Abstract
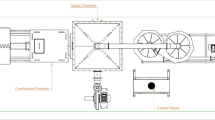
Combustion and emission characteristics of Egyptian sugarcane bagasse and cotton stalks powders were investigated in a bubbling fluidized bed combustor (BFBC) using silica sand as an inert bed material. Mixing and fluidizing characteristics of the two biomass materials and bed material of a certain size distribution were studied. It was found that, the feed rate ranged from 70 to 113 g/min and feed rate of 51 g/min for cotton stalks and sugarcane bagasse, respectively may be suitable for better combustion characteristics in the BFBC. The effect of different operating parameters on the axial temperature and gas concentration profiles (O2, CO2, CO, H2S, SO2 and NOx) was investigated. It was found that the formation of NOX during combustion doesn’t represent a problem as the nitrogen content of fuel is low, the bed temperature of fluidized bed is below 900 °C, and the particle size of the biomass is small. It was found that combustion efficiency ranged from 90 to 100% and from 93 to 98.8% for sugarcane bagasse and cotton stalks, respectively. Thermal efficiency was found to be in the range of (33.7–41%) and (32.5–48.7%) for sugarcane bagasse and cotton stalks, respectively. A verification model for mass and heat balance of combustion experiments was constructed to confirm that the measured values of different parameters were measured accurately with acceptable percent of error.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({d_p}\) :
-
Particle diameter (m)
- Ф:
-
Sphericity
- \({\rho _b}\) :
-
Bulk density (kg/m3)
- \({{\text{Q}}_{{\text{air~}}}}\) :
-
Theoretical amount of air required for combustion of one kilogram of fuel \(\left( {{\text{m}}_{{{\text{air}}}}^{3}/{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{f}}}} \right)\)
- \({{\text{m}}_{{\text{air}}}}~\) :
-
Amount of air required for complete combustion of one kilogram of fuel \(\left( {{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{{\text{air}}}}/{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{\text{f}}}} \right)\)
- \({\dot {Q}_C}\) :
-
Theoretical volume flow rate of air (m3/min)
- \(\dot {Q}\) :
-
Volume flow rate of total air at any velocity (m3/min)
- FR:
-
Biomass material feeding rate (g/min)
- \({{\text{U}}_{{\text{mf}}}}\) :
-
Minimum fluidization velocity (m/s)
- \({{\text{U}}_{{\text{mf}},{\text{m}}}}\) :
-
Minimum fluidization velocity of the binary mixture (m/s)
- U:
-
Fluidizing velocity (m/s)
- \({\text{A}}{{\text{U}}_{{\text{mf}}}}\) :
-
Amount of gas passing through the emulsion phase is equal to that required for minimum fluidization (m3/min)
- \({{\text{A}}_{\text{b}}}\left( {{\text{U}} - {{\text{U}}_{{\text{mf}}}}} \right)\) :
-
The remaining gas passes through the bubble phase (m3/min)
- \({{\text{A}}_{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Cross sectional area of the bed (m2)
- \({{\text{d}}_{\text{b}}}\) :
-
The equivalent volume diameter of a bubble (m)
- \({{\text{H}}_{\text{b}}}\) :
-
Height of the bed (m)
- Z:
-
Height of the bubble above the distributor (m)
- \({{\text{A}}_{\text{o}}}\) :
-
The nozzle area of the distributor (m2)
- \({{\text{d}}_{{\text{b}},{\text{max}}}}\) :
-
Maximum stable bubble size (m)
- D:
-
Diameter of the bed (m)
- \({X_{bio}}\) :
-
Biomass fraction
- \({T_a}\) :
-
Air temperature (°C)
- \({T_{exh}}\) :
-
Exhaust gas temperature (°C)
- \({\upeta _{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Combustion efficiency
- \({\upeta _{{\text{th}}}}\) :
-
Thermal efficiency
- \(m_{f}^{ \cdot }\) :
-
Fuel mass flow rate (kg/s)
- \(m_{a}^{ \cdot }\) :
-
Air mass flow rate (kg/s)
- \(m_{g}^{ \cdot }\) :
-
Flue gas flow rate (kg/s)
- \(C_{a}\) :
-
Heat capacity of air (kJ/kg K)
- \({C_g}\) :
-
Heat capacity of flue gas (kJ/kg K)
- HV:
-
Heating value of fuel (kJ/kg)
- \({T_g}\) :
-
Flue gas temperature (K)
- \({T_a}\) :
-
Ambient temperature (K)
- \({f_{ash}}\) :
-
Ash content in 1 kg fuel \(\left( {{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{ash}}/{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_f}} \right)\)
