Abstract
Objective
Facial anthropometric data vary significantly within the Indian population due to the racial, ethnic and geographic diversity. The anthropometric data of a given ethnic community may not match the other due to diverse ethnic variations, and hence, this study is intended to review the facial anthropometric data pertaining to the diverse Indian populace through a systematic literature survey.
Materials and Method
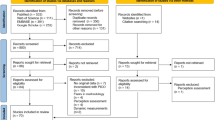
An electronic search done on Medline, Embase and Central databases was utilized to conduct a systematic review of literature. The available data were analyzed based on the various esthetic subunits of the face. The following inclusion criteria were considered: (1) studies depicting the anthropometric data of any ethnic group identified as belonging to India, (2) studies originating from Indian subcontinent, (3) studies which included data of male and female subjects separately and (4) articles in English language only. The following exclusion criteria were considered: (1) atudies conducted on participants with severe malocclusion, developmental craniofacial anomalies, post-traumatic facial deformities or with a history of previous craniofacial or cosmetic surgery, (2) studies which did not specify the anthropometric landmarks used to obtain the measurements, (3) studies in which the statistical analysis was not provided, or if data were grouped across genders and (4) editorials, commentaries, case reports, systematic reviews, meta-analyses and articles not available in English language.
Results
Twenty-one articles met the inclusion criteria. Majority of the Indians, particularly men, seem to have a mesoproscopic facial phenotype. The vertical and horizontal facial dimensions of the Indian male are comparably larger than the Indian female. There is sexual dimorphism among the Indian population with regard to the upper and lower thirds of the face, with little or no gender difference as regards the middle third of the face. It was observed that the nasal dimensions of the Indian race were not compatible with that of the occidental, oriental or the western race. The overall facial structure and the upper half of the face were critical in determining facial attractiveness in Indian males while the lower half of the face and the mandibular contour were critical in determining facial attractiveness in females.
Conclusion
It is observed that there is a paucity of facial anthropometric data for the Indian population considering the ethnic, racial and geographic diversity. Since the prevalence of craniofacial anomalies and dentofacial deformities in India is high and thus the scope for corrective surgery, it is important to compile baseline facial anthropometric data based on the ethnic diversity of the Indian population.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gomes LDEC, Horta KO, Goncalves JR, Santos-Pinto AD (2014) Systematic review: craniocervical posture and craniofacial morphology. Eur J Orthod 36(1):55–66
Raveendran M (2019) The South Asian facial anthropometric profifile: a systematic review. J Cranio Maxillo Fac Surg 47:263–272
Durtschi RB, Chung D, Gentry LR, Chung MK, Vorperian HK (2009) Developmental craniofacial anthropometry: assessment of race effects. Clin Anat 22(7):800–808
Farkas LG, Katic MJ, Forrest CR (2005) International anthropometric study of facial morphology in various ethnic groups/races. J Craniofac Surg 16(4):615–646
Uppada UK, Sinha R, Madishetti S, Pampana SG, Kumar S, Chidagam PR (2020) Ergonomics among oral and maxillofacial surgeons in the Indian States of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh—an evaluative study. Ann Maxillofac Surg 10:325–329
The World Bank. Available at: https://data.worldbank.org/region/India.[Accessed 21 June 2023]
Uppada UK, Tauro DP, Senthilnathan KP (2023) Patient satisfaction following orthognathic surgery: a systematic review. J Maxillofacial Oral Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-023-02066-4
