Abstract
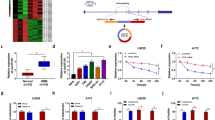
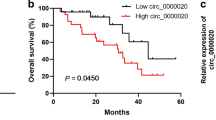
Circular RNA (circRNA) has been shown to be involved in the regulation of human disease progression. Our study aims to reveal the role of circ_0060055 in the progression of glioblastoma (GBM) and its potential molecular mechanism. The expression of circ_0060055, microRNA (miR)-197-3p, and apoptosis inhibitor 5 (API5) was determined by quantitative real-time PCR. GBM cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion were assessed using cell counting kit 8 assay, colony formation assay, EdU assay, flow cytometry, and transwell assay. Besides, the radiosensitivity of cells also was assessed using colony formation assay. The interaction between miR-197-3p and circ_0060055 or API5 was analyzed by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA pull-down assay. Animal experiments were conducted to measure the effect of circ_0060055 on GBM tumor growth and radiosensitivity in vivo. Circ_0060055 was overexpressed in GBM tumor tissues and cells, and its silencing suppressed GBM cell proliferation and invasion, while promoted apoptosis and radiosensitivity. In terms of mechanism, circ_0060055 could interact with miR-197-3p, and miR-197-3p could target API5. API5 expression also could be positively regulated by circ_0060055. Function experiments suggested that miR-197-3p inhibitor abolished the effect of circ_0060055 knockdown on GBM cell growth, invasion, and radiosensitivity. MiR-197-3p repressed GBM cell progression and improved radiosensitivity, and this effect was eliminated by API5 upregulation. In vivo experiments confirmed that circ_0060055 knockdown reduced GBM tumor growth and enhanced the radiosensitivity of tumors. This study revealed that circ_0060055 contributed to GBM progression and radioresistance through miR-197-3p/API5 pathway, providing a potential target for GBM treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
References
Aoki T, Hashimoto N, Matsutani M (2007) Management of glioblastoma. Expert Opin Pharmacother 8(18):3133–3146. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.8.18.3133
Baxter PA, Lin Q, Mao H, Kogiso M, Zhao X, Liu Z, Huang Y, Voicu H, Gurusiddappa S, Su JM, Adesina AM, Perlaky L, Dauser RC, Leung HC, Muraszko KM, Heth JA, Fan X, Lau CC, Man TK, Chintagumpala M, Li XN (2014) Silencing BMI1 eliminates tumor formation of pediatric glioma CD133+ cells not by affecting known targets but by down-regulating a novel set of core genes. Acta Neuropathol Commun. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40478-014-0160-4
Bousquet G, Feugeas JP, Gu Y, Leboeuf C, Bouchtaoui ME, Lu H, Espie M, Janin A, Benedetto MD (2019) High expression of apoptosis protein (Api-5) in chemoresistant triple-negative breast cancers: an innovative target. Oncotarget 10(61):6577–6588. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.27312
Butler M, Prasad S, Srivastava SK (2020) Targeting glioblastoma tumor microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol 1296:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59038-3_1
Cho H, Chung JY, Song KH, Noh KH, Kim BW, Chung EJ, Ylaya K, Kim JH, Kim TW, Hewitt SM, Kim JH (2014) Apoptosis inhibitor-5 overexpression is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with cervical cancer. BMC Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-545
Deng T, Liu Y, Yang Y, Yuan L, Liu F, Wang X, Zhang Q, Xie M (2022) Regulation of microRNA miR-197-3p/CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B (CKS1B) axis by circular RNA hsa_circ_0000285 promotes glioma progression. Bioengineered 13(3):4757–4772. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2031673
Guan YJ, Ma JY, Song W (2019) Identification of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in gastric cancer by analysis of microarray data. Cancer Cell Int. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0905-z
Han B, Chao J, Yao H (2018) Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: from the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther 187:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.010
Hsiao KY, Sun HS, Tsai SJ (2017) Circular RNA - new member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 242(11):1136–1141. https://doi.org/10.1177/1535370217708978
Hu T, Lei D, Zhou J, Zhang BO (2021) circRNA derived from CLSPN (circCLSPN) is an oncogene in human glioblastoma multiforme by regulating cell growth, migration and invasion via ceRNA pathway. J Biosci 46
Huang Q, Guo H, Wang S, Ma Y, Chen H, Li H, Li J, Li X, Yang F, Qiu M, Zhao S, Wang J (2020a) A novel circular RNA, circXPO1, promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by interacting with IGF2BP1. Cell Death Dis 11(12):1031. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03237-8
