Abstract
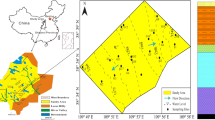
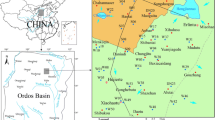
The effects of a water inrush event on the chemical composition of groundwater in a coal measures sandstone aquifer that is important for water supply was investigated at the Taoyuan coal mine in the Huaibei region in China. Changes in groundwater quality caused by the inrush event were investigated using statistical techniques, a Piper trilinear diagram, saturation index, ion combination ratios and a fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method. These investigations indicated that Na+ + K+ and SO42− were the main cation and anion, and the average contents were 272 mg/L and 732 mg/L before water inrush, and 394 mg/L and 779 mg/L after water inrush, respectively. The concentrations of anions in groundwater before the inrush event were in the order SO42− > HCO3− > Cl− and the cation concentrations were in the order Na+ + K+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+. The chemical composition of groundwater was mainly SO4·Cl–Ca·Mg before water inrush event, and SO4·Cl–Na and Na–HCO3–Cl after this event. According to the saturation index method, gypsum, calcite, magnesite, and aragonite controlling the chemical composition of groundwater were reactive minerals in groundwater system. The oxidation of pyrite, dissolution of sulfate and carbonate minerals were main geochemical process before and after the event; while the oxidation of pyrite and cation exchange were enhanced after the water inrush event. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation results showed that the type V water accounted for a large proportion of poor-quality groundwater. Groundwater quality in the aquifer near the mine generally deteriorated after the water inrush event.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brahim FB, Boughariou E, Makni J, Bouri S (2020) Evaluation of groundwater hydrogeochemical characteristics and delineation of geothermal potentialities using multi criteria decision analysis: case of Tozeur region Tunisia. Appl Geochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104504
Chen LW, Gui HR, Yin XX (2011) Monitoring of flow field based on stable isotope geochemical characteristics in deep groundwater. Environ Monit Assess 179:487–498
Chen LW, Xu DQ, Yin XX, Xie WP, Zeng W (2017) Analysis on hydrochemistry and its control factors in the concealed coal mining area in North China: a case study of dominant inrush aquifers in Suxian mining area. J China Coal Soc 42(4):996–1004
Dahiya S, Singh B, Gaur S, Garg VK, Kushwaha HS (2007) Analysis of groundwater quality using fuzzy synthetic evaluation. J Hazard Mater 147:938–946
Deutsch WJ (1997) Groundwater Geochemistry-Fundamentals and Applications to Contamination. CRC Press
Farid I, Trabelsi R, Zouari K et al (2013) Hydrogeochemical processes affecting groundwater in an irrigated land in Central Tunisia. Environ Earth Sci 68:1215–1231
Gui HR, Chen S (2016a) Isotopic geochemical characteristics of groundwater and its geological significance in Sunan mining area. Earth Sci Front 23(3):133–139
Gui H, Lin M (2016b) Types of water hazards in China coalmines and regional Characteristics. Nat Hazards 84:1501–1512
Hui Q, Zhiyuan M (2005) Hydrogeochemistry, Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Jiang Y, Gui H, Yu H et al (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of rivers in different regions of cities: a case study of Suzhou City in Northern Anhui Province China. Water 12:950. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12040950
Karmegam U, Chidambaram S, Prasanna MV et al (2011) A study on the mixing proportion in groundwater samples by using Piper diagram and Phreeqc model. Chin J Geochem 30(4):490–495
Li Z, Zhou B, Teng D, Yang W, Qiu D (2017) Comprehensive evaluation method of groundwater environment in a mining area based on fuzzy set theory. Geosystem Engineering 21:103–112
Lin ML, Gui HR, Peng WH et al (2016) Health risk assessment of health metlas in the groundwater of a coal mining area in Northern Anhui Province China. Nat Environ Poll Technol 15(1):11–18
Liu HH, Cao YQ (2010) Technologies of preventing coal mine water hazards for sustainable development in North China. Geotech Geol Eng 29:1–5
