Abstract
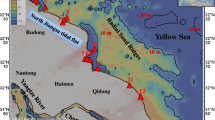
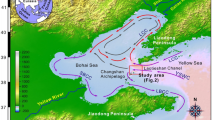
In 2014, three sediment cores were collected from the northern [Xinyanggang (XYG)], middle [Chuandonggang (CDG)], and southern [Xiaoyangkou (XYK)] parts of the coastal tidal flats of the North Jiangsu radial sand ridges (NJRSR), East China. The grain size and contents of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cr, Ni, Pb and As) in the cores were detected. The features of sediments and the accumulation of heavy metals were also investigated. Multivariate analyses (principal component analysis and correlation analysis) were applied to identify the sources of heavy metals. The enrichment factors (EF) were calculated to estimate the level of contamination stored in these sediments. The results showed that the vertical variations in the contents of heavy metals were compatible with the sedimentary features. The grain size in core XYG became coarser around the 1980s and the contents of heavy metals began to decrease. The grain size in core CDG was suddenly refined around the 1960s and the contents of heavy metals suddenly decreased. The grain size in core XYK coarsened initially before becoming finer and the contents of heavy metals were basically stable. The contents of heavy metals of the NJRSR coastal tidal flat were subject to the sedimentary parent materials of the abandoned Yellow River Delta and the offshore radial sand ridges. Several heavy metals were disturbed by anthropogenic activities after the middle and late 1980s. The content of Cr in core XYG was mainly from industries. The contents of Pb and Zn in core CDG were from agricultural, urban and industrial sources. Cu and As in XYK were from agricultural and industrial sources. The environment of sediments in the study area was generally good, but was polluted by individual elements after industrialisation. Cr in core XYG was moderately and significantly polluting, Pb and Zn in core CDG were lightly polluting, Cu was moderately and significantly polluting, and As was lightly polluting in core XYK.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bárcena JF, Claramunt I, García-Alba J (2017) A method to assess the evolution and recovery of heavy metal pollution in estuarine sediments: past history, present situation and future perspectives. Mar Pollut Bull 124(1):421–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.07.070
Barringer JL, Bonin JL, Deluca MJ et al (2007) Sources and temporal dynamics of arsenic in a New Jersey watershed, USA. Sci Total Environ 379(1):56–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.03.006
Bolan N, Adriano D, Mahimairaja S (2004) Distribution and bioavailability of trace elements in livestock and poultry manure by-products. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 34(3):291–338. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643380490434128
Chang IS, Kim BH (2007) Effect of sulfate reduction activity on biological treatment of hexavalent chromium [Cr (VI)] contaminated electroplating wastewater under sulfate-rich condition. Chemosphere 68(2):218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.01.03
Chen HM, Zheng CR, Tu C et al (1999) Heavy metal pollution in soils in China: status and countermeasures. Ambio 28(2):130–134
Chen J, Wang YG, Zhang RS (2007) Stability study on the Dongsha sandbanks in submarine radial sand ridges field off Jiangsu coast. The Ocean Engineering 25(1):105–113. https://doi.org/10.16483/j.issn.1005-9865.2007.01.017
Chen KF, Lu PD, Wang YH (2009) Effects of coastline changes on tide system of Yellow Sea off Jiangsu coast, China. China Ocean Engineering 23(4):741–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-92779-2-24
Chen J, Wang YG, Cai H (2010a) Profile characteristics study of the Jiangsu coastal area. Ocean Eng 28(04):90–96. https://doi.org/10.16483/j.issn.1005-9865.2010.04.009
Chen KF, Lu PD, Wang YH (2010b) Hydrodynamic mechanism of evolvement trends in radial sandbank of South Yellow Sea. Adv Water Sci 21(2):267–273. https://doi.org/10.14042/j.cnki.32.1309.2010.02.002
Chen KF, Wang YH, Lu PD (2013) Research on the abandoned Huanghe River Delta erosion process and impaction tidal current dynamic characteristic of the Huanghai Sea off the coast of North Jiangsu, China. Ac Oceano Sin 35(3):189–196. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2013.03.022
Chen B, Wang YG, Huang HM (2015) Feature analysis of whole suspended sediment transport on radial sand ridges of South Yellow Sea. Mar Sci Bull 34(3):310–315. https://doi.org/10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2015.03.010
Chen KF, Zheng JH, Zhang C (2017) The evolution characteristics of main waterways and their control mechanism in the radial sand ridges of the southern Yellow Sea. Ac Oceano Sin 36(3):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1042-y
Chester R, Stoner JH (1973) Pb in particulates from the lower atmosphere of the Eastern Atlantic. Nature 245(5419):27–28. https://doi.org/10.1038/245027b0
