Abstract
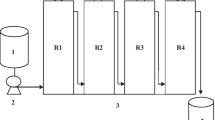
Corn stover is one of the dominant agricultural wastes in China, with high lignocellulose contents. Anaerobic digestion of corn stover converts biomass to biogas as sustainable energy. To improve the performance of anaerobic digestion, as well as for flexible biogas production, the effects of different feeding regimes on biogas production, system stability, and microbial community structure were investigated using laboratory-scale semi-continuously stirred tank reactors (semi-CSTRs) fed pretreated corn stover once a day (R1), every 2 days (R2) and every 3 days (R3) at an equivalent amount. The results showed that R3 and R2 produced 11.1% and 8.4% more methane, respectively. R3 correspondingly had higher lignocellulose conversion rates and system stability, followed by R2 and R1. Greater fluctuations in biogas, VFA concentrations and pH were found in less frequently fed reactors during the time interval between two feeds. Additionally, less feeding increased the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes during hydrolysis and acidogenesis, and the dominant genus of archaea in all reactors was Methanobacterium, which is a hydrogenotrophic methanogen. Therefore, appropriately reducing the feeding frequency can increase the process performance of anaerobic digestion of corn stover.
Graphic Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China: China statistical yearbook 2019. China Statistics Press, Beijing (2020)
Li, Y., Liu, C., Wachemo, A.C., Yuan, H., Zou, D., Liu, Y., Li, X.: Serial completely stirred tank reactors for improving biogas production and substance degradation during anaerobic digestion of corn stover. Bioresour. Technol. 235, 380–388 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.058
Wang, X., Song, X., Yuan, H., Li, X., Zuo, X.: Two-step pretreatment of hydrothermal with ammonia for cow bedding: pretreatment characteristics, anaerobic digestion performance and kinetic analysis. Waste Biomass Valorization (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01395-0
Weithmann, N., Mlinar, S., Sonnleitner, E., Sonnleitner, E., Weig, A.R., Freitag, R.: Flexible feeding in anaerobic digestion-impact on process stability, performance and microbial community structures. Anaerobe (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anaerobe.2020.102297
Yu, Q., Sun, C., Liu, R., Yellezuome, D., Zhu, X., Bai, R., Liu, M., Sun, M.: Anaerobic co-digestion of corn stover and chicken manure using continuous stirred tank reactor: the effect of biochar addition and urea pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 319, 124197 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124197
Guan, R., Yuan, H., Wachemo, A.C., Li, X., Zuo, X., Zou, D., Liu, Y., Gu, J.: Effect of narrow feeding regimes on anaerobic digestion performance and microbial community structure of rice straw in continuously stirred tank reactors. Energy Fuels 32(11), 11587–11594 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b02533
Szarka, N., Scholwin, F., Trommler, M., Jacobi, H., Eichhorn, M., Ortwein, A., Thran, D.: A novel role for bioenergy: a flexible, demand-oriented power supply. Energy 61, 18–26 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.12.053
Hahn, H., Krautkremer, B., Hartmann, K., Wachendorf, M.: Review of concepts for a demand-driven biogas supply for flexible power generation. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 29, 383–393 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2013.08.085
Mulat, D.G., Jacobi, H.F., Feilberg, A., Adamsen, A.P.S., Richnow, H.H., Nikolausz, M.: Changing feeding regimes to demonstrate flexible biogas production: effects on process performance, microbial community structure, and methanogenesis pathways. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 82(2), 438–449 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02320-15
Maurus, K., Ahmed, S., Kazda, M.: Beneficial effects of intermittent feedstock management on biogas and methane production. Bioresour. Technol. 304, 123004 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123004
Lu, F., Jiang, Q., Qian, F., Zhou, Q., Jiang, C., Shen, P.: Semi-continuous feeding combined with traditional domestication improved anaerobic performance during treatment of cassava stillage. Bioresour. Technol. 291, 121807 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121807
Svensson, K., Paruch, L., Gaby, J.C., Linjordet, R.: Feeding frequency influences process performance and microbial community composition in anaerobic digesters treating steam exploded food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 269, 276–284 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.08.096
Ziganshin, A.M., Schmidt, T., Lv, Z.P., Liebetrau, J., Richnow, H.H., Kleinsteuber, S., Nikolausz, M.: Reduction of the hydraulic retention time at constant high organic loading rate to reach the microbial limits of anaerobic digestion in various reactor systems. Bioresour. Technol. 217, 62–71 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.096
