Abstract
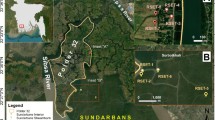
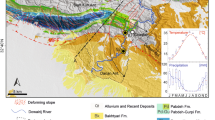
Jiangyin County is in the infamous Su–Xi–Chang land subsidence area caused by excessive groundwater withdrawal in Jiangsu province, China. The maximum accumulated land subsidence reached 1,310 mm near the centre of the subsiding trough in 2006 in southern Jiangyin, and earth fissures of significant vertical offsets have been observed at Changjing, Hetang and Wenlin which form an arc towards the subsidence trough. An ancient Yangtze River course is found underlying and passing through the depression in southern Jiangyin, forming a local basin surrounded by outcropped bedrock ridges in the north and south. The Quaternary stratigraphy demonstrates significant heterogeneities in the basin; the second confined aquifer is much thicker and deeper and encapsulated inside the basin and absent above the ridges. The development of earth fissures along the Changjing–Hetang–Wenlin arc might be a combination of an inward rotation of sediments due to a large differential subsidence, an inward movement driven by seepage force and a steeper slope along the south-eastern shoulder of the basin that facilitates the development of horizontal tensile strain and/or shear strain necessary for fissuring. The land subsidence has slowed down and no new earth fissure zone has occurred in the area after the banning of deep groundwater extraction was enacted in 2001.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin HZ, Djaja R, Darmawan D, Hadi S, Akbar A, Rajiyowiryono H, Sudibyo Y, Meilano I, Kasuma MA, Kahar J, Subarya C (2001) Land subsidence of Jakarta (Indonesia) and its geodetic monitoring system. Nat Hazards 23:365–387
Ayalew L, Yamagishi H, Reik G (2004) Ground cracks in Ethiopian Rift Valley: facts and uncertainties. Eng Geol 75:309–324
Bouwer H (1977) Land subsidence and cracking due to groundwater depletion. Ground Water 15(5):358–364
Chen CX, Pei SP, Jiao JJ (2003) Land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in Suzhou City, China. Hydrogeol J 11:275–287
Chen CT, Hu JC, Lu CY, Lee JC, Chan YC (2007) Thirty-year land elevation change from subsidence to uplift following the termination of groundwater pumping and its geological implications in the Metropolitan Taipei Basin, Northern Taiwan. Eng Geol 95:30–47
Helm DC (1994) Hydraulic forces that play a role in generating fissures at depth. Bull Assoc Eng Geol XXXI(3):293–304
Holzer TL, Johnson AI (1985) Land subsidence caused by ground water withdrawal in urban areas. GeoJournal 11(3):245–255
Hu JP, Wu SL (1998) Geohydrologic environment issues in Suzhou-Changzhou-Wuxi urban group. Chin J Hydrogeol Eng Geol (4):5–7
Jachens RC, Holtzer TL (1980) Geophysical investigations of ground failure related to groundwater withdrawal, Picacho basin, Arizona. Ground Water 17:574–585
Li CJ, Tang XM, Ma TH (2006) Land subsidence caused by groundwater exploitation in the Hangzhou-Jiaxing-Huzhou Plain, China. Hydrogeol J 14:1652–1665
Phien-wej N, Giao PH, Nutalaya P (2006) Land subsidence in Bangkok, Thailand. Eng Geol 82(4):187–201
Riley FS (1969) Analysis of borehole extensometer data from central California. In: Proceedings of Tokyo symposium of land subsidence, Tokyo, pp 423–431
Rojas E, Arzate J, Arroyo M (2002) A method to predict the group fissuring and faulting caused by regional groundwater decline. Eng Geol 65:245–260
Sheng Z, Helm DC, Li J (2003) Mechanism of earth fissuring caused by groundwater withdrawal. Environ Eng Geosci IX(4):351–362
Shi XQ, Xue YQ, Ye SJ, Wu JC, Zhang Y, Yu J (2007) Characterization of land subsidence induced by groundwater withdrawals in Su–Xi–Chang area, China. Env Geol 52:27–41
Shi XQ, Xue YQ, Wu JC, Ye SJ, Zhang Y, Wei ZX, Yu J (2008) Characterization of regional land subsidence in Yangtze Delta, China: the example of Su–Xi–Chang area and the city of Shanghai. Hydrogeol J 16:593–607
Wang Z (1998) Sustainable development suffering overexploitation of groundwater - Land subsidence and its conflicting in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area, Jiangsu Province. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 9(2):18–26
Wang GY, Shi B, Wang XM, Wu SL, Wu JQ (2009a) Land subsidence and earth fissuring in south Jiangyin. Chin J Hydrogeol Eng Geol 36(2):117–122
WangGY, You G, Shi B, Qiu ZL, Li HY, Tuck M (2009a) Earth fissures in Jiangsu Province, China and geological investigation of Hetang Earth Fissure. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0167-5
Wang GY, You G, Shi B, Yu J, Li HY, Zong KH (2009b) Earth fissures triggered by groundwater withdrawal and coupled by geological structures in Jiangsu Province, China (DOI 10.1007/s00254-008-1390-1). Env Geol 57(5):1047–1054
Wang GY, You G, Shi B, Yu J, Tuck M (2009c) Long-term land subsidence and strata compression in Changzhou, China. Eng Geol 104(1–2):109–118. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.09.00
Xu YS, Shen SL, Cai ZY, Zhou GY (2008) The state of land subsidence and prediction approaches due to groundwater withdrawal in China. Nat Hazards 45:123–135
Xue YQ, Wu JC, Zhang Y, Ye SJ, Shi XQ, Wei ZX, Li QF, Yu J (2008) Simulation of regional land subsidence in the southern Yangtze Delta. Sci China Ser D Earth Sci 51(6):808–825
Yu J, Wang XM, Su XS, Yu Q (2004) The mechanism analysis on ground fissure disaster formation in Suzhou-Wuxi-Changzhou area. J Jilin Univ (Earth Sci Ed) 34(2):236–241
Zhang Y, Xue YQ, Wu JC, Ye SJ, Wei ZX, Li QF, Yu J (2007a) Characteristics of aquifer system deformation in the Southern Yangtze Delta, China. Eng Geol 90:160–173
Zhang Y, Xue YQ, Wu JH, Yu J, Wei ZX, Li QF (2007a) Land subsidence and earth fissures due to groundwater withdrawal in the Southern Yangtze Delta, China. Environ Geol. doi:10.1007/s00254-007-1028-8
Zhu Q, Gao Z, Guo J (1993) Earth fissures and their genesis analysis in Dongting, Wuxi. Chin J Seismol (3):31–35
Acknowledgments
The study is supported by the cooperative fund—Geological Investigation and Monitoring of Jiangsu Province Environmental Ecosystem (Grant No. 200312300009)—between the Ministry of China National Land Resources and Jiangsu Provincial Government in the sub-project of “Visualized Three Dimensional Geological Modeling of Land Subsidence in Su–Xi–Chang Area”. The authors sincerely thank Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province for their support and Talia Barrett of University of Ballarat for proof reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G.Y., You, G.G., Shi, B. et al. Large differential land subsidence and earth fissures in Jiangyin, China. Environ Earth Sci 61, 1085–1093 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0430-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-009-0430-9