Cobelogarcía A, Prego R (2003) Heavy metal sedimentary record in a Galician Ria (NW Spain): background values and recent contamination. Mar Pollut Bull 46(10):1253–1262. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-326x(03)00168-1
Fatoba PO, Ogunkunle COO, Folarin OO (2016) Heavy metal pollution and ecological geochemistry of soil impacted by activities of oil industry in the Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environ Earth Sci 75(4):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5145-5
Gao YY (2011) Modern sedimentation rates and pollution of heavy metals at the estuary of the Sheyang River. Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing (in Chinese)
Gao S, Zhu DK (1988) The profile of Jiangsu’s mud coast. J Nanjing Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 24(1):75–84
Gąsiorek M, Kowalska J, Mazurek R (2017) Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal pollution in topsoil of historical urban park on an example of the Planty Park in Krakow (Poland). Chemosphere 179:148–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.106
Ge F, Cao D, Li D (1997) The ecological risk analysis of pesticide use and its reduction strategies in China. China Plant Grotection 17(2):35–37
Han YM, Du PX, Cao JJ et al (2006) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci Total Environ 355(1–3):176–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.02.026
Harikrishnan N, Ravisankar R, Chandrasekaran A et al (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in marine sediments of east coast of Tamil Nadu affected by different pollution sources. Mar Pollut Bull 121(1–2):418–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.05.047
Irabien MJ, Velasco F (1999) Heavy metals in Oka River sediments (Urdaibai National Biosphere Reserve, northern Spain): Lithogenic and anthropogenic effects. Environ Geol 37(1–2):54–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050360
Jahan S, Strezov V (2018) Comparison of pollution indices for the assessment of heavy metals in the sediments of seaports of NSW, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 128:295–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2018.01.036
Li Y, Li HG (2017) Historical records of trace metals in core sediments from the Lianyungang coastal sea, Jiangsu, China. Mar Pollut Bull 116(1–2):56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.12.063
Li CX, Zhang QJ, Fan DD et al (2001) Holocene regression and the tidal radial sand ridge system formation in the Jiangsu coastal zone, east China. Mar Geol 173(1–4):97–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-3227(00)00169-9
Li MJ, Liu ZW, Chen YC et al (2016a) Characteristics of iron corrosion scales and water quality variations in drinking water distribution systems of different pipe materials. Water Res 106:593–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.10.044
Li ML, Yang L, Gong XL (2016b) The geomorphologic response of accreting intertidal flat to reclamation: a case from Jianggang, Jiangsu. Mar Sci Bull 35(6):683–693:. https://doi.org/10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2016.06.011
Liu YL, Wang YP, Wu XB (2011) Mechanism of water and suspended sediment transport in the Xiyang channel along the southwestern Yellow Sea coast. Mar Sci 35(11):120–127. https://doi.org/10.11821/yj1989020001
Liu ZY, Pan SM, Sun ZY (2015) Heavy metal spatial variability and historical changes in the Yangtze River estuary and North Jiangsu tidal flat. Mar Pollut Bull 98(1–2):115–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.006
Lv JS (2015) The environmental geochemistry of heavy metal in soils and sediments in typical regions of Jiangsu coastal zone, Eastern China. Nanjing University, Nanjing, pp 112–113 (in Chinese)
Lv JS, Liu Y, Zhang ZL et al (2015) Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in soils of Ju country (Eastern China) using multivariate and geostatistical approach. J Soils Sediments 15(1):163–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-014-0937-x
Marine pollution baseline survey team of Jiangsu province (2001) Marine pollution baseline survey report of Jiangsu Province. Nanjing, China. Hehai University Press, China (in Chinese)
Meng K (2018) Study on modern sedimentary characteristics and temporal and spatial distribution of heavy metals in the sediments of coastal tidal flats in the north Jiangsu radial sand ridges. Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (1989) Summary of rural economic statistics by county in China. China Statistics Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (1992–2011) Statistical bulletin of national economic and social development of China (in Chinese)
National Bureau of Statistics of China (1999) China statistical yearbook. China Statistical Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Nethaji S, Kalaivanan R, Viswam A et al (2017) Geochemical assessment of heavy metals pollution in surface sediments of Vellar and Coleroon estuaries, southeast coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull 115(1–2):469–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.11.045
