Abstract
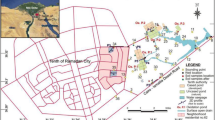
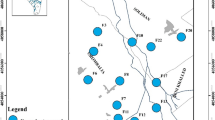
In Tunisia, chemical industries are thought to be the cause of various environmental problems and more particularly the cause of groundwater quality deterioration and contamination. Within this scope, this study assesses the shallow-water quality of the Gabes-North aquifer with regard to the phosphate industry and also to model current and possible future contamination. This allows also the identification of factors that govern the spatial–temporal variation of the main sources of pollution. For that, 60 shallow groundwater samples were collected during the years 2013 and 2014 within and around the industrial chemical phosphate complex of Ghannouche–Gabes. Hydrogeochemical investigation permitted the detection of high concentrations of fluoride and orthophosphates in the sampled waters reaching 12 mg/l and 47 mg/l, respectively. The H2PO4− and F− ion transport model using the Visual MODFLOW software was calibrated and validated by the 2013 and 2014 observed data and was simulated for 6205 days up to the year 2030. The model showed that from 365 to 6205 days, the ions H2PO4− and F− migrated from 100 to 250 m and from 80 to 200 m, respectively, depending on groundwater flow direction. Predictive simulations indicate that the transport rate of these ions can go up to 2.5 times in 2030 compared to those detected in 2014. This integrated investigation in this current study proves that regular pollution constitutes a threat at a given local scale, but can also be used as a reference for reasonable water resources management on a larger scale.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahri A (1998) Wastewater reclamation and reuse in Tunisia. In: Asano T (ed) Wastewater reclamation and reuse, water quality management library, vol 10. Technomic Publishing Co Inc, Lancaster, pp 877–916
Banton OLM (1999) Bangoy Multiscience environnementale des eaux souterraines. Presse de l’Université du Québec Hydrogéologie 460
Barnett B, Townley LR, Post V, Evans RE, Hunt RJ, Peeters L, Boronkay A (2012) Australian groundwater modelling guidelines. National Water Commission, Canberra
Bear J, Beljin MS, Ross RR (1992) Fundamentals of ground-water modelling ground Water Issue, EPA/540/S-92/005, 2–11
Ben Amor R (2007) Géochimie des eaux et des sédiments du littoral Ghannouche- Gabès (Golfe de Gabès), Impact des rejets de phosphogypse. Doc thesis, Univ. FST. Tunis, 189
Ben Baccar B (1982) Contribution à l’étude hydrologique de l’aquifère multicouche de Gabès-Sud. Doc thesis, Univ. Paris–Sud, 116
Ben Cheikh N (2013) Etude des relations hydrodynamiques entre la nappe profonde de Sfax et les systèmes aquifères méridionaux (Menzel Habib et Gabès Nord): Origines et mécanismes de minéralisation des eaux souterraines. Doc thesis, ENIS, Sfax, Tunisia: University of Sfax, 162
Ben Ouezdou H (1983) Etudes morphologique et stratigraphiques des formations quaternaires dans les alentours du golfe de Gabès. Doc thesis, Universitty of Tunis, 220
Bhutiani R, Kulkarni DB, Khanna DR, Gautam A (2016) Water quality, pollution source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of an industrial area in North India. Expo Health 8(1):3–18
Böhlke JK, Mroczkowski SJ, Coplen TB (2003) Oxygen isotopes in nitrate: New reference materials for 18O: 17O: 16O measurements and observations on nitrate-water equilibration. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17(16):1835–1846
Chernet T, Travi Y, Valles V (2001) Mechanism of degradation of the quality of natural water in the Lakes Region of the Ethiopian rift valley. Water Res 35(12):2819–2832
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133(3465):1702–1703
De Filippis G, Margiotta S, Branca C, Negri SL (2019) A modelling approach for assessing the hydrogeological equilibrium of the karst, coastal aquifer of the Salento Peninsula (Southeastern Italy): evaluating the effects of a mar facility for wastewater reuse. Groundwater Qual Mediterr Reg. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5714535
De Windt L, Spycher NF (2019) Reactive transport modeling: a key performance assessment tool for the geologic disposal of nuclear waste. Elements 15(2):99–102