- \({X_{{N_2}}}\) :
-
Nitrogen mole fraction
- \({X_{C{O_2}}}\) :
-
Carbon dioxide mole fraction
- \({X_{CO}}\) :
-
Carbon monoxide mole fraction
- \({X_{{O_2}}}\) :
-
Oxygen mole fraction
- \({m_{{N_2}}}\) :
-
Mass of nitrogen supplied by the combustion air per unit mass of fuel \(~\left( {{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{{N_2}}}/{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_f}} \right)\)
- \({\left( {{\raise0.7ex\hbox{$A$} \!\mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {A F}}\right.\kern-0pt}\!\lower0.7ex\hbox{$F$}}} \right)_{th,by{\text{~}}mass}}\) :
-
Theoretical air to fuel ratio by mass \(\left( {{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{air}}/{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{fuel}}} \right)\)
- \(\left( {{\raise0.7ex\hbox{$A$} \!\mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {A F}}\right.\kern-\nulldelimiterspace} \!\lower0.7ex\hbox{$F$}}} \right)_{{act,mass}}\) :
-
Actual air to fuel ratio by mass \(\left( {{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{air}}/{\text{k}}{{\text{g}}_{fuel}}} \right)\)
- Q:
-
Heat of combustion (KJ)
- \(h_{f}^{o}\) :
-
Enthalpy of formation (KJ/mol)
- \({h_i}\left( T \right)\) :
-
Sensible enthalpy of any species at any temperature (kJ/mol)
- \({h_i}\left( {{T_o}} \right)\) :
-
Sensible enthalpy of any species at STP (kJ/mol)
- \({n_i}\) :
-
Number of moles (mol)
References
Werther, J., Saenger, M., Hartge, E.U., Ogada, T., Siagi, Z.: Combustion of agricultural residues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 26, 1–27 (2000)
Permchart, W., Kouprianov, V.I.: Emission performance and combustion efficiency of a conical fluidized-bed combustor firing various biomass fuels. Bioresour. Technol. 92, 83–91 (2004)
Duan, F., Chyang, C.S., Lin, C.W., Tso, J.: Experimental study on rice husk combustion in a vortexing fluidized-bed with flue gas recirculation (FGR). Bioresour. Technol. 134, 204–211 (2013)
Fang, M., Yang, L., Chen, G., Shi, Z., Luo, Z., Cen, K.: Experimental study on rice husk combustion in a circulating fluidized bed. Fuel Process. Technol. 85, 1273–1282 (2004)
Abdullah, M.Z., Husain, Z., Pong, S.L.Y.: Analysis of cold test results for various biomass fuels. Biomass Bioenergy 24, 487–494 (2003)
Lin, W., Dam-Johansen, K., Frandsen, F.: Agglomeration in bio-fuel fired fluidized bed combustors. Chem. Eng. J. 96, 171–185 (2003)
Brus, E., Öhman, M., Nordin, A.: Mechanisms of bed agglomeration during fluidized-bed combustion of biomass fuels. Energy Fuels 19, 825–832 (2005)
Chirone, R., Miccio, F., Scala, F.: Mechanism and prediction of bed agglomeration during fluidized bed combustion of a biomass fuel: effect of the reactor scale. Chem. Eng. J. 123, 71–80 (2006)
Chaivatamaset, P., Sricharoon, P., Tia, S.: Bed agglomeration characteristics of palm shell and corncob combustion in fluidized bed. Appl. Therm. Eng. 31, 2916–2927 (2011)
Sun, Z., Jin, B., Zhang, M., Liu, R., Zhang, Y.: Experimental studies on cotton stalk combustion in a fluidized bed. Energy 33, 1224–1232 (2008)
Han, J., Kim, H., Minami, W., Shimizu, T., Wang, G.: The effect of the particle size of alumina sand on the combustion and emission behavior of cedar pellets in a fluidized bed combustor. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 3782–3786 (2008)
Chyang, C.S., Duan, F., Lin, S.M., Tso, J.: A study on fluidized bed combustion characteristics of corncob in three different combustion modes. Bioresour. Technol. 116, 184–189 (2012)
Armesto, L., Bahillo, A., Veijonen, K., Cabanillas, A., Otero, J.: Combustion behaviour of rice husk in a bubbling fluidised bed. Biomass Bioenergy 23, 171–179 (2002)
Yu, C., Tang, Z., Zeng, L., Chen, C., Gong, B.: Experimental determination of agglomeration tendency in fluidized bed combustion of biomass by measuring slip resistance. Fuel 128, 14–20 (2014)
Kuprianov, V.I., Permchart, W., Janvijitsakul, K.: Fluidized bed combustion of pre-dried Thai bagasse. Fuel Process. Technol. 86, 849–860 (2005)