Nguyen TT, Zhang WG, Li Z et al (2016) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in Red River surface sediments, Vietnam. Mar Pollut Bull 113(1–2):513–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.08.030
Nicholson FA, Chambers BJ, Williams JR et al (1999) Heavy metal contents of livestock feeds and animal manures in England and Wales. Bioresour Technol 70(1):23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-8524(99)00017-6
Ouki SK, Neufeld RD (1997) Use of activated carbon for the recovery of chromium from the industrial wastewater. J Chem Tech Biotechnol 70(1):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.199749275
Peerzada N, Rohoza W (1989) Some heavy metals in sediments from Darwin Harbour, Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 20(2):91–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(89)90234-8
Rao WB, Mao CP, Wang YG et al (2015) Geochemical constraints on the provenance of surface sediments of radial sand ridges off the Jiangsu coastal zone, East China. Mar Geol 359(4):35–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2014.11.007
Ren SR, Shao YC, Wang ZX (2005) Analyze on heavy metals content of merchandise compost produced by animal wastes. J Agro-environmental Sci 24:216–318. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1672-2043.2005.z1.051
Rumpa S, Rumki N, Bidyut S (2011) Sources and toxicity of hexavalent chromium. J Coord Chem 64(10):1782–1806. https://doi.org/10.1080/00958972.2011.583646
Shafie NA, Aris AZ, Zakaria MP et al (2013) Application of geoaccumulation index and enrichment factors on the assessment of heavy metal pollution in the sediments. J Environ Sci Health Part A 48(2):182–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934529.2012.717810
Sindern S, Tremöhlen M, Dsikowitzky L et al (2016) Heavy metals in river and coast sediments of the Jakarta Bay region (Indonesia)-Geogenic versus anthropogenic sources. Mar Pollut Bull 110(2):624–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.06.003
Song H, Liu J, Yin P (2017) Distribution, enrichment and source of heavy metals in Rizhao offshore area, southeast Shandong Province. Mar Pollut Bull 119(2):175–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.04.017
Soto-Jiménez MF, Páez-Osuna F (2001) Distribution and normalization of heavy metal concentrations in mangrove and lagoonal sediments from Mazatlán harbor (Se gulf of California). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 53(3):259–274. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.2000.0814
Sreekanth A, Mrudulrag SK, Cheriyan E et al (2015) Trace metal enrichment and organic matter sources in the surface sediments of Arabian Sea along southwest India (Kerala coast). Mar Pollut Bull 101(2):938–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.10.040
Summers JK, Wade TL, Engle VD et al (1996) Normalization of metal concentrations in estuarine sediments from the Gulf of Mexico. Estuaries 19(3):581–594. https://doi.org/10.2307/1352519
Sutherland RA (2000) Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ Geol 39(6):611–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002540050473
Wang YH (2006) Variations and overall protection of the abandoned yellow river delta in the coastal erosion process [doctoral dissertation].Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University;40p(in Chinese)
Wang R, Zhang YZ, Xia F (2012a) Grain size distribution and transportation treads of bottom sediments in the sand ridge field of the south Yellow sea, China. Marine Geology Quaternary Geology 32(6):1–8. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1140.2012.06001
Wang YP, Gao S, Jia JJ (2012b) Sediment transport over an accretional intertidal flat with influences of reclamation, Jiangsu coast, China. Mar Geo291: 147–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2011.01.004
Wang WH, Gao S, Xu YP (2014) Numerical experiments for the characteristic deposition rates over the tidal flat, central Jiangsu coast. Nanjing: Journal of Nanjing University 50:656–664. https://doi.org/10.13232/j.cnki.jnju.2014.05.014
Wang J, Liu GJ, Lu LL et al (2015) Geochemical normalization and assessment of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Ni) in sediments from the Huaihe River, Anhui, China. Catena 129:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.02.008
Wang AJ, Bong CW, Xu YH et al (2017a) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surficial sediments from a tropical river-estuary-shelf system: A case study of Kelantan River, Malaysia. Mar Pollut Bull 125(1–2):492–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.08.010
Wang Y, Ling M, Liu RH et al (2017b) Distribution and source identification of trace metals in the sediment of Yellow River Estuary and the adjacent Laizhou Bay. Physics Chemistry of the Earth Parts A/B/C 97:62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2017.02.002
Wei GJ, Liu Y, Li XH (2008) Climatic impact on Al, K, Sc and Ti in marine sediments: Evidence from ODP Site 1144, South China Sea. Geochem J 37(5):593–602. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.37.593
