Abstract
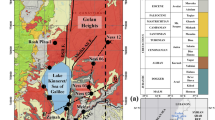
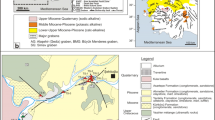
The hydrodynamic groundwater data and stable isotopes of water have been used jointly for better understanding of upward leakage and mixing processes in the Djerid aquifer system (southwestern Tunisia). The aquifer system is composed of the upper unconfined Plio-Quaternary (PQ) aquifer, the intermediate (semi-)confined Complex Terminal (CT) aquifer and the deeper confined Continental Intercalaire (CI) aquifer. A total of 41 groundwater samples from the CT and PQ aquifers were collected during June 2001. The stable isotope composition of waters establishes that the CT deep groundwater (depleted as compared to present Nefta local rainfall) is ancient water recharged during late Quaternary time. The relatively recent water in the shallow PQ aquifer is composed of mixed water resulting from upward leakage and sporadic meteoric recharge. In order to characterize the meteoric input signal for PQ in the study area, rainfall water samples were collected during 4 years (2000–2003) at the Nefta meteorological station. Weighted mean values of isotopic contents with respect to rainfall amounts have been computed. Despite the short collection period in the study area, results agree with those found in Beni Abbes (southwestern Algerian Sahara) by Fontes on 9 years of rainfall surveillance. Stable isotopic relationships provide clear evidence of shallow PQ aquifer replenishment by deep CT groundwater. The 18O/upward leakage rate allowed the identification of distinctive PQ waters related to CT aquifer configuration (confined in the western part of the study area, semi-permeable in the eastern part). These trends were confirmed by the relation 18O/TDS. The isotope balance model indicated a contribution of up to 75% of the deep CT groundwater to the upper PQ aquifer in the western study area, between Nefta and Hazoua.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castany G (1982) Bassin sédimentaire du Sahara septentrional (Algérie-Tunisie)—Aquifères du Continental Intercalaire et du Complexe Terminal. Bulletin Bureau Recherches Géologiques Minières (BRGM). Série 2. 3:127–147
Celle H, Zouari K, Travi Y, Daoud A (2001) Caractérisation isotopique des pluies en Tunisie Essai de typologie dans la région de Sfax. C.R. Acad Sci Paris 6:625–631
Coque R (1962) La Tunisie présaharienne: étude géomorphologique. Armond Colin, Paris
Dlala M, Hfaiedh M (1993) Le seisme du 7 Novembre à Metlaoui (Tunisie méridionale): une tectonique active en compression. C.R. Acad Sci Paris 317(II):1297–1307
Edmunds WM, Shand P, Guendouz AH, Moula A, Mamou A, Zouari K (1997) Recharge characteristics and groundwater quality of the grand Erg oriental basin. Tech Rep Wd/97/46R, IAEA, Vienna
Edmunds WM, Guendouz AH, Mamou A, Moula A, Shand P, Zouari K (2003) Groundwater evolution in the Continental Intercalaire aquifer of southern Algeria and Tunisia: trace element and isotopic indicators. Appl Geochem 18:805–822
Epstein S, Mayeda TK (1953) Variations of 18O content of waters from natural sources. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 4:213–224
Fitts CR (2002) Groundwater science. Academic Press, Amsterdam
Fontes JC (1976) Isotopes du milieu et cycles des eaux naturelles: quelques aspects—Thèse Doctorat. Univ. Paris VI, France
Fontes JC, Edmunds WM (1989) The use of environmental isotope techniques in arid zone hydrology—a critical review. UNESCO. IHP-III Project 5.2, Paris
Gautier M (1953) Les chotts, machines évaporitives complexes. Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS). Colloques Internationaux 35:317–325
