and hydrophysical parameters were integrated to delineate saline and fresh aquifer zones and propose simplified conceptual models for adequate groundwater characterisation and development. The qualitative interpretation of the borehole logs revealed a complex lithology of alternating sequences of sand and clay layers. The study also showed that the subsurface was variably intruded by saline water indicated by low resistivity values with freshwater/saline water boundaries occurrence at depths ranging between 14 and 157 m from west to east. The variation in depths of occurrence of freshwater/saline water interface is dependent principally on the proximity to saline/brackish water source as well as variation in lithology. Complementarily, the average electrical conductivity (EC) of 1770 μS/cm (GW1–7) and 1676 μS/cm (GW8–13) recorded in groundwater at Apapa in the west and Island at the central part, respectively, further confirmed saline incursion of the coastal aquifers in the region. This study demonstrates versatility of geophysical borehole logs in identification and differentiation of the subsurface lithology and its fluid content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adekeye OA (2005) Aspects of sedimentology, geochemistry and hydrocarbon potentials of cretaceous–tertiary sediments in the Dahomey Basin, Southwestern Nigeria. Thesis, University of Ilorin
Adeoti L, Alile OM, Uchegbulam O (2010) Geophysical investigation of saline water intrusion into freshwater aquifers: a case study of Oniru, Lagos state. Sci Res Essays 5:248–259
Adepelumi AA (2008) Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. The 3rd international conference on Water Resources and Arid Environments and the 1st Arab Water Forum
Adepelumi AA, Ako BD, Ajayi TR, Afolabi O, Omotoso EJ (2008) Delineation of saltwater intrusion into the freshwater aquifer of Lekki Peninsula, Lagos, Nigeria. J Environ Geol 56:927–933
Akoteyon IS, Mbata UA, Olalude GA (2011) Investigation of heavy metal contamination in groundwater landfill site in a typical sub-urban settlement in Alimosho, Lagos, Nigeria. J Appl Sci Environ Sanitation 6:155–163
Arnell NW (1999) Climate change and global water resource. Glob Environ Change 9:S31–S49
Arnell NW (2004) Climate change and global water resources: SRES emissions and socio-economic scenarios. Glob Environ Change 14:31–52
Ayolabi EA, Folorunso AF, Odukoya MA, Adeniran AE (2013) Mapping the saline water intrusion into the coastal aquifer with geophysical and geochemical techni-ques: the university of Lagos campus case (Nigeria). Springplus 2(433):2013
Badaruddin S, Werner AD, Morgan LK (2015) Water table salinization due to seawater intrusion. Water Resour Res 51:8397–8408
Barlow PM (2003) Ground water in fresh water–salt water environments of the Atlantic Coast, U.S. Geological survey circular 1262
Batayneh AT (2006) Use of electrical resistivity methods for detecting subsurface fresh and saline water and delineating their interfacial configuration: a case study of the eastern Dead Sea coastal aquifers, Jordan. Hydrogeol J 14:1277–1283
Billman HG (1976) offshore stratigraphy and palaeontology of the Dahomey Embayment. Proceedings 7th Afro Macropal College, Ile–Ife
Buckley DK (1994) unconsolidated sedimentary aquifers: Review no. 3—geophysical logging in boreholes. British Geological Survey, Technical Report WC/94/
Buckley DK, Hinsby K, Manzano M (2001) Application of geophysical borehole logging techniques to examine coastal aquifer palaeohydrogeology. In: Edmunds WM & Milne CJ (eds.) Palaeowaters in coastal Europe: evolution of groundwater since the Late Pleistocene. Geological Society, London, Special Publication 189: 251–270
Coode B, Oteri AU, Rofe KL (1996) Hydrogeological investigation of Lagos State. Final Report, Vol I & II
Doveton JH, Prensky SE (1992) Geological applications of wireline logs: a synopsis of developments and trends. Log Anal 33:286–303
El-Sioufi M (2010) Climate change and sustainable cities: Major challenges facing cities and urban settlements in the coming decades, UN-Habitat Article of the Month, June 2010
Freeze A, Cherry J (1979) Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Galloway DL, Burbey TJ (2011) Review: regional land subsidence accompanying groundwater extraction. Hydrogeol J 19:1459–1486
Galloway D, Jones DR, Ingebritsen SE (1999) Land subsidence in the United States, Circular 1182. https://doi.org/10.3133/cir1182