Lloyd JW, Heathcote JA (1985) Natural inorganic hydrogeochemistry in relation to groundwater. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Ma Y, Zhen X, Li Y, Song S (2009) Improvement and application of fuzzy synthetic evaluation of groundwater quality. China Univ Min Technol 38:745–750 ((In Chinese))
Marghade D, Malpe DB, Zade AB (2011) Geochemical characterization of groundwater from northeastern part of Nagpur urban Central India. Environ Earth Sci 62(7):1419–1430
Meybeck M (1987) Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am J Sci 287:401–428
Murkute YA (2014) Hydrogeochemical characterization and quality assessment of groundwater around Umrer coal mine area Nagpur District, Maharashtra India. Environ Earth Sci 72(10):4059–4073
Narany TS, Ramli MF, Aris AZ et al (2014) Identification of the hydro—geochemical processes in groundwater using classic integrated geo—chemical methods and geostatistical techniques, in Amol—Babolplain Iran. Sci World J 2014(2):983–990
Qiu HL, Gui HR, Song QX (2018) Composing characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes and tracing of hydrological cycle in mid-layer groundwater within coal mining area, northern Anhui Province. China Fresen Environ Bull 27:559–566
Schoeller H (1967) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources: methods and techniques of groundwater investigations and development. Water Res 33:54–83
Stephen FR, Mullican WF (1997) Hydrochemical Evolution of Sodium–Sulfate and Sodium–Chloride Groundwater Beneath the Northern Chihuahuan Dezert. Trans-Pecos, Texas. Hydrogeol J 5(2):4–16
Wang H, Jiang XW, Wan L et al (2015) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater flow systems in the discharge area of a river basin. J Hydrol 527:433–441
Wang M, Gui H, Rongjie Hu (2019) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of carboniferous Taiyuan formation limestone water in Sulin Mining Area in Northern Anhui, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:2512
Wu Q (2014) Progress, problems and prospects of prevention and control technology of mine water and reutilization in China. China Coal Soc 39(5):795–805 ((in Chinese))
Xia Y, Gui H, Li J, Guan L (2019) Temporal variability of hydrochemical characteristics and water quality assessment of collapse pond in Zhuxianzhuang coal mining area China. Fresenius Environ Bull 28(1):402–409
Xie F, Zhang YX, Ren Z, Wang H, Ran LX (2014) Application of method of improved fuzzy comprehensive evaluation in assessment of groundwater quality. Water Resour Water Eng 25(125–128):260 ((In Chinese))
Yang X, Hu JL, Liu JS, Luo CH, Zhang Y, Liu FZ, Zhao ZG, Li YA (2018) Hydrogeochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Xianghualing Mining area Hunan Province. Acta Sci Circumstantiae 38(7):2575–2585
Zhang RQ, Liang X, Jin MG et al (2011) General Hydrogeology (The sixth edition). Geological Publishing House, Beijing, pp 59–65
Zhang JT, Shi MZ, Wang GC, Jiang J, Yang BC (2020) Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution law of groundwater in Dachaidan area of Qaidam Basin. Earth Science Front. https://doi.org/10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.6.40
Zhu BQ, Wang XM, Rioual P (2017) Multivariate indicators between environment and ground water recharge in a sedimentary drainage basin in northwestern China. J Hydrol 549:92–113
Acknowledgements
This article is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41773100, 41373095), and School Level Key Scientific Research Project (2020yzd07), and Research on the Teaching Reform of Drilling Engineering Course in Local Applied Colleges(szxy2017jy10), and Research Project of Huaibei Mining Group Co. (2019).The authors would like to thank the National Engineering Research Center of Coal Mine Water Hazard Controlling (Suzhou University). Thanks to Taoyuan Coal Mine of Huaibei Mining Co. Ltd. for providing convenient sampling data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Wei, J., Gui, H. et al. Evaluation of changes in groundwater quality caused by a water inrush event in Taoyuan coal mine, China. Environ Earth Sci 79, 528 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09243-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09243-5