Heyer, R., Klang, J., Hellwig, P., Schallert, K., Kress, P., Huelsemann, B., Theuerl, S., Reichl, U., Benndorf, D.: Impact of feeding and stirring regimes on the internal stratification of microbial communities in the fermenter of anaerobic digestion plants. Bioresour. Technol. 314, 123679 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123679
Piao, Z.H., Lee, J., Kim, J.Y.: Effect of substrate feeding frequencies on the methane production and microbial communities of laboratory-scale anaerobic digestion reactors. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 20(1), 147–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0556-2
Ziels, R.M., Beck, D.A.C., Stensel, H.D.: Long-chain fatty acid feeding frequency in anaerobic codigestion impacts syntrophic community structure and biokinetics. Water Res. 117, 218–229 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.03.060
Li, Y., Liu, C., Wachemo, A.C., Li, X.: Effects of liquid fraction of digestate recirculation on system performance and microbial community structure during serial anaerobic digestion of completely stirred tank reactors for corn stover. Energy 160, 309–317 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.06.082
Rice, E.W., Barid, R.B., Eaton, A.D.: Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 23rd ed. American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation (2017)
Mauky, E., Jacobi, H.F., Liebetrau, J., Nelles, M.: Flexible biogas production for demand-driven energy supply-feeding strategies and types of substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 178, 262–269 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.08.123
Vital-Jacome, M.A., Buitron, G.: Thermophilic anaerobic digestion of winery effluents in a two-stage process and the effect of the feeding frequency on methane production. Chemosphere 272, 129865 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129865
Zhong, W., Zhang, Z., Luo, Y., Sun, S., Qiao, W., Xiao, M.: Effect of biological pretreatments in enhancing corn straw biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 102(24), 11177–11182 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.09.077
Herrmann, C., Idler, C., Heiermann, M.: Biogas crops grown in energy crop rotations: Linking chemical composition and methane production characteristics. Bioresour. Technol. 206, 23–35 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.058
Sambusiti, C., Monlau, F., Ficara, E., Musatti, A., Rollini, M., Barakat, A., Malpei, F.: Comparison of various post-treatments for recovering methane from agricultural digestate. Fuel Process. Technol. 137, 359–365 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2015.04.028
Ruile, S., Schmitz, S., Moench-Tegeder, M., Oechsner, H.: Degradation efficiency of agricultural biogas plants: a full-scale study. Bioresour. Technol. 178, 341–349 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.053
Ye, J., Li, D., Sun, Y., Wang, G., Yuan, Z., Zhen, F., Wang, Y.: Improved biogas production from rice straw by co-digestion with kitchen waste and pig manure. Waste Manage. 33(12), 2653–2658 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.05.014
Wei, Y., Li, X., Yu, L., Zou, D., Yuan, H.: Mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of cattle manure and corn stover with biological and chemical pretreatment. Bioresour. Technol. 198, 431–436 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2013.05.014
Wang, X., Duan, X., Chen, J., Fang, K., Feng, L., Yan, Y., Zhou, Q.: Enhancing anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge by pretreatment: effect of volatile to total solids. Environ. Technol. 37(12), 1520–1529 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2015.1120783
Rawoof, S.A.A., Kumar, P.S., Vo, D.V.N., Subramanian, S.: Sequential production of hydrogen and methane by anaerobic digestion of organic wastes: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01122-6
Kafle, G.K., Kim, S.H.: Sludge exchange process on two serial CSTRs anaerobic digestions: process failure and recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 102(13), 6815–6822 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.013
Hu, Y., Shen, F., Yuan, H., Zou, D., Pang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhu, B., Chufo, W.A., Jaffar, M., Li, X.: Influence of recirculation of liquid fraction of the digestate (LFD) on maize stover anaerobic digestion. Biosyst. Eng. 127, 189–196 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2014.09.006
Bonk, F., Popp, D., Weinrich, S., Strauber, H., Kleinsteuber, S., Harms, H., Centler, F.: Intermittent fasting for microbes: how discontinuous feeding increases functional stability in anaerobic digestion. Biotechnol. Biofuels 11, 274 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1279-5