Ghazavi R, Vali AB, Eslamian S (2010) Impact of flood spreading on infiltration rate and soil properties. Water Resour Manag 24:2781–2793
Hwang S, Shin J, Park I, Lee S (2004) Assessment of seawater intrusion using geophysical well logging and electrical soundings in a coastal aquifer. Youngkwang-gun, Korea. Explor Geophys 35:99–104
Ibrahim E (2008) Identification of groundwater spreading by using geoelectrical resistivity method. Int J Sci Eng Technol 1:55–59
Jakovovic D, Werner AD, De Louw PGB, Post VEA, Morgan LK (2016) saltwater upcoming zone of influence. Adv Water Resource 94:75–86
Jimoh RA, Bankole MO, Ahmed K, Christopher OA, Adeniji MA, Ebhodaghe J, Sedara SO, Obende PW, Alebu O, Ezima EA (2018) Use of geophysical logs in hydrogeological studies and borehole designs: case study of Apapa coastal area, Lagos, Nigeria. Appl Water Sci 8:191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0804-9
Kampsax-Kruger and Sshwed Associates (1977) Underground water resources of the Metropolitan Lagos, Final Report to Lagos State Ministry of Works
Keys WS (1997) A practical guide to borehole geophysics in environmental investigations. Lewis, Boca Raton
Kingston DR, Dishroon CP, Williams PA (1983) Global basin classification system. AAPG Bull 67:2175–2193
Kobr M, Mares S, Paillet F (2005) Geophysical well logging—Borehole geophysics for hydrogeological studies: principles and applications. In: Rubin Y, Hubbard SS (eds) Hydrogeophysics. Springer, Amsterdam, pp 291–331
Krammer K (1997) Geophysikalische Bohrlochmessungen bei der Erkundung von Deponiestandorten. In: Beblo M (ed) Umweltgeophysik. Ernst, Berlin
Labregére D, Delhomme JP, Priestley A. (2006) Mitigating salt water advance using horizontal wells: Risk based comparison of different approaches. Integrated Geophysical and Geochemical Investigations 1287 Proceedings 1st SWIM-SWICA Joint Saltwater Intrusion Conference, Cagliari-Chia Laguna, Italy, Section 8—Intrusion Barriers, pp 273–280
Lee C-H, Chang RT-S (1974) on sea water encroachment in coastal aquifers. Water Resourc Res 10:1039–1104. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR010i005p01039
Lee J-Y, Song SH (2007) Groundwater chemistry and ionic ratios in a Western Coastal Aquifer of Buan, Korea: implication for seawater intrusion. Geosci Journ Hyd 3:259–270
Leopold LB (1974) Water: a primer. WH Freeman and Co, San Francisco
Longe EO (2011) Groundwater resources potential in the coastal plain sands aquifers, Lagos, Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 3:1–7
Longe EO, Malomo S, Olorunniwo MA (1987) Hydrogeology of Lagos metropolis. J Afr Earth Sci 6:163–174
Nace RL (ed.) (1971) Scientific framework of world water balances. UNESCO Technical Papers Hydrology, 7:27
Obaje NG (2009) Geology and mineral resources of Nigeria. Lecture notes in earth sciences. Springer, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-92685-6
Oke SA, Vermeulen D, Gomo D (2016) Aquifer vulnerability assessment of Dahomey basin using the RTt method. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–9
Okosun EA (1990) A review of the Cretaceous stratigraphy of the Dahomey Embayment, West Africa. Cretaceous Res 11:17–27
Onwuka MO, Amadi UMP (1989) Borehole design against saltwater intrusion in the coastal areas of Lagos State, Nigeria. Proceedings of the NIWASA Symposium, Port Harcourt, 19–21 October, pp 17:1–17:12
Oteri AU, Atolagbe FP (2003) saltwater intrusion into coastal aquifers in Nigeria. Paper presented at the 2nd International Conference on Saltwater Intrusion and Coastal Aquifers–Monitoring, Modelling and Management, Merida, Yucatain, Mexico, March 30–April 2
Oyedele KF (2001) Hydrogeophysical and hydrogeochemical investigation of groundwater quality in some parts of Lagos. Nigeria Afr Journ Env Studies 2:31–37
Oyedele KF, Momoh EI (2009) Evaluation of seawater intrusion in freshwater aquifers in a Lagoon Coast: a case study of the University of Lagos Lagoon, Akoka, Nigeria. N Y Sci J 2(3)
Oyeyemi KD, Aizebeokhai AP, Oladunjoye MA (2015) Integrated and geochemical investigations of saline water intrusion in a coastal alluvial terrain, Southwestern Nigeria. Int J Appl Environ Sci 10:1275–1288
Phongpiyah K, Helmut D (2012) Geophysical logging for groundwater investigations in Southern Thailand Songklanakarin. J Sci Technol 34:433–444
