Abstract
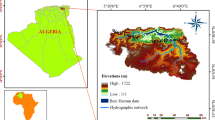
An understanding of erosive processes and the washing away of sediments to watersheds is an essential tool for decision makers planning water resource use. This study assessed the potential for surface runoff due to natural attributes together with land use/land cover to highlight the potential for accelerated erosion in the Araras River Watershed (352.77 km2) at a 1:50,000 scale. The analytic hierarchy process was used with the data provided to combine geoenvironmental attributes (soil, rock, water, relief and land use/land cover) that trigger erosive processes. Just over 51 % of the basin area presented an average potential for surface runoff, while 76.5 % presented a low to average potential for accelerated erosion. Despite this, upstream areas used for water collection for Araras city show a medium to high potential for surface runoff and accelerated erosion, reducing water infiltration and recharge, and resulting in the silting of reservoirs and water quality damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar ADC (1995) Mapeamento geotécnico da folha de Conchal, SP. Escala 1:50,000. São Carlos. M.S. thesis. Curso de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia. Escola de Engenharia de São Carlos. Departamento de Geotecnia. Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil, p 125 (in Portuguese)
Aksoy H, Kavvas ML (2005) A review of hillslope and watershed scale erosion and sediment transport models. Catena 64(2–3):247–271
Alves AC (2007) Estudo da interação de vinhoto com uma argila de baixa plasticidade da região do município de Campos dos Goytacazes—RJ. Rio de Janeiro. M.S. thesis. Centro de Ciência e Tecnologia. Departamento de Engenharia Civil. Universidade Estadual Norte Fluminense, Brazil, p 75 (in Portuguese)
Assunção JC, Cunha SB (2009) Relações entre o Crescimento Urbano Desordenado e a Qualidade das Águas Fluviais na Cidade do Rio de Janeiro [Relations between Urban Growth Disorder and Quality of River Waters in the City of Rio de Janeiro]. 13th Simpósio Brasileiro de Geografia Física Aplicada, Viçosa/MG. A Geografia e as Dinâmicas de Apropriação da Natureza. Cópias and Cópias, pp 01-14, Viçosa, Minas Gerais, Brazil (in Portuguese)
Bertoni J, Lombardi Neto A (1999) Conservação do solo [soil conservation]. Icone, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Bigarella JJ, Mazuchowski JZ (1985) Visão integrada da problemática da erosão [Integrated view the erosion problem]. In: 3th Simpósio Nacional De Controle De Erosão, Maringá. Livro Guia. Maringá: ABGE, Maringá, Paraná, Brazil (in Portuguese)
Blodgett D, Hoopes J (2010) Impacts of radar indicated rainfall on distributed rainfall-runoff modeling. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 136(10):1448–1458
Brollo MJ (1991) Mapeamento geotécnico da quadrícula de Araras, SP. Escala 1:50,000. São Carlos. M.S. thesis. Curso de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia. Escola de Engenharia de São Carlos. Departamento de Geotecnia. Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil, p 88 (in Portuguese)
Chen CN, Tsai CH, Tsai CT (2006) Simulation of sediment yield from watershed by physiographic soil erosion–deposition model. J Hydrol 327(3–4):293–303
Christofoletti A (1974) Geomorfologia [Geomorphology], Edgard Blücher, Ed. da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil (in Portuguese)
Costa CW, Piga FG, Moraes MCP, Dorici M, Sanguinetto EC, Lollo JA, Moschini LE, Lorandi R, Oliveira LJ (2015) Fragilidade ambiental e escassez hídrica em bacias hidrográficas: Manancial do Rio das Araras—Araras, SP [Environmental Fragility and water scarcity in catchment basins: Headwaters of Araras River—Araras, SP]. Revista Brasileira de Recursos Hídricos, vol 20, no 4, October/December (in Portuguese)
Coulthard TJ, Hancock GR, Lowry JBC (2012) Modelling soil erosion with a downscaled landscape evolution model. Earth Surf Proc Land 37(10):1046–1055
