Abstract
Little is known about the REEs characteristics and distribution in groundwater in the Simao Basin in southwest China. In this study, hydrochemical analyses and models are used to examine the REE inorganic speciation, characteristics and controls of REE concentrations, and fractionation of spring waters in different types of rocks in the basin. REE contents in the spring waters are relatively low, which are positively correlated with TDS. Relatively high concentrations of REEs are observed in the spring waters in the red beds rather than in the carbonate rocks. Speciation calculations indicate that dissolved REEs mainly composed of LnCO3+ and Ln(CO3)2− complexes (the sum ranging from 30.8 to 98.2%). The carbonate complexes account for a larger proportion in the spring waters in the carbonate rocks than in the red beds. LnSO4+ also accounts for a certain proportion up to 67.5% in the spring waters in the red beds. Relatively low pH and Eh values and high concentration of HCO3 contribute to the REEs enrichment in the groundwater. Carbonate complexation and preferential adsorption may result in the enrichment of MREEs and HREEs. The positive Eu anomalies in the spring waters are related to the interaction of groundwater with the carbonate rocks, because Eu can exist in the Ca site of certain calcium-rich minerals (especially carbonate rocks). The negative Ce anomalies are related to redox conditions. Under the oxidation conditions, Ce3+ is oxidized to Ce4+ and coprecipitates with oxides of iron and manganese in the form of CeO2 or Ce(OH)4.

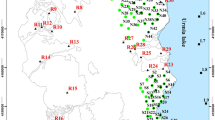
(Modified from Yunnan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources 1990)







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bau M (1999) Scavenging of dissolved yttrium and rare earths by precipitating iron oxyhydroxide: experimental evidence for Ce oxidation, Y–Ho fractionation, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63(1):67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00014-9
Brioschi L, Steinmann M, Lucot E, Pierret MC, Stille P, Prunier J, Badot PM (2013) Transfer of rare earth elements (REE) from natural soil to plant systems: implications for the environmental availability of anthropogenic REE. Plant Soil 366(1–2):143–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1407-0
Dia A, Gruau G, Olivié-Lauquet G, Riou C, Molénat J, Curmi P (2000) The distribution of rare earth elements in groundwaters: assessing the role of source-rock composition, redox changes, and colloidal particles. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64(24):4131–4151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00494-4
Genna D, Gaboury D, Roy G (2014) Evolution of a volcanogenic hydrothermal system recorded by the behavior of LREE and Eu: case study of the Key Tuffite at Bracemac–McLeod deposits, Matagami, Canada. Ore Geol Rev 63:160–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.04.019
Guo H, Zhang B, Wang G, Shen Z (2010) Geochemical controls on arsenic and rare earth elements approximately along a groundwater flow path in the shallow aquifer of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia. Chem Geol 270:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.11.010
He S, Li P, Wu J, Elumalai V, Adimalla N (2019) Groundwater quality under land use/land cover changes: a temporal study from 2005 to 2015 in Xi’an, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1684186
Janssen RPT, Verweij W (2003) Geochemistry of some rare earth elements in groundwater, Vierlingsbeek, The Netherlands. Water Res 37:1320–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00492-X
Johannesson KH, Hendry MJ (2000) Rare earth element geochemistry of groundwaters from a thick till and clay-rich aquitard sequence, Saskatchewan, Canada. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64(9):1493–1509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00402-0
Laul JC, Lepel EA, Smith MR (1988) Trace rare-earth element analysis of briny groundwaters. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 123(1):349–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02036402
Laveuf C, Cornu S, Guilherme LRG, Guerin A, Juillot F (2012) The impact of redox conditions on the rare earth element signature of redoximorphic features in a soil sequence developed from limestone. Geoderma 170:25–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.10.014
Lee SG, Lee DH, Kim Y, Chae BG, Kim WY, Woo NC (2003) Rare earth elements as indicators of groundwater environment changes in a fractured rock system: evidence from fracture-filling calcite. Appl Geochem 18:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00071-9
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2018) Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North–West China. Int J Water Resour Dev 34(3):337–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1443059
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in shallow alluvial aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(7):3133–3145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2691-6
Li P, Tian R, Xue C, Wu J (2017) Progress, opportunities and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(15):13224–13234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8753-7
