Abstract
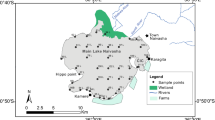
This research presents a detailed study which was performed to infer the quantity of metal (Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Cu and Fe) contents in sediments of Daye Lake, Central China. The geo-accumulation (I geo) and potential ecological risk (PER) of these metals were assessed. The results reveal that: (1) the mean value of I geo ranked an order of Fe (class 6) > Cd (class 5) > Pb (class 3) > Zn (class 2) > Cr (Class 1) > Cu (Class 0); (2) Potential ecological risk (PER) values calculated for all these metals at different sampled points in Daye Lake exceeded the value of very high risk. Multivariate statistical analyses were carried out to determine the relationship between these six metals and to identify the possible pollution sources, with the results suggesting that the metal content in the sediments has three patterns: the first pattern includes Pb, Cd and Cr which were mainly present due to discharged water by smelting industries; second pattern contains Zn and Cu which mainly originated from the waste residue of the copper mining industry; the third pattern is Fe which is mainly related to mine tailing leaches. This study indicates very high metal content levels in the sediments, which may have adverse risks (average PER = 7,771.62) for the lake’s ecosystem and human beings associated with Daye Lake.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
An YJ, Kampbell DH (2003) Total, dissolved, and bioavailable metals at Lake Texoma marinas. Environ Pollut 122(2):253–259
Blowes D (1997) The environmental effects of mine wastes. Fourth decennial international conference on mineral exploration
Cai H-s, Chao-hui T et al (1998) Research on water pollution and its background remote sensing in Daye Lake. Geol Surv Saf 4:3 (in Chinese)
Chen H, Ouyang J et al (2003) Status quo of and counter measures for Cd contamination of farm land in the vicinity of Daye smeltery. Soil 35(1):76–79
Cheng SP (2003) Heavy metal pollution in China: origin, pattern and control. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10(3):192–198
Fördtner U, Whitman GTW (1981) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Berlin, Springer
Fytianos K, Lourantou A (2004) Speciation of elements in sediment samples collected at lakes Volvi and Koronia, N. Greece. Environ Int 30(1):11–17
Guo G, Wu F et al (2012) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China. J Environ Sci 24(3):410–418
Hakanson L (1980) An Ecological Risk Index for aquatic pollution-control—a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14(8):975–1001
He L (2009) Study on flotation copper sulfide minerals from Daye tailings. Wuhan Science and Technology University, Master
He Y, Hu Y et al (2011) Analysis on the source of heavy metals in the Dagang River, Daye County, Hubei Province. Geochimica 40(3):258–265 (in Chinese)
Huang Z, Lin Q (1990) Analyze research on residents’ death rate in heavy metal pollution area of Daye county Hubei Province. Journal Tongji medical science university 19(4):283–285 (in Chinese)
Ke Y (2012) Heavy metal pollution status in the main river/creeks of Daye City. China Sci Technol Rev, pp 180–181 (in Chinese)
Keskin TE, Toptas S (2012) Heavy metal pollution in the surrounding ore deposits and mining activity: a case study from Koyulhisar (Sivas-Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 67(3):859–866
Li ZH, Zhang YD (2010) Study on the water pollution control of Daye Lake. Chinese Science Press, Beijing
Li G, Liu G et al (2012) Spatial distribution and multiple sources of heavy metals in the water of Chaohu Lake, Anhui, China. Environ Monit Assess 184(5):2763–2773
Ling Q, Yan S et al (2006) The environmental pollution character and its ecological effect of a large scale smelter. China Environ Sci 26(5):603–608
Liu H, Li W (2011) Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River region, China. Environ Earth Sci 62(7):1503–1511
Liu B, Hu K et al (2010) Distribution and enrichment of heavy metals in a sediment core from the Pearl River Estuary. Environ Earth Sci 62(2):265–275
Liu E, Birch GF et al (2012) Comprehensive evaluation of heavy metal contamination in surface and core sediments of TaihuLake, the third largestfreshwater lake in China. Environ Earth Sci 67(1):39–51