Da Silva AM, Alvares CA, Watanabe CW (2011) Natural Potential for Erosion for Brazilian Territory, Soil Erosion Studies. http://www.intechopen.com/books/soil-erosion-studies/natural-potential-for-erosion-for-brazilian-territory. Accessed on 05 Sept 2015
Da Silva RM, Santos CAG, Silva VCL, Silva LP (2013) Erosivity, surface runoff, and soil erosion estimation using GIS-coupled runoff–erosion model in the Mamuaba catchment, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 185(11):8977–8990
Environmental Systems Research Institute (ESRI) (2013) ArcGIS for the desktop 10.2
Folley JA, Defries R, Asner GP, Barford C, Bonan G, Carpenter SR, Chapin FS, Coel MT, Daily GC, Gibbs HK, Helkowski JH, Holloway T, Howard EA, Kucharik CJ, Mondreda C, Patz JA, Prentice C, Ramankutty N, Snyder PK (2005) Global consequences of land use. Science 309(5734):570–574
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) (2011) The state of the world’s land and water resources for food and agriculture (SOLAW)—managing systems at risk. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome and Earthscan, London
Gabarrón-Galeote MA, Martínez-Murillo JF, Quesada MA, Ruiz-Sinoga JD (2013) Seasonal changes of the soil hydrological and erosive response in contrasted Mediterranean eco-geomorphological conditions at patch scale. Soil Earth Discuss 5:1423–1460
Gross JA, Stuetzle CS, Chen Z, Cutler B, Franklin WR, Zimmie TF (2010) Simulating levee erosion with physical modeling validation. In: The 5th international conferrence on scour and erosion (ICSE 2010), San Fransisco, CA
Guerra AJT, Fullen MA, Jorge MCO, Alexandre ST (2014) Soil erosion and conservation in Brazil. Anuário do Instituto de Geociências UFRJ 37(1):81–91
Hasui Y (2012) Compartimentação Geológica do Brasil [Geological subdivision of the Brazil]. In: Hasui Y, Carneiro CDR, De Almeida FFM, Bartorelli A (eds) Geologia do Brasil [Brazil’s geology]. Beca, São Paulo, pp 112–122 (in Portuguese)
Hrissanthou V (2005) Estimate of sediment yield in a basin without sediment data. Catena 64(2–3):333–347
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE) [Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics] (1971) Cartas topográficas. Folhas Topográficas de Leme (SF-23-Y-A-II-1), Araras (SF-23-Y-A-II-3) e Conchal—SF-23-Y-A-II-4. Escala 1:50,000 (in Portuguese)
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE) [Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics] (2005) Resolução Nº 1/2005. Estabelece o Sistema de Referência Geocêntrico para as Américas (SIRGAS) [Resolution No. 1/2005. Establishes the Geocentric Reference System for the Americas (SIRGAS)]. Brasília, Brazil
Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas do Estado de São Paulo (IPT) [São Paulo State Institute of Technological Research] (1981) Mapa Geomorfológico do Estado de São Paulo [Geomorphological map of the State of São Paulo]. São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais (INPE) (National Institute for Space Research) TOPODATA, banco de dados geomorfométricos do Brasil (TOPODATA, geomorphometric database of the Brazil). http://www.dsr.inpe.br/topodata/index.php. Accessed on May 18, 2015 (in Portuguese)
Jinno K, Tsutsumi A, Alkaeed O, Saita S, Berndtsson R (2009) Effects of land-use change on groundwater recharge model parameters. Hydrol Sci J 54(2):300–315
Leh M, Bajwa S, Chaubey I (2011) Impact of land use change on erosion risk: an integrated remote sensing, geographic information system and modeling methodology. Land Degrad Dev 24(5):409–421
Lenhart C, Brooks K, Magner J, Suppes B (2010) Attenuating excessive sediment and loss of biotic habitat in an intensively managed midwestern agricultural watershed. In: Innovations in watershed management under land use and climate change. Proceedings of the 2010 watershed management conference, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, 23–27 August 2010. American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), pp 333–342