Wu GH, Shang JM, Pan L (2014) Heavy metals in surface sediments from nine estuaries along the coast of Bohai Bay, Northern China. Mar Pollut Bull 82(1–2):194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.02.033
Wu SS, Yang H, Guo F (2017) Spatial patterns and origins of heavy metals in Sheyang River catchment in Jiangsu, China based on geographically weighted regression. Sci Total Environ 580:1518–1529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.137
Xing F, Wang YP, Wang HV (2012) Tidal hydrodynamics and fine-grained sediment transport on the radial sand ridge system in the southern Yellow Sea. Mar Geol 291–294:192–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2011.06.006
Xu M, Li PY, Lu PD (2012) Research on appropriate reclamation scale of prograding tidal flat: A case study of Jiangsu Province. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Xu G, Liu J, Pei SF (2014) Distribution and source of heavy metals in the surface sediments from the near-shore area, north Jiangsu Province, China. Mar Pollut Bull 83(1):275–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.03.041
Xu FJ, Hu BQ, Yuan SQ (2018) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the continental shelf of the South Yellow Sea and East China Sea: sources, distribution and contamination. Catena 160:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.09.022
You KY, WangY WXY (1998) Foraminiferal distribution and its indications of sedimentation environment in the bottom sediments of radial submarine sand ridges along North Jiangsu. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences) 34(6):650–654. https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/15/3/016
Yu WJ, Zou XQ, Zhu DK (2007) Accumulation characteristics of heavy metal Pb, Cu, Zn in Wanggang tidal flat based on Renyi theory. Acta Ecol Sin 27(8):3162–3171. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2032(07)60071-7
Zhang Y (1990) A study of characteristics and sources of clay minerals of sediments in coastal areas of Jiangsu Province. Mar Sci 04:34–42
Zhang L (2016) The coastal erosion—deposition evolution and controlling factors of the abandoned Yellow River delta in northern Jiangsu Province. East China Normal University, Shanghai (in Chinese)
Zhang RS, Chen CJ (1992) Study on evolution of sandbars off Jiangsu coast and prospects of land consolidation with Tiaozini. Ocean press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang L, Chen S (2012) Spatial and temporal variation in sediment distribution in the abandoned Yellow River delta of north Jiangsu. Marine Geology Quaternary Geology 32(3):11–19. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1140.2012.03011
Zhang J, Liu C (2002) Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 54:1051–1070. https://doi.org/10.1006/ecss.2001.0879
Zhang WG, Ma HL, Ye LP (2012) Magnetic and geochemical evidence of Yellow and Yangtze River influence on tidal flat deposits in northern Jiangsu Plain, China. Mar Geol 319–322(2):47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2012.07.002
Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhang F et al (2013) Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 74(1):403–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpo1bul.2013.06.019
Zhang L, Chen SL, Liu XX (2014) Evolution of the abandoned Huanghe River delta in north Jiangsu Province in 800 years. Oceanlogia et Limnologia Sinica 45(3):626–636. https://doi.org/10.11693/hyhz20130228002
Zhang L, Chen SL, Yi L (2016) The sediment source and transport trends around the abandoned Yellow River Delta, China. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 34(5):440–449. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2015.1025928
Zhou LY, Liu J, Saito Y et al (2014) Coastal erosion as a major sediment supplier to continental shelves: example from the abandoned Old Huanghe (Yellow River) delta. Cont Shelf Res 82(3):43–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2014.03.015
Zhou Z, Coco G, Mick VDW et al (2015) Modeling sorting dynamics of cohesive and non-cohesive sediments on intertidal flats under the effect of tides and wind waves. Con Shelf Res 104:76–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2015.05.010
Zhu QG, Feng ZX, Xu X (2014) Evolution of tidal flat profiles under the influence of land reclamation in Jiangsu Province. Marine Geology Quaternary Geology 34(3):21–29. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1140.2014.03021
Zhu L, Liu JW, Xu SG et al (2017) Deposition behavior, risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in reservoir sediments of Northeast China. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 142:454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.04.039
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41373112).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, K., Xu, M., Zhao, Y. et al. Accumulation, sources and pollution of heavy metals in the sediments of coastal tidal flats in the North Jiangsu Radial Sand Ridges, China. Environ Earth Sci 78, 128 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8125-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8125-3