Abstract
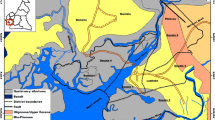
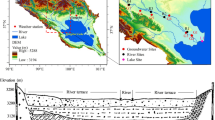
Hanjiang River, the largest tributary of Yangtze, faces environmental pressures from South-to-North Water Transfer project and anthropogenic influences. In order to reveal the chemical characteristics of river and contribution of groundwater to the river along mid-lower reaches of Hanjiang River, field works have been conducted in wet and dry seasons. The major ion compositions are characterized by the dominance of Ca2+, and HCO3 − in surface water and groundwater. As a result, calcite weathering is a dominant process for surface water and groundwater. Additionally, dolomite weathering also contributes to hydrochemical evolution in the groundwater of the basin. Stable isotopes (δ18O, δD) show that both surface and groundwater most probably originate from present-day precipitation. Isotopic of both surface water and groundwater can provide greater confidence in identifying the weathering and extent of interaction processes. It was found that river water was mainly recharged by tributaries in wet season while recharged by groundwater in dry season. Dissolved solute flux from tributaries and groundwater to the river was estimated by water balance budget model and environmental tracer mass balance approach. Tributaries and groundwater contribute to mid-lower reach of Hanjiang River in wet season and dry season, respectively. From section H1 to H9, there were 455.4 kg/s of total dissolved solute (TDS) transferred from tributaries to the main channel and 99.8 kg/s of TDS fluxed from groundwater to river water in dry season.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams S, Titus R, Pietersen K, Tredoux G, Harris C (2001) Hydrochemical characteristics of aquifers near Sutherland in the Western Karoo, South Africa. J Hydrol 241:91–103. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(00)00370-X
Banaszuk P, Wysocka-Czubaszek A, Kondratiuk P (2005) Spatial and temporal patterns of groundwater chemistry in the river riparian zone. Agric Ecosyst Environ 107:167–179. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2004.11.004
Bowling L, Baker P (1996) Major cyanobacterial bloom in the Barwon-Darling River, Australia, in 1991, and underlying limnological conditions. Mar Freshw Res 47:643–657. doi:10.1071/MF9960643
Brennan ST, Lowenstein TK (2002) The major-ion composition of Silurian seawater. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:2683–2700. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00870-0
Chen J, Wang F, Xia X, Zhang L (2002) Major element chemistry of the Changjiang (Yangtze River). Chem Geol 187:231–255. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00032-3
Chetelat B, Liu C-Q, Zhao Z, Wang Q, Li S, Li J, Wang B (2008) Geochemistry of the dissolved load of the Changjiang Basin rivers: anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:4254–4277. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2008.06.013
Cook P, Lamontagne S, Berhane D, Clark J (2006) Quantifying groundwater discharge to Cockburn River, southeastern Australia, using dissolved gas tracers 222Rn and SF6. Water Resour Res. doi:10.1029/2006WR004921
Dalai T, Krishnaswami S, Sarin M (2002) Major ion chemistry in the headwaters of the Yamuna river system: chemical weathering, its temperature dependence and CO2 consumption in the Himalaya. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:3397–3416. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00937-7
Davis JR, Koop K (2006) Eutrophication in Australian rivers, reservoirs and estuaries: a southern hemisphere perspective on the science and its implications. Hydrobiologia 559:23–76. doi:10.1007/s10750-005-4429-2
Dessert C, Dupré B, François LM, Schott J, Gaillardet J, Chakrapani G, Bajpai S (2001) Erosion of Deccan Traps determined by river geochemistry: impact on the global climate and the 87Sr/86Sr ratio of seawater. Earth Planet Sci Lett 188:459–474. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00317-X
Ellins KK, Roman-Mas A, Lee R (1990) Using 222Rn to examine groundwater/surface discharge interaction in the Rio Grande de Manati, Puerto Rico. J Hydrol 115:319–341. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(90)90212-G
Gaillardet J, Dupre B, Allegre CJ, Négrel P (1997) Chemical and physical denudation in the Amazon River Basin. Chem Geol 142:141–173. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00074-0
Genereux D, Pringle C (1997) Chemical mixing model of streamflow generation at La Selva biological station, Costa Rica. J Hydrol 199:319–330. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(96)03333-1
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170:1088–1090. doi:10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Herczeg AL, Simpson HJ, Mazor E (1993) Transport of soluble salts in a large semiarid basin: river Murray, Australia. J Hydrol 144:59–84. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(93)90165-6
Jiongxin X (1996) Channel pattern change downstream from a reservoir: an example of wandering braided rivers. Geomorphology 15:147–158. doi:10.1016/0169-555X(95)00119-P
Kalbus E, Reinstorf F, Schirmer M (2006) Measuring methods for groundwater–surface water interactions: a review. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 10:873–887. doi:10.5194/hess-10-873-2006
