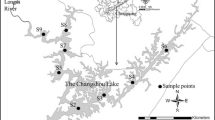
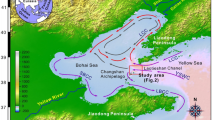
Abstract
Heavy metals in sediments from the tidal flats of northern Nantong are investigated for the first time. Twelve sediment cores were analyzed to learn the vertical profiles of heavy metals. Averagely, the sediment cores contain 67.77 mg/kg of Cr, 20.13 mg/kg of Cu, 61.95 mg/kg of Zn, 0.13 mg/kg of Cd, 16.49 mg/kg of Pb, 7.36 mg/kg of As, and 0.005 mg/kg of Hg. To assess the contamination levels of heavy metals, geo-accumulation index (Igeo) and enrichment factor (EF) values were calculated. The Igeo values of heavy metals range from −6.721 to 0.957, showing that most sediments are in uncontaminated condition and a few are moderately contaminated by heavy metals. EF values of most samples are smaller than 1.5, which indicates that most heavy metals in the samples are from natural weathering processes. Also, Pearson correlation coefficients and principal component analysis is applied to find out the sources of the heavy metals. The correlation further indicates that Pb, As, and Hg are likely from natural weathering processes while Cu, Cr, and Zn have both natural and a small portion of anthropogenic sources. Additionally, anthropogenic sources such as vehicles and agricultural irrigations mainly contribute to the slight Cd contamination in Haimen tidal flats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aendo P, Thongyuan S, Songserm T, Tulayakul P (2019) Carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in duck eggs and meat as a warning scenario in Thailand. Sci Total Environ 689:215–222
Ali I, Aboul-Enein HY (2002) Speciation of arsenic and chromium metal ions by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography. Chemosphere. 48(3):275–278
Ali I, Alharbi OML, Tkachev, Galunin A, Grachev E (2018) Water tre atment by new-generation graphene materials: hope for bright future. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(18):7315–7329
Ali I, Alharbi OML, ALOthman ZA, Al-Mohaimeed AM, Alwarthan A (2019a) Modeling of fenuron pesticide adsorption on CNTs for mechanistic insight and removal in water. Environ Res 170:389–397
Ali I, Alharbi OML, ALOthman ZA, Alwarthan A, Al-Mohaimeed M (2019b) Preparation of a carboxymethylcellulose-iron composite for uptake of atorvastatin in water. Int J Biol Macromol 132:244–253
Ali I, Basheer AA, Mbianda XY, Burakov A, Galunin E, Burakova I, Mkrtchyan E, Tkachev A, Grachev V (2019c) Graphene based adsorbents for remediation of noxious pollutants from wastewater. Environ Int 127:160–180
Al-Shaalan N, Ali I, ALOthman Z, Al-Wahaibi LH, Alabdulmonem H (2019) High performance removal and simulation studies of diuron pesticide in water on MWCNTs. J Mol Liq 289:111039
Bai J, Xiao R, Cui B, Zhang K, Wang Q, Liu X, Gao H, Huang L (2011) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ Pollut 159:817–824
Barbieri M (2016) The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. J Geol Geophys 5:1
Barbieri M, Nigro A, Sappa G (2015) Soil contamination evaluation by enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index. Senses Sci:94–97
Basheer AA (2017) Chemical chiral pollution: impact on the society and science and need of the regulations in the 21st century. Chirality 30:402–406
Chen Z, Kostasnuck R, Yang M (2001) Heavy metals on the tidal flats in the Yangtze Estuary, China. Environ Geol 40(6):742–749
Chen HY, Teng YG, Lu SJ, Wang YY, Wang JS (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512-513:143–153
Dawson EJ, Macklin MG (1998) Speciation of heavy metals in floodplain and flood sediments: a reconnaissance survey of the Aire Valley, West Yorkshire, Great Britain. Environ Geochem Health 20(2):67–76
Gao X, Chen C (2012) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res 46:1901–1911
Gao W, Du Y, Gao S, Ingels J, Wang D (2016) Heavy metal accumulation reflecting natural sedimentary processes and anthropogenic activities in two contrasting coastal wetland ecosystems, eastern China. J Soils Sediments 16:1093–1108
Huang L, Pu X, Pan JF, Wang B (2013) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of Swan Lake lagoon and Rongcheng Bay in the northern Yellow Sea. Chemosphere 93:1957–1964
