Abstract
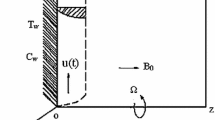
Non-Newtonian flows arise in numerous industrial transport processes including materials fabrication systems. Micropolar theory offers an excellent mechanism for exploring the fluid dynamics of new non-Newtonian materials which possess internal microstructure. Magnetic fields may also be used for controlling electrically-conducting polymeric flows. To explore numerical simulation of transport in rheological materials processing, in the current paper, a finite element computational solution is presented for magnetohydrodynamic, incompressible, dissipative, radiative and chemically-reacting micropolar fluid flow, heat and mass transfer adjacent to an inclined porous plate embedded in a saturated homogenous porous medium. Heat generation/absorption effects are included. Rosseland’s diffusion approximation is used to describe the radiative heat flux in the energy equation. A Darcy model is employed to simulate drag effects in the porous medium. The governing transport equations are rendered into non-dimensional form under the assumption of low Reynolds number and also low magnetic Reynolds number. Using a Galerkin formulation with a weighted residual scheme, finite element solutions are presented to the boundary value problem. The influence of plate inclination, Eringen coupling number, radiation-conduction number, heat absorption/generation parameter, chemical reaction parameter, plate moving velocity parameter, magnetic parameter, thermal Grashof number, species (solutal) Grashof number, permeability parameter, Eckert number on linear velocity, micro-rotation, temperature and concentration profiles. Furthermore, the influence of selected thermo-physical parameters on friction factor, surface heat transfer and mass transfer rate is also tabulated. The finite element solutions are verified with solutions from several limiting cases in the literature. Interesting features in the flow are identified and interpreted.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
A C Eringen J. Appl. Math. Mech. 16 1 (1996)
A C Eringen J. Math. Anal. Appl. 38 480 (1972)
A C Eringen Micro-continuum Field Theories II Fluent Media (New York: Springer) (2001)
G Lukaszewicz Micropolar Fluids, Modelling and Simulation (Boston: Birkhauser Boston) (1999)
T Ariman, M A Turk and N D Sylvester Int. J. Eng. Sci. 11 905 (1973)
T Ariman, M A Turk and N D Sylvester Int. J. Eng. Sci. 12 273 (1974)
G Swapna, L Kumar, O Anwar Bég and Bani Singh Heat Transf. Asian Res. 1 (2014). doi:10.1002/htj.21134
S Jangili and J.V. Murthy Front. Heat Mass Transf. 6(1) 1 (2015)
S Rawat, R Bhargava, R Bhargava and O Anwar Bég Proc. IMechE Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 223 2341 (2009)
O Anwar Bég, J Zueco and T B Chang Chem. Eng. Commun. 198(3) 312 (2010)
O Anwar Bég, J Zueco, M Norouzi, M Davoodi, A A Joneidi and A F Elsayed Comput. Biol. Med. 44 44 (2014)
F M Abo-Eldahab and A F Ghonaim Appl. Math. Comput. 169(1) 500 (2005)
M Ferdows, P Nag, A Postelnicu and K Vajravelu J. Appl.Fluid Mech. 6(2) 285 (2013)
B I Olajuwon and J I Oahimire Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 84 015 (2013)
P K Kundu, K Das and S Jana Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 38 1185 (2015)
M M Rahman and Y Sultana Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 13 71 (2008)
P Cheng Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 20 807 (1977)
P K Singh Int. J. Sci. Eng. Research 3 2229 (2012)
M Sudheer Babu, J Girish Kumar and T Shankar reddy Int. J. Appl. Math. Mech. 9(6) 48 (2013)
P Roja, T Shankar Reddy and N Bhaskar Reddy Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 3 (2013) Issue 6
C H Chen Acta Mech. 172 219 (2004)
Aurangzaib, A R M Kasim, N F Mohammad and S Shafie Heat Transf. Asian Res. 42(2) 89 (2013). doi:10.1002/htj.21034
J Srinivas, J V Ramana Murthy and A J Chamkha Int.J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 26(3) 1027 (2016). doi:10.1108/HFF-09-2015-0354
S K Bhaumik and R Behera, ICCHMT, Procedia Eng. 127 155 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.proeng.201.11.318
M K Nayak and G C Dash Model. Meas. Control B 84(2) 1 (2015)
M E M Khedr, A J Chamkha and M Bayomi Nonlinear Anal. Model. Control 14 27 (2009)
E Magyari and A J Chamkha Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49 1821 (2010)
A J Chamkha and A R A Khaled Heat Mass Transf. 37 117 (2001)
M M Rahman, M J Uddin and A Aziz Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48(3) 2331 (2009)
D Srinivasacharya and M Upender Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 38 184 (2015)
S Siva Reddy and M D Shamshuddin, ICCHMT, Procedia Eng. 127 885 (2015)
S Siva Reddy and M D Shamshuddin Theor. Appl. Mech. 43 117 (2016)
S Rawat, S Kapoor, R Bhargava and O Anwar Bég Int. J. Comput. Appl. 44 40 (2012)
K Das Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 70(1) 96 (2012)
D Pal and B Talukdar Central Eur. J. Phys. 10 1150 (2012)
D Srinivasacharya and M Upender Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q 20(2) 183 (2014)
T G Cowling Magnetohydrodynamics (New York: Wiley inter Science) (1957)
O Anwar Bég New Developments in Hydrodynamics Research Ch1. 1 (eds.) Maximiano J Ibragimov and A Anisimov (New York: Nova Science) (2012)
T Adunson and B Gebhart J. Fluid Mech. 52 57 (1972)
A Rapits and C Perdikis ZAMP 78 277 (1998)
R Cortell Chin. Phys. Lett. 25 1340 (2008)
S R Rao The Finite Element Method in Engineering, 2nd edn. (Exeter USA: BPCC Wheatons Ltd.) (1989)
J N Reddy An Introduction to the Finite Element Method (New York: McGraw-Hill) (1985)
O Anwar Bég, M M Rashidi and R Bhargava Numerical Simulation in Micropolar Fluid Dynamics Lambert: 288 pp, Germany: Sarbrucken (2011)
D Gupta, L Kumar, O Anwar Bég and B Singh Comput. Therm. Sci. 6 (2) 155 (2014)
O Anwar Bég, S Rawat, J Zueco, L Osmond and R S R Gorla Theor. Appl. Mech. 41(1) 1 (2014)
R Bhargava, S Sharma, P Bhargava, O Anwar Bég and A Kadir Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. (2016). DOI: 10.1007/s40819-106-0180-9 (13 pages)
J Zueco, O Anwar Bég and H S Takhar Comput. Mater. Sci. 46(4) 1028 (2009)
A Mohammadein, M A El-Hakiem, S M M El-Kabeir and M A Mansour Int. J. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2 187 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamshuddin, M., Anwar Bég, O., Sunder Ram, M. et al. Finite element computation of multi-physical micropolar transport phenomena from an inclined moving plate in porous media. Indian J Phys 92, 215–230 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-017-1095-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-017-1095-y
Keywords
- Heat source/sink
- Chemical reaction
- Inclined porous plate
- Micropolar fluid
- FEM
- Radiative heat transfer
- Thermal convection
- Viscous heating
- Materials processing