Monteiro FF, Cordeiro RC et al (2012) Sedimentary geochemical record of historical anthropogenic activities affecting Guanabara Bay (Brazil) environmental quality. Environ Earth Sci 65(6):1661–1669
Müler G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geol J 2(3):109–118
Najar IA, Khan AB (2012) Assessment of water quality and identification of pollution sources of three lakes in Kashmir, India, using multivariate analysis. Environ Earth Sci 66(8):2367–2378
Nguyen HL, Leermakers M et al (2005) Heavy metals in Lake Balaton: water column, suspended matter, sediment and biota. Sci Total Environ 340(1–3):213–230
Song Q, Qi S et al (2011) Distribution characteristic and soil pollution status of heavy metal in the soil of Tonglushan region, Daye city. Environ Chem 30(9):1672–1673
Sun Z, Wu Y et al (2009) Study on effective species of heavy metals in lacustrine sediment core from Xijiu Lake, Taihu Lake catchment, China. Environ Earth Sci 59(2):371–377
Suresh G, Ramasamy V et al (2011) Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide concentrations in the river sediments. Appl Radiat Isot 69(10):1466–1474
Suresh G, Sutharsan P et al (2012) Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:117–124
Tao Y, Liu Q et al (2007) Magnetic signature of heavy metals pollution of sediments: case study from the East Lake in Wuhan, China. Environ Geol 52:1639–1650
USEPA (1977) Ecological evaluation of proposed discharge of dredged material into ocean waters.implementation manual for Section 103 of Public Law. Vicksburg, Mississippi, Environmental Effects Laboratory, US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station, pp 95–532
Varol M, Sen B (2012) Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. Catena 92:1–10
Wang L, Wang L (2007) Survey of Cd, PB and As pollution in the water of Donggangqu Trench in Luoqiao, Daye City. Saf Environ Eng 14(1):16–19
Wang H, Zhu Y et al (1981) Study on heavy metal pollution in the sediments of Sanli Qi Lake. J Cent China Norm Univ 1:72–80
Wu S, Zhou S et al (2010) Heavy-metal accumulation trends in Yixing, China: an area of rapid economic development. Environ Earth Sci 61(1):79–86
Ye C, Li S et al (2011) Assessing soil heavy metal pollution in the water-level-fluctuation zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J Hazard Mater 191(1–3):366–372
Yi Y, Yang Z et al (2011) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediment and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in fishes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River basin. Environ Pollut 159(10):2575–2585
Yu T, Zhang Y et al (2012) Characterization of heavy metals in water and sediments in Taihu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 184(7):4367–4382
Zhang X, Hu M (2006) Heavy metal distribution of creek water the its sediments in Tieshan, Daye, Hubei Province. Geol Sci Technol Inf 25(2):89–92 (in Chinese)
Zhang XJ, Hu MA et al (2005) Analysis of the heavy metal pollution in Tieshan district, Daye city. Environ Sci Technol 28(1):40–43
Zhang Y, Hu X et al (2012) Distribution and risk assessment of metals in sediments from Taihu Lake, China using multivariate statistics and multiple tools. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89(5):1009–1015
Zheng L-G, Liu G-J et al (2010) Some potential hazardous trace elements contamination and their ecological risk in sediments of western Chaohu Lake, China. Environ Monit Assess 166:379–386
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Guido Luechter at the Center for Development Research (ZEF), Bonn University for his statistic suggestions; and Mr. Gurnoor Singh for his contribution on improving the language. This work was supported by Chinese National Agricultural Technology Achievements Transform Foundation through the project of “trial the ecological planting coupling technologies based on the resources utilization” (2011GB23320005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Li, Z.H., Chen, J. et al. Assessment of heavy metal contamination status in sediments and identification of pollution source in Daye Lake, Central China. Environ Earth Sci 72, 1279–1288 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3047-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3047-6