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2014) Hydrogeochemistry and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the southern part of the Yellow River alluvial plain (Zhongwei section), Northwest China. Earth Sci Res J 18(1):27–38. https://doi.org/10.15446/esrj.v18n1.34048
Liu H, Guo H, Xing L, Zhan Y, Li F, Shao J, Niu H, Liang X, Li C (2016) Geochemical behaviors of rare earth elements in groundwater along a flow path in the North China Plain. J Asian Earth Sci 117:33–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.11.021
Noack CW, Dzombak DA, Karamalidis AK (2014) Rare earth element distributions and trends in natural waters with a focus on groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 48(8):4317–4326. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4053895
Ohta A, Kawabe I (2001) REE(III) adsorption onto Mn dioxide (δ-MnO2) and Fe oxyhydroxide: Ce(III) oxidation by δ-MnO2. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:695–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00578-0
Qu Y, Yuan P, Suai K, Zhang Y, Cai K, Jia S, Chen C (1998) Potash-forming rules and prospect of lower tertiary in Lanping-Simao Basin, Yunnan. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Senera MF, Baba A (2019) Geochemical and hydrogeochemical characteristics and evolution of Kozaklı geothermal fluids, Central Anatolia, Turkey. Geothermics 80:69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2019.02.012
Su F, Wu J, He S (2019) Set pair analysis-Markov chain model for groundwater quality assessment and prediction: a case study of Xi’an City, China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):158–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1568860
Tang J, Johannesson KH (2006) Controls on the geochemistry of rare earth elements along a groundwater flow path in the Carrizo Sand aquifer, Texas, USA. Chem Geol 225(1–2):156–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.09.007
Tang J, Johannesson KH (2010) Rare earth elements adsorption onto Carrizo sand: influence of strong solution complexation. Chem Geol 279(3–4):120–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2010.10.011
Tweed SO, Weaver TR, Cartwright I, Schaefer B (2006) Behavior of rare earth elements in groundwater during flow and mixing in fractured rock aquifers: an example from the Dandenong Ranges, southeast Australia. Chem Geol 234(3):291–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.006
Vázquez-Ortega A, Perdrial J, Harpold A, Zapata-Ríos X, Rasmussen C, McIntosh J, Schaap M, Pelletier JD, Brooks PD, Amistadi MK, Chorover J (2015) Rare earth elements as reactive tracers of biogeochemical weathering in forested rhyolitic terrain. Chem Geol 391:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.10.016
Verplancka PL, Nordstrom DK, Taylor HE, Kimball BA (2004) Rare earth element partitioning between hydrous ferric oxides and acid minewater during iron oxidation. Appl Geochem 19:1339–1354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.01.016
Wang D, Wu J, Wang Y, Ji Y (2019) Finding high-quality groundwater resources to reduce the hydatidosis incidence in the Shiqu County of Sichuan Province, China: analysis, assessment, and management. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00314-y
Willis SS, Johannesson KH (2011) Controls on the geochemistry of rare earth elements in sediments and groundwaters of the Aquia aquifer, Maryland, USA. Chem Geol 285(1–4):32–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.02.020
Wood SA (1990) The aqueous geochemistry of the rare-earth elements and yttrium: 2. Theoretical predictions of speciation in hydrothermal solutions to 350 ℃ at saturation water vapor, pressure. Chem Geol 82(1):159–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(90)90080-Q
Wu J, Zhou H, He S, Zhang Y (2019) Comprehensive understanding of groundwater quality for domestic and agricultural purposes in terms of health risks in a coal mine area of the Ordos basin, north of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 78(15):446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8471-1
Yunnan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (1986) Geology of the saline deposits in Simao District, Yunnan. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Yunnan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (1990) Regional geology of Yunnan Province. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Tan H, Zhang W, Wei H, Dong T (2015) Geochemical constraint on origin and evolution of solutes in geothermal springs in western Yunnan, China. Chemie der Erde 76(1):63–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2015.11.002
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Liu H, Yu M, Hai K, Tan M, Huo D (2019) Hydrogeochemistry, geothermometry, and genesis of the hot springs in the Simao Basin in southwestern China. Geofluids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7046320
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41772261, 41572223).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of the Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Water in Large Basins” guest edited by Peiyue Li and Jianhua Wu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhou, X., Liu, H. et al. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in the hot springs in the Simao Basin in southwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 79, 121 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8883-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8883-y