Abstract
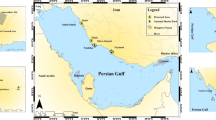
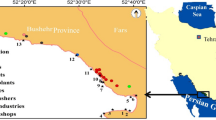
Coastal areas are critical parts of the Persian Gulf with regard to high populations and economically driven activity. They pose major concerns because of the presence of toxic chemicals, and hence harmful effects on marine ecosystems. In this study, 14, 15 and 12 coastal sediment samples were collected in Bushehr province and analyzed, respectively, for potentially toxic elements (PTEs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and microplastics (MPs). The results showed that almost all PTEs were not significantly enriched. Most elements exhibited their highest levels at stations close to urban areas and along the pathway of ships and boats. Based on enrichment factor and statistical evaluations, two main sources of trace elements were identified: anthropogenic (Mo, Cu, Pb, As and Sb) and geogenic (Zn, Ni, Co, Mn, Fe, Cd, Cr and Al). Regarding MPs, a total of 577 pieces were observed with sizes ranging between 500 and 1000 µm. The dominant shape of the MPs was fibrous with the dominant colors being white and black. The concentration of total PAHs were fairly low in the sediments, with their source determined to be pyrogenic in origin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi S, Keshavarzi B (2019) Source identification of total petroleum hydrocarbons and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM10 and street dust of a hot spot for petrochemical production: Asaluyeh County, Iran. Sustain Cities Soc 45:214–230
Abbasi S, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Delshab H, Soltani N, Sorooshian A (2017) Investigation of microrubbers, microplastics and heavy metals in street dust: a study in Bushehr city, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 76(23):798
Abbasi S, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Mahmoudi MR (2018a) Fractionation, source identification and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in street dust of the most important center for petrochemical products, Asaluyeh County, Iran. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7854-z
Abbasi S, Soltani N, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Turner A, Hassanaghaei M (2018b) Microplastics in different tissues of fish and prawn from the Musa Estuary, Persian Gulf. Chemosphere 205:80–87
Agarwal A, Singh R, Mishra S, Bhunya P (2005) ANN-based sediment yield models for Vamsadhara river basin (India). Water SA 31:85–100
Arslan H (2001) Heavy metals in street dust in Bursa, Turkey. J Trace Microprobe Tech 19(3):439–445. https://doi.org/10.1081/TMA-100105058
Ashayeri NY, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Kersten M, Yazdi M, Lahijanzadeh AR (2018) Presence of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments and surface water from Shadegan wetland–Iran: a focus on source apportionment, human and ecological risk assessment and sediment-water exchange. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 148:1054–1066
Barnes DKA, Galgani F, Thompson RC, Barlaz M (2009) Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B: Biol Sci 364(1526):1985–1998
Browne MA, Underwood AJ, Chapman MG, Williams R, Thompson RC, van Franeker JA (2015) Linking effects of anthropogenic debris to ecological impacts. Proc R Soc B: Biol Sci 282(1807):20142929
Bruemer GW, Gerth J, Tiller KG (1988) Reaction kinetics of the adsorption and desorption of nickel, zinc and cadmium by goethite: 1. Adsorption and diffusion of metals. J Soil Sci 39:37–52
Bryan G, Langston W (1992) Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: a review. Environ Pollut 76:89–131
Canesi L, Ciacci C, Bergami E, Monopoli MP, Dawson KA, Papa S, Canonico B, Corsi I (2015) Evidence for immunomodulation and apoptotic processes induced by cationic polystyrene nanoparticles in the hemocytes of the marine bivalve Mytilus. Mar Environ Res 111:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2015.06.008
Chabukdhara M, Nema AK (2012) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in Hindon River sediments: a chemometric and geochemical approach. Chemosphere 87:945–953
Cheng H, Li M, Zhao C, Yang K, Li K, Peng M, Yang Z, Liu F, Liu Y, Bai R (2015) Concentrations of toxic metals and ecological risk assessment for sediments of major freshwater lakes in China. J Geochem Explor 157:15–26
Chopra AK, Pathak C (2015) Accumulation of heavy metals in the vegetables grown in wastewater irrigated areas of Dehradun, India with reference to human health risk. Environ Monit Assess 187:445
Dai L, Wang L, Li L, Liang T, Zhang Y, Ma C, Xing B (2018) Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake in China. Sci Total Environ 621:1433–1444
Delistraty D (1997) 16 A critical review of the application of toxic equivalency factors to carcinogenic effects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in mammals. PAHs Relat Compd Biol 3:311
Desforges JPW, Galbraith M, Ross PS (2015) Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the northeast Pacific ocean. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69:e330
dos Santos IF, Ferreira SLC, Domínguez C, Bayona JM (2018) Analytical strategies for determining the sources and ecotoxicological risk of PAHs in river sediment. Microchem J 137:90–97
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) (2005) Predicting toxicity to amphipods from sediment chemistry. EPA/600/R–04/030, Washington DC
Fendall LS, Sewell MA (2009) Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar Pollut Bull 58(8):1225–1228