Raghunath HM (2006) Hydrology (principles, analysis and design). 2nd Eds. New Age International, New Delhi
Raicy MC, Parimala RS, Brindha K, Elango L (2012) Mitigation of seawater intrusion by managed aquifer recharge. In: Elango L, Goyal VC, Thomas W (eds.), Managed aquifer recharge: Methods, hydrogeological requirements, pre and post treatment systems, pp 83–99
Ringler C (2008) the impact of climate variability and climate change on water and food outcomes: a framework for analysis. International Food Policy Research Institute, Research brief 15-1 http://ebrary.ifpri.org/utils/getfile/collection/p15738coll2/id/13805/filename/13806.pdf
Saber M, Abdel-Fattah M, Kantoush SA, Sumi T (2017) Implications of land subsidence due to groundwater over-pumping: monitoring methodology using GRACE data. Int J Geomate 14:52–59. https://doi.org/10.21660/2018.41.76894
Sinha MK, Verma MK, Ahmad I, Baier K, Jha R, Azzam R (2016) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability using modified DRASTIC Model in Kharun Basin, Chhattisgarh, India. Arab J Geosci 9:1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2180-1
Taylor K, Hess J, Wheatcraft S (1990) Evaluation of selected borehole geophysical methods for hazardous waste site investigations and monitoring. Final Report, United States Environmental Protection Agency, EPA/600/490/029, Las Vegas, Nevada
United Nations (2009) Economic Commission for Europe Convention on the Protection and Use of Transboundary Watercourses and International Lakes. Guidance on water and adaptation to climate change, UN Publications
United Nations Development Programme (2006) Country evaluation: assessment of development results of Nigeria, pp 1–80
USDA (2008) Climate change and water perspectives from the forest service. The US Department of agriculture (USDA), 2008
Villeneuve J, Banton O, Lafrance P (1990) A probabilistic approach for the groundwater vulnerability to contamination by pesticides: the Vulpest Model. Ecol Modell 51:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3800(90)90057-N
Warner JC, Armstrong B, He R, Zambon JB (2010) Development of a coupled ocean–atmosphere–wave–sediment transport (COAWST) modelling system. Ocean Model 35:230–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocemod.2010.07.010
Wikipedia (2021) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lagos_State
World Health Organization (2006) Guidelines for drinking water quality. Volume 1, Recommendations. World Health Organization, Geneva
Yusuf MA, Abiye TA (2019) Risks of groundwater pollution in the coastal areas of Lagos, southwestern Nigeria. J Ground Water Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100222
Yusuf MA, Abiye TA, Butler MJ, Ibrahim KO (2018) Origin and residence time of shallow groundwater resources in Lagos coastal basin, south-west Nigeria: an isotopic approach. Heliyon 4:e00932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e00932
Zohdy AAR, Martin RJ (1993) A study of seawater intrusion using direct-current soundings in the southern part of the Oxward plain: California, Open-File Report 93-524 U.S Geological Survey 139
Zohdy AAR, Martin PM, Bisdorf RJ (1993) A study of seawater intrusion using direct–current soundings in the southern part of the Oxnard plain, California. Open-File Report 93-524, US Geological Survey 139. https://doi.org/10.3133/ofr93524
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr Oyebade, Mr Kuseju, Mr Adeogun and Mr Agbalaya of the Lagos State Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources for providing geophysical logs. We are very grateful to the Groundwater and Geophysical Services Limited for providing parts of the geophysical logs. The logistic support and useful discussions provided by Mr Ilori of the Lagos State Water Corporation, is highly appreciated. The anonymous reviewers whose comments helped to significantly improve the quality of this manuscript are highly acknowledged.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicting/competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yusuf, M.A., Abiye, T.A., Ibrahim, K.O. et al. Assessment of saltwater–freshwater interactions using water samples and borehole logging information in the Lagos coastal region, Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 80, 679 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09968-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09968-x