Gonfiantini R, Conrad G, Fontes JC, Sauzy G, Payne BR (1974) Etude isotopique de la nappe du Continental Intercalaire et de ses relations avec les autres nappes du Sahara septentrional. In: Isotope techniques in groundwater hydrology 1974. Proceed. Symp. IAEA, Vienna, I:227–241
Guendouz A, Moulla AS, Remini B, Michelot JL (2006) Hydrochemical and isotopic behaviour of a Saharan phreatic aquifer suffering severe natural and anthropic constraints (case of Oued-Souf region, Algeria). J Hydrol 14:955–968
IAEA/GNIP (1999) Global Network of Isotopes in Precipitation. The GNIP Database, Release 3, October 1999. Available at http://www.iaea.org/programs/gnip/gnipmain.htm
Kamel S (2007) Caractérisation hydrodynamique et géochimique des aquifères du Djérid (Sud Tunisien)—Thèse Doctorat, Univ. de Tunis
Kamel S, Dassi L, Zouari K, Abidi B (2005) Geochemical and isotopic investigation of the aquifer system in the Djerid-Nefzaoua basin, southern Tunisia. Environ Geol 49:159–170
Kamel S, Dassi L, Zouari K (2006) Approche hydrogéologique et hydrochimique des échanges hydrodynamiques entre aquifères profond et superficiel du basin du Djérid, Tunisie (Hydrogeological and hydrochemical approach of hydrodynamic exchanges between deep and shallow aquifers in the Djerid basin Tunisia). J Hydrol Sci 51:713–730
Kamel S, Younes H, Chkir N, Zouari K (2008) The hydrogeochemical characterization of ground waters in Tunisian Chott’s region. Environ Geol 54:843–854
Maliki MA (2000) Etude hydrogéologique, hydrochimique et isotopique de système aquifère de Sfax (Tunisie), Thèse Doctorat, Univ. de Tunis II
Mamou A (1989) Caractéristiques et évaluation et gestion des ressources en eau du Sud tunisien—Thèse Doctorat, Univ. de Paris Sud, France
Moumni L (2002) Compte rendu du forage Horchani 2bis. Tech Rep. Direction Générale des Ressources en Eau. Tunis
OSS (2003) Système aquifère du Sahara septentrional. Observatoire du Sahara et du Sahel. UNESCO. Tech. Rep. 9973–856, Tunis
Schulz E, Abichou A, Chkir N, Hachicha T, Pomel S, Salzman U, Zouari K (2002) Sebkhas as ecological archives and the vegetation and landscape history of southeastern Tunisia during the last two millennia. J Afr Earth Sci 34:223–229
Swezey CS (2003) The role of climate in the creation and destruction of continental stratigraphic records : an example from the northern margin of the Sahara Desert. Climate controls on stratigraphy. SEPM Spec Publ 77:207–225
UNESCO (1972) Etude des ressources en eau du Sahara Septentrional. Projet ERESS. Nappe du Complexe Terminal. Tech Rep 6:44
Yurtsever Y, Gat JR (1981) Atmospheric waters. In: Gat JR, Gonfiantini R (eds) Stable isotope hydrology: deuterium and oxygen-18 in the water cycle. Technical Report Series no. 210. IAEA, Vienna, pp 103–139
Zargouni F (1986) Tectonique de l’Atlas méridional de Tunisie, évolution géométrique et cinématique des structures en zones de cisaillement. Thèse Doctorat. Univ. Louis Pasteur Strasbourg, France
Zouari K, Chkir N, Ouda B (2003) Palaeoclimatic variation in Maknassi basin (central Tunisia) during Holocene period using pluridisciplinary approaches. IAEA, Vienna. CN 80-28
Zouari K, Kamel S, Chkir N (2006) Long term dynamic isotope and hydrochemical changes in the deep aquifer of Complex Terminal (Southern Tunisia). IAEA-TECDOC 507:127–156
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamel, S. Recharge of the plio-quaternary water table aquifer in Tunisian chotts region estimated from stable isotopes. Environ Earth Sci 63, 189–199 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0683-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0683-3