Frias JPGL, Sobral P, Ferreira AM (2010) Organic pollutants in microplastics from two beaches of the Portuguese coast. Mar Pollut Bull 60(11):1988–1992
Gallagher A, Rees A, Rowe R, Stevens J, Wright P (2016) Microplastics in the Solent estuarine complex, UK: an initial assessment. Mar Pollut Bull 102(2):243–249
Gauquie J, Devriese L, Robbens J, De Witte B (2015) A qualitative screening and quantitative measurement of organic contaminants on different types of marine plastic debris. Chemosphere 138:348–356
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis 1. Methods of soil analysis: part 1—physical and mineralogical methods, (methodsofsoilan1), pp 383–411
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
Hidalgo-Ruz V, Gutow L, Thompson RC, Thiel M (2012) Microplastics in the marine environment: a review of the methods used for identification and quantification. Environ Sci Technol 46(6):3060–3075
Hong W-J, Jia H, Li Y-F, Sun Y, Liu X, Wang L (2016) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and alkylated PAHs in the coastal seawater, surface sediment and oyster from Dalian, Northeast China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 128:11–20
Hu N, Shi X, Liu J, Huang P, Liu Y, Liu Y (2010) Concentrations and possible sources of PAHs in sediments from Bohai Bay and adjacent shelf. Environ Earth Sci 60:1771–1782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0313-0
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C, Siegler TR, Perryman M, Andrady A, Narayan R, Law KL (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347:768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352
Jiries AG, Hussein HH, Halaseh Z (2001) The quality of water and sediments of street runoff in Amman, Jordan. Hydrol Process 15(5):815–824. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.186
Keshavarzi B, Abbasi HS, Moore F, Delshab H, Soltani N (2017) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in street dust of Bushehr City, Iran: status, source, and human health risk assessment. Polycyclic Aromat Compd 30:1–15
Keshavarzi B, Hassanaghaei M, Moore F, Mehr MR, Soltanian S, Lahijanzadeh AR, Sorooshian A (2018a) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in three commercial fish species in the Persian Gulf. Mar Pollut Bull 129(1):245–252
Keshavarzi B, Abbasi S, Moore F, Mehravar S, Sorooshian A, Soltani N, Najmeddin A (2018b) Contamination level, source identification and risk assessment of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in street dust of an important commercial center in Iran. Environ Manag 62(4):803–818
Khan S, Cao Q, Zheng YM, Huang YZ, Zhu YG (2008) Health risks of heavy metals in contaminated soils and food crops irrigated with wastewater in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut 152(3):686–692
Kim KH, Jahan SA, Kabir E, Brown RJ (2013) A review of airborne polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and their human health effects. Environ Int 60:71–80
Leite NF, Peralta-Zamora P, Grassi MT (2011) Distribution and origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from an urban river basin at the Metropolitan Region of Curitiba, Brazil. J Environ Sci 23:904–911
Liu M, Cheng SB, Ou DN, Hou LJ, Gao L, Wang LL, Xie YS, Yang Y, Xu SY (2007) Characterization, identifcation of road dust PAHs in central Shanghai Areas, China. Atmos Environ 41(38):8785–8795
Liu S et al (2016) Levels, sources and risk assessment of PAHs in multi-phases from urbanized river network system in Shanghai. Environ Pollut 219:555–567
Long ER, Field LJ, MacDonald DD (1998) Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environ Toxicol Chem 17(4):714–727
Long ER, MacDonald DD, Severn CG, Hong CB (2000) Classifying probabilities of acute toxicity in marine sediments with empirically derived sediment quality guidelines. Environ Toxicol Chem 19(10):2598–2601
Malferrari D, Brigatti MF, Laurora A, Pini S (2009) Heavy metals in sediments from canals for water supplying and drainage: mobilization and control strategies. J Hazard Mater 161:723–729
Manno Emanuela, Varrica Daniela, Dongarrà Gaetano (2006) Metal distribution in road dust samples collected in an Urban Area close to a petrochemical plant at Gela. Sicily. Atmos Environ 40(30):5929–5941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.020 (Pergamon)
Nisbet C, LaGoy P (1992) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 16:290–300
Pan K, Wang WX (2012) Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci Total Environ 421:3–16
Paul-Pont I, Lacroix C, Fernandez CG, Hegaret H, Lambert C, Le Goïc N, Frere L, Cassone A-L, Sussarellu R, Fabioux C, Guyomarch J, Albentosa M, Huvet A, Soudant P (2016) Exposure of marine mussels Mytilus spp. to polystyrene microplastics: toxicity and influence on fluoranthene bioaccumulation. Environ Pollut Barking Essex 1987(216):724–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.06.039
Peng C-Y, Korshin GV, Valentine RL, Hill AS, Friedman MJ, Reiber SH (2010) Characterization of elemental and structural composition of corrosion scales and deposits formed in drinking water distribution systems. Water Res 44(15):4570–4580
Qi L, Gregoire DC (2000) Determination of trace elements in twentysix Chinese geochemistry reference materials by inductively coupled plasma-mass spec trometry. Geostand Geoanal Res 24:51–63
Qiu Q, Peng J, Yu X, Chen F, Wang J, Dong F (2015) Occurrence of microplastics in the coastal marine environment: first observation on sediment of China. Mar Pollut Bull 98:274–280