Keery J, Binley A, Crook N, Smith JW (2007) Temporal and spatial variability of groundwater–surface water fluxes: development and application of an analytical method using temperature time series. J Hydrol 336:1–16. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.12.003
Lambs L (2004) Interactions between groundwater and surface water at river banks and the confluence of rivers. J Hydrol 288:312–326. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2003.10.013
Li S, Gu S, Liu W, Han H, Zhang Q (2008) Water quality in relation to land use and land cover in the upper Han River Basin, China. Catena 75:216–222. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2008.06.005
Li S, Xu Z, Wang H, Wang J, Zhang Q (2009) Geochemistry of the upper Han River basin, China: 3: anthropogenic inputs and chemical weathering to the dissolved load. Chem Geol 264:89–95. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.02.021
Meredith K, Hollins S, Hughes C, Cendón D, Hankin S, Stone D (2009) Temporal variation in stable isotopes (18O and 2H) and major ion concentrations within the Darling River between Bourke and Wilcannia due to variable flows, saline groundwater influx and evaporation. J Hydrol 378:313–324. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.09.036
Meybeck M (1987) Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am J Sci 287:401–428. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00031-5
Moon S, Huh Y, Qin J, van Pho N (2007) Chemical weathering in the Hong (Red) River basin: rates of silicate weathering and their controlling factors. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:1411–1430. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2006.12.004
Negrel P, Allègre CJ, Dupré B, Lewin E (1993) Erosion sources determined by inversion of major and trace element ratios and strontium isotopic ratios in river water: the Congo Basin case. Earth Planet Sci Lett 120:59–76. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(93)90023-3
Ojiambo SB, Lyons WB, Welch KA, Poreda RJ, Johannesson KH (2003) Strontium isotopes and rare earth elements as tracers of groundwater–lake water interactions, Lake Naivasha, Kenya. Appl Geochem 18:1789–1805. doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00104-5
Panda DK, Mishra A, Jena S, James B, Kumar A (2007) The influence of drought and anthropogenic effects on groundwater levels in Orissa, India. J Hydrol 343:140–153. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.06.007
Qin J, Huh Y, Edmond JM, Du G, Ran J (2006) Chemical and physical weathering in the Min Jiang, a headwater tributary of the Yangtze River. Chem Geol 227:53–69. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.09.011
Sami K (1992) Recharge mechanisms and geochemical processes in a semi-arid sedimentary basin, Eastern Cape, South Africa. J Hydrol 139:27–48. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(92)90193-Y
Scanlon BR, Healy RW, Cook PG (2002) Choosing appropriate techniques for quantifying groundwater recharge. Hydrogeol J 10:18–39. doi:10.1007/s10040-001-0175-3
Scibek J, Allen DM, Cannon AJ, Whitfield PH (2007) Groundwater–surface water interaction under scenarios of climate change using a high-resolution transient groundwater model. J Hydrol 333:165–181. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.08.005
Simpson H, Herczeg A (1991) Stable isotopes as an indicator of evaporation in the River Murray, Australia. Water Resour Res 27:1925–1935. doi:10.1029/91WR00941
Sophocleous M (2002) Interactions between groundwater and surface water: the state of the science. Hydrogeol J 10:52–67. doi:10.1007/s10040-001-0170-8
Tizro AT, Voudouris K (2008) Groundwater quality in the semi-arid region of the Chahardouly basin, West Iran. Hydrol Process 22:3066–3078. doi:10.1002/hyp.6893
Tsujimura M et al (2007) Stable isotopic and geochemical characteristics of groundwater in Kherlen River basin, a semi-arid region in eastern Mongolia. J Hydrol 333:47–57. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.07.026
Xiao J, Jin ZD, Zhang F, Wang J (2012) Solute geochemistry and its sources of the groundwaters in the Qinghai Lake catchment, NW China. J Asian Earth Sci 52:21–30. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.02.006
Xu Z, Shi C, Tang Y, Han H (2011) Chemical and strontium isotopic compositions of the Hanjiang Basin Rivers in China: anthropogenic impacts and chemical weathering. Aquat Geochem 17:243–264. doi:10.1007/s10498-011-9132-5
Zhou Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Zwahlen F, Boillat J (2013) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of central Jianghan Plain. China Environ Earth Sci 68:765–778. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1778-9
Zhu Y, Zhang H, Chen L, Zhao J (2008) Influence of the South-North Water Diversion Project and the mitigation projects on the water quality of Han River. Sci Total Environ 406:57–68. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.08.008
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professor Song Xianfang and Dr. Zhang Bing form Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Science for the analysis of hydrogen and oxygen isotope.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Tang, C., Han, Z. et al. Hydrochemical characteristic and interaction process of surface and groundwater in mid-lower reach of Hanjiang River, China. Environ Earth Sci 75, 418 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5175-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5175-z