Lepsch IF (2010) Formação e Conservação dos Solos [formation and conservation soil], 2nd edn. Oficina de Textos, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Libardi PL (2005) Dinâmica da água no solo [Water dynamics in soil]. EDUSP, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Lima CA, Palácio HAQ, Andrade EM, Santos JCN, Brasil PP (2013) Characteristics of rainfall and erosion under natural conditions of land use in semiarid regions. Rev Bras Eng Agríc Ambient 17(11):1222–1229
Lollo JA (1991) Mapeamento geotécnico da folha de Leme, SP: utilização da geomorfologia para a caracterização preliminar de Unidades Geotécnicas”. São Carlos. M.S. thesis. Curso de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia. Escola de Engenharia de São Carlos. Departamento de Geotecnia. Universidade de São Paulo, p 87 (in Portuguese)
Lollo JA, Sena JN (2013) Establishing erosion susceptibility: analytical hierarchical process and traditional approaches. Bull Eng Geol Environ 72(3–4):589–600
Mendonça F, Danni-Oliveira IM (2007) Climatologia: noções básicas e climas do Brasil [Climatology: basic notions and Brazil’s climate]. Oficina de Textos, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Merritt WS, Letcher RA, Jakeman AJ (2003) A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environ Model Softw 18(8–9):761–799
Merten GH, Araújo AG, Barbosa GMC, Conte O (2015) No-till surface runoff and soil losses in southern Brazil. Soil Tillage Res 152:85–93
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment (2005) Ecosystems and human well-being: synthesis. Island Press, Washington. http://www.millenniumassessment.org/documents/document.356.aspx.pdf. Accessed on 10 Sept 2015)
Morgan RPC, Quinton JN, Smith RE, Govers G, Poesen JWA, Auerswald K, Chisci G, Torri D, Styczen ME (1998) The European soil erosion model (EUROSEM): a dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf Proc Land 23:527–544
Palm C, Sanches P, Ahamed S, Awiti A (2007) Soils: a contemporary perspective. Ann Rev Environ Resour 32:99–129
Pejon OJ (1992) Mapeamento geotécnico da folha de Piracicaba-SP (escala 1:100,000): estudo de aspectos metodológicos, de caracterização e de apresentação dos atributos. São Carlos. Doctoral thesis. Curso de Pós-Graduação em Engenharia. Escola de Engenharia de São Carlos. Departamento de Engenharia Civil. Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil, p 224 (in Portuguese)
Pourghasemi HR, Pradhan B, Gokceoglu C (2012) Application of fuzzy logic and analytical hierarchy process (AHP) to landslide susceptibility mapping at Haraz watershed, Iran. Nat Hazards 63(2):965–996
Raposo AA, Barros LFP, Junior APM (2010) O uso de taxas de turbidez da bacia do Alto Rio das Velhas—Quadrilátero Ferrífero/MG—como indicador de pressões humanas e erosão acelerada. Revista de Geografia UFPE—DCF/NAPA, v. especial VIII SINAGEO (3): 34–50 (in Portuguese)
Rocha BP, Michette JF, Zuquette LV (2014) Uso do DPL e do geoprocessamento como suporte na avaliação da variabilidade da resistência da camada superficial de solo arenoso. In: Proceedings of 17th Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Geotécnica. Associação Brasileira de Mecânica dos Solos e Engenharia Geotécnica. Goiânia (in Portuguese)
Saad R, Koellner T, Margni M (2013) Land use impacts on freshwater regulation, erosion regulation, and water purification: a spatial approach for a global scale level. Int J Life Cycle Assess 18(6):1253–1264
Salgado AAR, Magalhães Júnior AP (2006) Impactos da Silvicultura de Eucalipto no aumento das taxas de turbidez das águas fluviais: o caso de mananciais de abastecimento público de Caeté/MG. Geografias 2:47–57 (in Portuguese)
Santos MS, Santos ER, Dos Santos KR (2013) Ocupação na Bacia do Córrego Cesários em Anápolis (GO) e os processos erosivos decorrentes (Occupation of basin Cesários River in Anapolis (GO) and the resulting erosive processes). Revista Equador (UFPI) 2(2):189–206