Uppada UK, Tauro DP, Senthilnathan KP (2023) Is there a need for greater emphasis on clinical facial analysis than cephalometrics & 3D software solutions in the diagnosis and treatment planning of patients with dentofacial deformities? J Maxillofac Oral Surg 22(4):820–826
Uppada UK, Sinha R, Reddy DS, Paul D (2014) Soft tissue changes and its stability as a sequlae to mandibular advancement. Ann Maxillofac Surg 4:132–137
Agarwal AS, Abhyankar S, Juneja M, Borgaonkar A (2022) Anthropometric facial proportions in indian population compared to Caucasian population. J Clin Exp Dermatol Res 13(2):044
Duggal S, Kapoor DN, Verma S, Sagar M, Lee YS, Moon H et al (2016) Photogrammetric analysis of attractiveness in Indian faces. Arch Plast Surg 43:160–171
Gupta S, Narwal A, Kamboj M, Sharma P, Makkar V, Raman RK (2019) Baseline data of facial parameters in the population of Haryana: an anthropometric study. J Forensic Dent Sci 11:28–34
Saurabh R, Piyush B, Sourabh B, Preeti O, Trivedi R, Vishnoi P (2016) Assessment of facial golden proportions among central Indian population. J Int Soc Prevent Communit Dent 6:S182–S186
Tripathi AA, Tandon RP, Hantodkar N (2013) Facial divine proportions in attractive North Indian females: a photographic study. World J Dent 4(1):41–46
Mane DR, Kale AD, Bhai MB, Hallikerimath S (2010) Anthropometric and anthroposcopic analysis of different shapes of faces in group of Indian population: a pilot study. J Forenic Legal Med 17:421–425
Shetti RV, Pai SR, Sneha GK, Gupta C, Chethan P (2011) Study of prosopic (facial) index of Indian and Malaysian students. Int J Morphol 29(3):1018–1021
Mani R (2012) Comparitive study of facial index of pushkarna brahmin community of Bikaner district of Rajasthan and other communities and races. J Anat Soc India 61(2):254–257
Kumar P, Kaur B, Bala M (2020) Anthropometric study of facial morphology in male population of Haryana and Himachal Pradesh. Int J Health Sci Res 10(3):28–31
Prasanna PL, Suresh P, Srinivasan K (2020) Anthropometric study of the facial (prosopic) indices: a proof for gender dimorphism. J Dent Educ 13(2):53–59
Prasanna LC, Bhosale S, D’Souza AS, Mamatha H, Thomas RH, Sachin KS (2013) Facial indices of North and South Indian adults: reliability in stature estimation and sexual dimorphism. J Clin Diag Res 7(8):1540–1542
Chitta M, Malathi L (2023) Facial anthropometric analysis of a representative. Indian J Plast Surg. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-1761596
Chandra HJ, Ravi MS, Sharma SM, Prasad BR (2012) Standards of facial esthetics: an anthropometric study. J Maxillofac Oral Surg 11(4):384–389
Kalra S, Bagga DK, Agrawal P (2015) Evaluation of various anthropometric proportions in Indian beautiful faces: a photographic study. APOS Trends Orthod 5:190–196
Kunjur J, Sabesan T, Illankovan V (2006) Anthropometric analysis of eyebrows and eyelids: an inter-racial study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 44:89–93
Vasanthakumar P, Kumar P, Rao M (2013) Anthropometric analysis of palpebral fissure dimensions and its position in south Indian ethnic adults. Oman Med J 28(1):26–32
Price KM, Gupta PK, Woodward JA, Stinnett SS, Murchison AP (2009) Eyebrow and eyelid dimensions: an anthropometric analysis of African Americans and Caucasians. Plast Reconstr Surg 124(2):615–623
Adler FH (1975) Physiology of the eye, 2nd edn. Mosby, St. Louis, p 13
Maseedupalli S, Priyanka PV, Konda S, Kolli LN (2023) Head and facial anthropometry of the Indian population for designing a spectacle frame. Indian J Ophthalmol 71:989–993
Ellenbogen R (1983) Transcoronal eyebrow lift with concomitant upper blepharoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 71:490–499
Whitaker LA, Morales L, Farkas LG (1986) Aesthetic surgery of the supraorbital ridge and forehead structures. Plast Reconstr Surg 78:23–32
Yu P, Nathan P, Meng CS (2019) Periocular anthropometry of normal Chinese and Indian populations in Singapore. JOJ Ophthalmol 7(5):555722