Jaishankar M, Tseten T, Anbalagan N, Mathew BB, Beeregowda KN (2014) Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip Toxicol 7(2):60–72
Li QS, Wu ZF, Chu B, Zhang N, Cai SS, Fang JH (2007) Heavy metals in coastal sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ Pollut 149:158–164
Li GG, Hu BQ, Bi JQ, Leng QN, Xiao CQ, Yang ZC (2013) Heavy metals distribution and contamination in surface sediments of the coastal Shandong Peninsula (Yellow Sea). Mar Pollut Bull 76:420–426
Liu ZY, Pan SM, Sun ZY, Ma RF, Chen LH, Wang YL, Wang SA (2015) Heavy metal spatial variability and historical changes in the Yangtze River estuary and North Jiangsu tidal flat. Mar Pollut Bull 98:115–129
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China) (2009) Background value of soil environment in China. China environmental monitoring press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Murray NJ, Phinn SR, DeWitt M, Ferrari R, Johnston R, Lyons MB, Clinton N, Thau D, Fuller RA (2019) The global distribution and trajectory of tidal flats. Nature 565:222–225
Qiao Y, Yang Y, Gu J, Zhao J (2013) Distribution and geochemical speciation of heavy metals in sediments from coastal area suffered rapid urbanization, a case study of Shantou Bay, China. Mar Pollut Bull 68:140–146
Qiu J, Liu J, Li M, Wang S, Bai W, Zhang D (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the nearshore zone, southern Jiangsu Province, China. Mar Pollut Bull 133:281–288
Salomons W, Forstner U (2012) Metals in the hydrocycle. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang L, Hu S, Yu G, Ma M, Liao M (2017) Comparative study on magnetic minerals of tidal flat deposits from different sediment sources in Jiangsu coast, Eastern China. Stud Geophys Geod 61:754–771
Wang YY, Peng BH, Wei G, Elahi E (2019) Comprehensive evaluation and spatial difference analysis of regional ecological carrying capacity: a case study of the Yangtze River urban agglomeration. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(18):3499–3514
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36(1):169–182
Yuan HM, Song JM, Li XG, Li N, Duan LQ (2012) Distribution and contamination of heavy metals in surface sediments of the South Yellow Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 64:2151–2159
Zeng H, Wu J (2013) Heavy metal pollution of lakes along the mid-lower reaches of the Yangtze River in China: intensity, sources and spatial patterns. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10:793–807
Zhang W, Yu L, Hutchinson SM, Xu S, Chen Z, Gao X (2001) China’s Yangtze Estuary: I. Geomorphic influence on heavy metal accumulation in intertidal sediments. Geomorphology 41:195–205
Zhang W, Feng H, Chang J, Qu J, Xie H, Yu L (2009) Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of Yangtze River intertidal zone: an assessment from different indexes. Environ Pollut 157:1533–1543
Zhang R, Zhou L, Zhang FZ, Ding YJ, Gao JR, Chen J, Yan HQ, Shao W (2013) Heavy metal pollution and assessment in the tidal flat sediments of Haizhou Ba, China. Mar Pollut Bull 74:403–412
Zhang M, He P, Qiao G, Huang J, Yuan X, Li Q (2019) Heavy metal contamination assessment of surface sediments of the Subei Shoal, China: spatial distribution, source apportionment and ecological risk. Chemosphere 223:211–222
Zhuang QF, Li G, Liu ZY (2018) Distribution, source and pollution level of heavy metals in river sediments from South China. Catena 170:386–396
Zhuo H, Fu S, Liu H, Song H, Ren L (2019) Soil heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment associated with development zones in Shandong, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:30016–30028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05979-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Amjad Kallel
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 4152 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Zhang, G., Peng, X. et al. Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the tidal flat sediments of Nantong, East China. Arab J Geosci 14, 416 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06814-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06814-z