Sun, L., Liu, T., Muller, B., Schnurer, A.: The microbial community structure in industrial biogas plants influences the degradation rate of straw and cellulose in batch tests. Biotechnol. Biofuels 9, 128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-016-0543-9
Goux, X., Calusinska, M., Lemaigre, S., Marynowska, M., Klocke, M., Udelhoven, T., Benizri, E., Delfosse, P.: Microbial community dynamics in replicate anaerobic digesters exposed sequentially to increasing organic loading rate, acidosis, and process recovery. Biotechnol. Biofuels 8, 122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0309-9
Lim, J.W., Chen, C.L., Ho, I.J.R., Wang, J.Y.: Study of microbial community and biodegradation efficiency for single- and two-phase anaerobic co-digestion of brown water and food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 147, 193–201 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.038
Riviere, D., Desvignes, V., Pelletier, E., Chaussonnerie, S., Guermazi, S., Weissenbach, J., Li, T., Camacho, P., Sghir, A.: Towards the definition of a core of microorganisms involved in anaerobic digestion of sludge. ISME J. 3(6), 700–714 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.2
Flint, H.J., Bayer, E.A., Rincon, M.T., Lamed, R., White, B.A.: Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6(2), 121–131 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro1817
Zhao, X., Liu, J., Liu, J., Yang, F., Zhu, W., Yuan, X., Hu, Y., Cui, Z., Wang, X.: Effect of ensiling and silage additives on biogas production and microbial community dynamics during anaerobic digestion of switchgrass. Bioresour. Technol. 241, 349–359 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.183
Tian, G., Zhang, W., Dong, M., Yang, B., Zhu, R., Yin, F., Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Xiao, W., Wang, Q., Cui, X.: Metabolic pathway analysis based on high-throughput sequencing in a batch biogas production process. Energy 139, 571–579 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.08.003
Shi, X., Ng, K.K., Li, X.R., Ng, H.Y.: Investigation of intertidal wetland sediment as a novel inoculation source for anaerobic saline wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49(10), 6231–6239 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00546
Yuan, Y., Wen, H., Huang, X., Li, Z., Liu, X., Li, D., Yan, Z.: Biogas production using cornstalks and prokaryotic community composition (in Chinese). CIESC Journal 65(5), 1784–1791 (2014)
Xu, Z., Yuan, H., Li, X.: Anaerobic bioconversion efficiency of rice straw in continuously stirred tank reactor systems applying longer hydraulic retention time and higher load: One-stage vs. Two-stage. Bioresour. Technol. 321, 124206 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124206
Lee, B., Park, J.G., Shin, W.B., Tian, D.J., Jun, H.B.: Microbial communities change in an anaerobic digestion after application of microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresour. Technol. 234, 273–280 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.022
Li, J., Rui, J., Pei, Z., Sun, X., Zhang, S., Yan, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, X., Zheng, T., Li, X.: Straw- and slurry-associated prokaryotic communities differ during co-fermentation of straw and swine manure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98(10), 4771–4780 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5629-3
Gagliano, M.C., Ismail, S.B., Stams, A.J.M., Plugge, C.M., Temmink, H., Van Lier, J.B.: Biofilm formation and granule properties in anaerobic digestion at high salinity. Water Res. 121, 61–71 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.05.016
Garcia, J.L., Patel, B.K.C., Ollivier, B.: Taxonomic phylogenetic and ecological diversity of methanogenic Archaea. Anaerobe 6(4), 205–226 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1006/anae.2000.0345
Conklin, A., Stensel, H.D., Ferguson, J.: Growth kinetics and competition between Methanosarcina and Methanosaeta in mesophilic anaerobic digestion. Water Environ. Res. 78(5), 486–496 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2175/106143006X95393
Funding
This study was supported by the Intergovernmental International Cooperation on Science and Technology Key Innovation Project from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People Republic of China (grant number 2018YFE0111000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL: Conceptualization; Methodology; Investigation; Writing—original draft. JM: Writing—review& editing. HY: Writing—review& editing; XL: Conceptualization; Methodology; Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Ma, J., Yuan, H. et al. Effects of Feeding Regimes on Process Performance and Microbial Community Structure in Anaerobic Semi-continuously Stirred Tank Reactors Treating Corn Stover. Waste Biomass Valor 13, 1003–1014 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01573-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-021-01573-0