São Paulo (2009) Inventário Florestal da Vegetação Natural do Estado de São Paulo [Forest Inventory of Natural Vegetation the State of Sao Paulo]. IF the State of Sao Paulo, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
São Paulo, Secretaria de Energia e Saneamento, Departamento de Águas e Energia Elétrica (1990) Controle de Erosão: bases conceituais e técnicas; diretrizes para o planejamento urbano e regional; orientação para o controle de voçorocas urbanas [Control of erosion: conceptual and technical bases; guidelines for urban and regional planning; orientation for the control of urban gullies]. DAEE/IPT, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Severiano EC, Oliveira GC, Dias Júnior MS, Castro MB, Oliveira LFC, Costa KAP (2010) Compactação de solos cultivados com cana-de-açúcar: I—modelagem e quantificação da compactação adicional após as operações de colheita [Compaction of soils cultivated with sugarcane: I—modeling and quantification of the additional soil compaction after harvest operations]. Eng Agríc 30(3):404–413 (in Portuguese)
Shi ZH, Fang NF, Wu L, Wang L, Yue BJ, Wu GL (2012) Soil erosion processes and sediment sorting associated with transport mechanisms on steep slopes. J Hydrol 454–455:123–130
Strahler AN (1952) Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. Geol Soc Am Bull 63(11):1117–1142
Tundisi JG, Matsumura-Tundisi TM (2010) Impactos potenciais das alterações do Código Florestal nos recursos hídricos [Potencial impacts of changes in the Forest Law in relation to water resources]. Biota Neotrop 10(4):67–76 (in Portuguese)
United Nations World Water Assessment Programme—WWAP (2015) The United Nations world water development report 2015: water for a sustainable World. UNESCO, Paris
United States Geological Survey (USGS) Imagens LANDSAT. Disponível em: http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/. Acesso em: 22 June 2015
Valeriano MM (2008) Topodata: guia para utilização de dados geomorfológicos locais [Topodata: guide to using local geomorphological data]. Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas Espaciais—INPE-15318-RPQ/818, São José dos Campos, São Paulo (in Portuguese)
Vente J, Poesen J (2005) Predicting soil erosion and sediment yield at the basin scale: scale issues and semi-quantitative models. Earth Sci Rev 71(1–2):95–125
Vente J, Poesen J, Verstraeten G, Govers G, Vanmaercke M, Rompaey AV, Arabkhedri M, Boix-Fayos C (2013) Predicting soil erosion and sediment yield at regional scales: where do we stand? Earth Sci Rev 127:16–29
Vitousek PM, Mooney HA, Lubchenco J, Melillo JM (1997) Human domination of earth’s ecosystems. Science 277(5325):494–499
Zhang L, O`Neill AL, Lacey S (1996) Modelling approaches to the prediction of soil erosion in catchments. Environ Softw 11(1–3):123–133
Zhao G, Mu X, Wen Z, Wang F, Gao P (2013) Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the loess Plateu of China. Land Degrad Dev 24:499–510
Zhou J, Fu B, Gao G, Lü Y, Liu Y, Lü N, Wang S (2016) Effects of precipitation and restoration vegetation on soil erosion in a semi-arid environment in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 137:1–11
Ziadat FM, Taimeh AY (2013) Efect of rainfall intensity, slope, land use and antecedente soil moisture on soil erosion in an arid environment. Land Degrad Dev 24(6):582–590
Zuquette LV, Palma JB, Pejon OJ (2006) Initial assessment of the infiltration and overland flow for different rainfall events in land constituted of sandstones of the Botucatu Formation (Guarani Aquifer), State of São Paulo. Environ Geol 50(3):371–387
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education (CAPES) and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for supporting the development of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorici, M., Costa, C.W., de Moraes, M.C.P. et al. Accelerated erosion in a watershed in the southeastern region of Brazil. Environ Earth Sci 75, 1301 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6102-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6102-7