Dhaoui Z, Zouari K, Taupin JD, Farouni R (2016) Hydrochemical and isotopic investigations as indicators of recharge processes of the continental intercalaire aquifer (eastern piedmont of Dahar, southern Tunisia). Environ Earth Sci 75(16):1186
Drever JI (1988) The geochemistry of natural waters, Vol 437, prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Emvoutou HC, Tandia BK, Nkot SNB, Ebonji RC, Nlend YB, Ekodeck GE, Faye S (2018) Geologic factors controlling groundwater chemistry in the coastal aquifer system of Douala/Cameroon: implication for groundwater system functioning. Environ Earth Sci 77(5):219
Falkenmark M, Rockstrom J, Rockström J (2004) Balancing water for humans and nature: the new approach in ecohydrology. Earthscan, p 246. ISBN 1-85383-927-2
Fritz B (1981) Thermodynamic study and modelling of hydrothermal and diagenetic reactions. State Doctorate of sciences, University Louis Pasteur, in French: Etude thermodynamique et modélisation des réactions hydrothermales et diagénétiques. Published in: Sci Géol, Mém., 65, 197
Gauthier C (2002) Contribution to the study of fractionation of free aluminium in solutions of forest soils Faculté des Sciences et Techniques, Université de Limoges Influence of quality and nature of organic matter 156
GCT (2003) Groupe Chimique Tunisien Etude d’impact des rejets de phosphogypse de l’unité de l’acide phosphorique. Internal Report, 191
GCT (2009) Groupe chimique Tunisien. Rapport de reconnaissance géotechnique des sites des usines à Sfax, Skhira et Gabès. Internal report of the Tunisian Phosphate Company, 67, 2009
GCT (2011) GroupeChimiqueTunisien. Rapport complet pour le Lot 1 pour la caractérisation environnementale des sites des usines à Sfax, Skhira et Gabès. Internal report of the Tunisian phosphate company, 84
Gueddari M (1983) Géochimie et thermodynamique des évaporites continentals, étude du lac Natron en Tanzanie et du Chott El Jrid en Tunisie University of Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg Thesis 143
INM (2015) National Institute of Meteorology of Tunisia, climate data report for the period 2005–2015
Jedoui Y, Kallel N, Fontugne M, Ismail HB, M'Rabet A, Montacer M (1998) A high relative sea-level stand in the middle Holocene of southeastern Tunisia. Mar Geol 147(1–4):123–130
Lapworth DJ, Nkhuwa DCW, Okotto-Okotto J, Pedley S, Stuart ME, Tijani MN, Wright J (2017) Urban groundwater quality in sub-Saharan Africa: current status and implications for water security and public health. Hydrogeol J 25(4):1093–1116
Lee L, Helsel D (2005) Statistical analysis of water-quality data containing multiple detection limits: S-language software for regression on order statistics. Comput Geosci 31(10):1241–1248
Li P, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016) Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in and around a mountainous tourist town of China. Expo Health 8(2):239–252
Liu D, Jivkov AP, Wang L, Si G, Yu J (2017) Non-Fickian dispersive transport of strontium in laboratory-scale columns: modelling and evaluation. J Hydrol 549:1–11
Luckner L (2017) Migration Processes in the Soil and Groundwater Zone (1991). CRC Press, Boca Raton
Ma J, Stevens GW, Mumford KA (2018) The performance of diphenyldichlorosilane coated ammonium exchange zeolite and its application in the combination of adsorption and biodegradation of hydrocarbon contaminated ground water. Chem Eng J 347:415–423
Machiwal D, Cloutier V, Güler C, Kazakis N (2018) A review of GIS-integrated statistical techniques for groundwater quality evaluation and protection. Environ Earth Sci 77(19):681
Maliki MA, Krimissa M, Michelot JL, Zouari K (2000) Relation entre nappes superficielles et aquifère profond dans le bassin de Sfax (Tunisie). Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sci-Ser IIA-Earth Planet Sci 331(1):1–6
Mamou A (1990) Caractéristiques et évaluation des ressources en eau du Sud tunisien. Doc thesis, 403
McCance W, Jones OAH, Edwards M, Surapaneni A, Chadalavada S, Currell M (2018) Contaminants of emerging concern as novel groundwater tracers for delineating wastewater impacts in urban and peri-urban areas. Water Res 146:118–133
Melki S, Gueddari M (2018) Impact Assessment of phosphogypsum leachate on groundwater of sfax-agareb (Southeast of Tunisia): using geochemical and isotopic investigation. J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/2721752