Maseedupalli S, Priyanka PV, Konda S, Kolli LN (2023) Head and facial anthropometry of the Indian population for designing a spectacle frame. Ind J Ophthalmol 71:989–993
Verma P, Sandhu HK, Verma KG, Goyal S, Sudan M, Ladgotraet A (2016) Morphological variations and biometrics of ear: an aid to personal identification. J Clin Diag Res 10(5):138–142
Maitreyee M (2019) Analysis of morphometric and somatoscopic traits of auricle of ear in India: relation with diversified ethnicities. J Exp Clin Anat 18:1–5
Sharma A, Sidhu NK, Sharma MK, Kapoor K, Singh B (2007) Morphometric study of ear lobule in northwest Indian male subjects. Ana Sci Int 82:98–104
Purkait R, Singh P (2007) Anthropometry of the normal human auricle: a study of adult Indian men. Aesthetic Plast Surg 31(4):371–379
Chattopadhyay PK, Bhatia S (2009) Morphological examination of ear: a study of an Indian population. Leg Med 11:S190–S193
Singh P, Purkait R (2009) Observations of external ear—an Indian study. HOMO-J Comp Hum Biol 60(5):461–472
Krishan K, Kanchan T, Thakur S (2019) A study of morphological variations of the human ear for its applications in personal identification. Egyp J Foren Sci 9:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41935-019-0111-0
Bhandari PS, Dhar S, Gulati A (2021) Anthropometric analysis of linear parameters of the Indian nose: a cross-sectional study and comparison with Literature. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 74(12):3421–3430
Parab SR, Khan MM (2019) Do aesthetic average nasal parameters matter for rhinoplasty in India? Ind J Otolaryng Head Neck Surg 71(Suppl 3):S2011–S2018
Husein OF, Sepehr A, Garg R, Sina-Khadiv M, Gattu S, Waltzman J et al (2010) Anthropometric and aesthetic analysis of the Indian American woman’s face. J Plast Recons Aesthet Surg 63(11):1825–1831
Shinde SA, Sable RB, Patil AS (2016) Craniofacial anthropometric measurements of adult Indians in angles class I malocclusion. Int J Orthod Rehabil 7:130–134
Mehta N, Srivastava RK (2017) The Indian nose: an anthropometric analysis. J Plast Recon Aesth Surg 70(10):1472–1482
Negus V (1958) The comparative anatomy & physiology of the nose and paranasal sinuses. E & S Livingstone Ltd, Edinburg
Packiriswamy V, Bashour M, Nayak S (2016) Anthropometric analysis of the South Indian woman’s nose. Facial Plast Surg 32:304–308
Tardy MEJ (1997) Patient evaluation and preparation. In: Tardy MEJ, Mc Grew L (eds) Rhinoplasty: the art and the science. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 36–49
Farkas LG, Ngim RC, Lee ST (1994) Craniofacial norms in 6, 12, 18 year old Chinese subjects. In: Farkas LG (ed) Anthropometry of the head and face. Raven Press, New York, pp 201–218
Simans RL (1975) Adjunctive measures in rhinoplasty. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 8(3):717–742
Khandekar B, Srinivasan S, Mokal N, Thatte MR (2005) Anthropometric analysis of lip-nose complex in Indian population. Indian J Plast Surg 38(2):128–131
Goel A, Patnaik VVG, Puri N (2015) Lip morphometry in 600 North Indian adults: a data base study for sexual dimorphism. Med Sci Law 55(1):16–21
Sharma RL, Pancholi P, Sharma SK, Sastya A (2017) Anthropometric measurement of lips in adults of MP India. Int J App Res 3(2):210–212
Funding
Self-funded.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Uday Kiran Uppada, David P. Tauro and KP Senthilnathan were involved in design of study, data acquisition, data analysis and manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Consent to Participate
Patient consent not required taken.
Ethical Approval
Institutional ethical clearance not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uppada, U.K., Tauro, D.P. & Senthilnathan, K.P. Anthropometric Analysis of Indian Faces: A Systematic Review. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02185-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12663-024-02185-6