Raissy M, Ansari M (2011) In vitro antimicrobial effect of silver nanoparticles on Lactococcus garvieae and Streptococcus iniae. African J Microbiol Res 5(25):4442–4445
Ramachandra TV, Sudarshan PB, Mahesh MK, Vinay S (2018) Spatial patterns of heavy metal accumulation in sediments and macrophytes of Bellandur wetland, Bangalore. J Environ Manag 206:1204–1210
Ribeiro F, Garcia AR, Pereira BP, Fonseca M, Mestre NC, Fonseca TG, Ilharco LM, Bebianno MJ (2017) Microplastics effects in Scrobicularia plana. Mar Pollut Bull 122:379–391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.06.078
Rocha-Santos T, Duarte AC (2015) A critical overview of the analytical approaches to the occurrence, the fate and the behavior of microplastics in the environment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 65:47–53
Rochman CM, Hentschel BT, Teh SJ (2014) Long-term sorption of metals is similar among plastic types: implications for plastic debris in aquatic environments. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85433
Schwientek M, Rügner H, Scherer U, Rode M, Grathwohl P (2017) A parsimonious approach to estimate PAH concentrations in river sediments of anthropogenically impacted watersheds. Sci Total Environ 601–602:636–645
Shaw BJ, Handy RD (2011) Physiological effects of nanoparticles on fish: a comparison of nanometals versus metal ions. Environ Int 37(6):1083–1097
Sprovieri M et al (2007) Heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biphenyls in surface sediments of the Naples harbour (southern Italy). Chemosphere 67(5):998–1009
Sussarellu R, Suquet M, Thomas Y, Lambert C, Fabioux C, Pernet MEJ, Goïc NL, Quillien V, Mingant C, Epelboin Y, Corporeau C, Guyomarch J, Robbens J, Paul-Pont I, Soudant P, Huvet A (2016) Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:2430–2435. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1519019113
Tiwari M, Sahu SK, Pandit GG (2017) Distribution of PAHs in different compartment of creek ecosystem: ecotoxicological concern and human health risk. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 50:58–66
Turner A (2010) Marine pollution from antifouling paint particles. Mar Pollut Bull 60:159–171
Turner A, Holmes LA (2015) Adsorption of trace metals by microplastic pellets in fresh water. Environ Chem 12(5):600–610
Van Cauwenberghe L, Devriese L, Galgani F, Robbens J, Janssen CR (2015) Microplastics in sediments: a review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Mar Environ Res 111:5–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2015.06.007
Von Moos N, Burkhardt-Holm P, Kohler A (2012) Uptake and effects of micro- € plastics on cells and tissue of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an experimental exposure. Environ Sci Technol 46:11327–11335. https://doi.org/10.1021/es302332w
Wang W, Huang M-J, Kang Y, Wang H-S, Leung AOW, Cheung KC, Wong MH (2011) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Urban surface dust of Guangzhou, China: status, sources and human health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 409(21):4519–4527
Wang J et al (2017) Microplastics in the surface sediments from the Beijiang River littoral zone: composition, abundance, surface textures and interaction with heavy metals. Chemosphere 171:248–258
Wegner A, Besseling E, Foekema EM, Kamermans P, Koelmans AA (2012) Effects of nanopolystyrene on the feeding behavior of the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.). Environ Toxicol Chem SETAC 31:2490–2497. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.1984
Xiang N et al (2018) Occurrence and distribution of Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in seawater, sediments and corals from Hainan Island, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 152:8–15
Yongming H, Peixuan D, Junji C, Posmentier ES (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355:176–186
Yuan GL, Liu C, Chen L, Yang Z (2011) Inputting history of heavy metals into the inland lake recorded in sediment profiles: Poyang Lake in China. J Hazard, Mater, pp 185–345
Yuan GL, Sun TH, Han P, Li J, Lang XX (2014) Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: typical urban renewal area in Beijing. J Geochem Explor 136:40–47
Yunker MB, Macdonald RW, Vingarzan R, Mitchell RH, Goyette D, Sylvestre S (2002) PAHs in the Fraser River Basin: a critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org Geochem 33(4):489–515
Zakaria MP, Mahat AA (2006) Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAHs) in sediments in the Langat Estuary. International Coastal Research Center, Ocean Research Institute, the University of Tokyo
Zeng Q, Jeppesen E, Gu X, Mao Z, Chen H (2018) Distribution, fate and risk assessment of PAHs in water and sediments from an aquaculture-and shipping-impacted subtropical lake, China. Chemosphere 201:612–620
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Bushehr Environmental Protection Office. The authors wish to express their gratitude to the Research Committee and Medical Geology Center of Shiraz University for logistic and technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, S., Keshavarzi, B., Moore, F. et al. Geochemistry and environmental effects of potentially toxic elements, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and microplastics in coastal sediments of the Persian Gulf. Environ Earth Sci 78, 492 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8420-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8420-z