Melki S, Asmi E, Mabrouk A, Gueddari M (2019) Inferred Industrial and agricultural activities impact on groundwater quality of Skhira coastal phreatic aquifer in Southeast of Tunisia (Mediterranean Region). Geofluids. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9465498
Mondal NC, Singh VS (2009) Mass transport modeling of an industrial belt using visual MODFLOW and MODPATH: a case study. J Geogra Reg Plan 2(1):001–019
O'Connor D, Hou D, Ok YS, Song Y, Sarmah AK, Li X, Tack FM (2018) Sustainable in situ remediation of recalcitrant organic pollutants in groundwater with controlled release materials: a review. J Control Release 283:200–213
Okere UV, Semple KT (2012) Biodegradation of PAHs in ‘Pristine’ soils from different climatic regions. J Bioremed Biodegrad S1:006. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.S1-006
Padilla I, Irizarry C, Steele K (2011) Historical contamination of groundwater resources in the north coast karst aquifers of Puerto Rico. Revista Dimens 3:7
Panno SV, Hackley KC, Hwang HH, Greenberg SE, Krapac IG, Landsberger S, O'kelly DJ (2006) Characterization and identification of Na–Cl sources in ground water Groundwater 44(2):176–187
Parkhurst D L, Appelo CAJ (2013) Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3: a computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations (No. 6-A43). US Geological Survey
Pavlidis G, Tsihrintzis VA (2018) Environmental benefits and control of pollution to surface water and groundwater by agroforestry systems: a review. Water Resour Manage 32(1):1–29
Rutherford PM, Dudas MJ, Samek RA (1994) Environmental impacts of phosphogypsum. Sci Total Environ 149:1–38
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR, Ishaque W, Kamran MA, Matloob A, Hussain S (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721
Skinner BJ (1979) Earth resources. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76(9):4212–4217
Spitz K, Moreno J (1996) A practical guide to groundwater and solute transport modeling. Wiley, New York
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1970) Aquatic chemistry An introduction emphasizing chemical equilibria in natural water. Wiley Interscience Ed, New York, pp 450
Telahigue F, Agoubi B, Souid F, Kharroubi A (2018) Assessment of seawater intrusion in an arid coastal aquifer, south-eastern Tunisia, using multivariate statistical analysis and chloride mass balance. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 106:37–46
Trabelsi R, Abid K, Zouari K, Yahyaoui H (2012) Groundwater salinization processes in shallow coastal aquifer of Djeffara plain of Medenine. Southeast Tunisia Environ Earth Sci 66(2):641–653
Travi Y (1993) Hydrologie et Hydrochirnie des aquiferes du Sénégal, Hydrogéochimie du fluor dans les eaux souterraines. Mémoire N095, institut de géologie, Université Louis Pasteur de Strabourg et Centre de Géochimie de la surface, CNRS, 1, rue Blessig, F-67084 STRABOURG Cedex France : 155
Turkeltaub T, Kurtzman D, Dahan O (2016) Real-time monitoring of nitrate transport in the deep vadose zone under a crop field–implications for groundwater protection. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20(8):3099–3108
Wolthoorn A, Temminghoff EJ, Van Riemsdijk WH (2004) Effect of synthetic iron colloids on the microbiological NH4+ removal process during groundwater purification. Water Res 38(7):1884–1892
Worthington EB (2013) Arid land irrigation in developing countries: environmental problems and effects. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Zheng C, Wang P (1999) MT3DMS: a modular three-dimensional multispecies transport model for simulation of advection, dispersion, and chemical reactions of contaminants in groundwater systems; documentation and user's guide. Alabama Univ University
Zheng Z, Aagaard P, Breedveld GD (2002) Sorption and anaerobic biodegradation of soluble aromatic compounds during groundwater transport. 1. Laboratory column experiments. Environ Geol 41(8):922–932
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melki, S., Asmi, A.M.E., Sy, M.O.B. et al. A geochemical assessment and modeling of industrial groundwater contamination by orthophosphate and fluoride in the Gabes-North aquifer, Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 79, 135 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8857-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8857-0