Wang, C., Wang, F., Yang, Q., Liang, R.: Thermogravimetric studies of the behavior of wheat straw with added coal during combustion. Biomass Bioenergy 33, 50–56 (2009)
Varol, M., Atimtay, A.T., Bay, B., Olgun, H.: Investigation of co-combustion characteristics of low quality lignite coals and biomass with thermogravimetric analysis. Thermochim. Acta 510, 195–201 (2010)
Yang, Z., Zhang, S., Liu, L., Li, X., Chen, H., Yang, H., Wang, X.: Combustion behaviours of tobacco stem in a thermogravimetric analyser and a pilot-scale fluidized bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 110, 595–602 (2012)
Kuprianov, V.I., Arromdee, P.: Combustion of peanut and tamarind shells in a conical fluidized-bed combustor: a comparative study. Bioresour. Technol. 140, 199–210 (2013)
Youssef, M.A., Wahid, S.S., Mohamed, M.A., Askalany, A.A.: Experimental study on Egyptian biomass combustion in circulating fluidized bed. Appl. Energy 86, 2644–2650 (2009)
Kaewklum, R., Kuprianov, V.I., Janvijitsakul, K.: Influence of fuel moisture and excess air on formation and reduction of CO and NOx in a fluidized-bed combustor fired with Thai rice husk. Asian J. Energy Environ. 8, 97–115 (2007)
Sun, Z.-A., Jin, B.-S., Zhang, M.-Y., Liu, R.-P., Zhang, Y.: Experimental study on cotton stalk combustion in a circulating fluidized bed. Appl. Energy 85, 1027–1040 (2008)
Arromdee, P., Kuprianov, V.I.: Combustion of peanut shells in a cone-shaped bubbling fluidized-bed combustor using alumina as the bed material. Appl. Energy 97, 470–482 (2012)
EL-Sayed, S.A., Mostafa, M.E.: Analysis of grain size statistic and particle size distribution of biomass powders. Waste Biomass Valor. 5, 1005–1018 (2014)
ASTM D1895: Standard test methods for apparent density, bulk factor, and pourability of plastic materials, https://www.astm.org/Standards/D1895.htm
El-Sayed, S.A., Mostafa, M.E.: Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetic parameters determination of biomass fuel powders by differential thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA/DTG). Energy Convers. Manag. 85, 165–172 (2014)
Yang, W.-C.: Handbook of Fluidization and Fluid-Particles Systems. Marcel Dekker, Inc (2003)
Basu, P.: Combustion and Gasification of Fluidized Beds. Taylor & Francis Group, LLC (2006)
Geldart, D.: Gas Fluidization Technology. Wiley, New York (1987)
Sami, M., Annamalai, K., Wooldridge, M.: Co-firing of coal and biomass fuel blends. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 27, 171–214 (2001)
Madhiyanon, T., Lapirattanakun, A., Sathitruangsak, P., Soponronnarit, S.: A novel cyclonic fluidized-bed combustor (ψ-FBC): combustion and thermal efficiency, temperature distributions, combustion intensity, and emission of pollutants. Combust. Flame 146, 232–245 (2006)
Sirisomboon, K., Kuprianov, V.I., Arromdee, P.: Effects of design features on combustion efficiency and emission performance of a biomass-fuelled fluidized-bed combustor. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 49, 270–277 (2010)
Raji, T.O., Oyewola, O.M., Salau, T.A.O.: New features for performance enhancement of experimental model bubbling fluidized bed combustor. Int J. Sci. Eng. Res. 3, 1–10 (2012)
Keating, E.L.: Applied Combustion, 2nd edn. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis (2007)
Culp, A.W.: Principles of Energy Conversion. McGraw-Hill (1979)
Taylor, J.R.: An Introduction to Error Analysis: The Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements. University Science Books, California (1997)
Coleman, H.W., Steele, W.G.: Experimentation, Validation, and Uncertainty Analysis for Engineers. Wiley (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sayed, S.A., Mostafa, M.E. Combustion and Emission Characteristics of Egyptian Sugarcane Bagasse and Cotton Stalks Powders in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed Combustor. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 2015–2035 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0199-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0199-8