Huang Q, Ma B, Su Y, Chan K, Qu H, Huang J, Wang D, Qiu J, Liu H, Yang X, Wang Z (2020b) MiR-197-3p represses the proliferation of prostate cancer by regulating the VDAC1/AKT/beta-catenin signaling axis. Int J Biol Sci 16(8):1417–1426. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.42019
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB (2019) The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 20(11):675–691. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7
Li D, Li L, Chen X, Yang W, Cao Y (2021) Circular RNA SERPINE2 promotes development of glioblastoma by regulating the miR-361–3p/miR-324–5p/BCL2 signaling pathway. Mol Ther Oncolytics 22:483–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omto.2021.07.010
Liu Z, Zhou Y, Liang G, Ling Y, Tan W, Tan L, Andrews R, Zhong W, Zhang X, Song E, Gong C (2019) Circular RNA hsa_circ_001783 regulates breast cancer progression via sponging miR-200c-3p. Cell Death Dis 10(2):55. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1287-1
Minniti G, Niyazi M, Alongi F, Navarria P, Belka C (2021) Current status and recent advances in reirradiation of glioblastoma. Radiat Oncol 16(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-021-01767-9
Peng QS, Cheng YN, Zhang WB, Fan H, Mao QH, Xu P (2020) circRNA_0000140 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting miR-31 to inhibit Hippo signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 11(2):112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2273-y
Quinones A, Le A (2018) The multifaceted metabolism of glioblastoma. Adv Exp Med Biol 1063:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77736-8_4
Sang Y, Chen B, Song X, Li Y, Liang Y, Han D, Zhang N, Zhang H, Liu Y, Chen T, Li C, Wang L, Zhao W, Yang Q (2019) circRNA_0025202 regulates tamoxifen sensitivity and tumor progression via regulating the miR-182-5p/FOXO3a axis in breast cancer. Mol Ther 27(9):1638–1652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.05.011
Tian LQ, Liu EQ, Zhu XD, Wang XG, Li J, Xu GM (2016) MicroRNA-197 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting GAB2 in glioblastoma. Mol Med Rep 13(5):4279–4288. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5076
Tykocki T, Eltayeb M (2018) Ten-year survival in glioblastoma. A systematic review. J Clin Neurosci 54:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.05.002
Upraity S, Kazi S, Padul V, Shirsat NV (2014) MiR-224 expression increases radiation sensitivity of glioblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 448(2):225–230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.095
Wang X, Cao Q, Shi Y, Wu X, Mi Y, Liu K, Kan Q, Fan R, Liu Z, Zhang M (2021) Identification of low-dose radiation-induced exosomal circ-METRN and miR-4709-3p/GRB14/PDGFRalpha pathway as a key regulatory mechanism in glioblastoma progression and radioresistance: functional validation and clinical theranostic significance. Int J Biol Sci 17(4):1061–1078. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.57168
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Wang P, Fu X, Lin W (2020) Circular RNAs in renal cell carcinoma: implications for tumorigenesis, diagnosis, and therapy. Mol Cancer 19(1):149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01266-7
Wang Z, Liu H, Liu B, Ma W, Xue X, Chen J, Zhou Q (2010) Gene expression levels of CSNK1A1 and AAC-11, but not NME1, in tumor tissues as prognostic factors in NSCLC patients. Med Sci Monit 16(8):CR357-364
Wirsching HG, Galanis E, Weller M (2016) Glioblastoma. Handb Clin Neurol 134:381–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-802997-8.00023-2
Xie W, Shui C, Fang X, Peng Y, Qin L (2020) MiR-197–3p reduces epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting ABCA7 in ovarian cancer cells. 3 Biotech 10(8):375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02362-7
Zhang G, Sun W, Zhu L, Feng Y, Wu L, Li T (2019) Overexpressed circ_0029426 in glioblastoma forecasts unfavorable prognosis and promotes cell progression by sponging miR-197. J Cell Biochem 120(6):10295–10302. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.28313
Zhang H, Xu W (2021) CircABCC3 knockdown inhibits glioblastoma cell malignancy by regulating miR-770–5p/SOX2 axis through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Brain Res 1764:147465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2021.147465
Zhang T, Li M, Lu H, Peng T (2021) Up-regulation of circEIF6 contributes to pancreatic cancer development through targeting miR-557/SLC7A11/PI3K/AKT signaling. Cancer Manag Res 13:247–258. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S280307
Zhu F, Cheng C, Qin H, Wang H, Yu H (2020) A novel circular RNA circENTPD7 contributes to glioblastoma progression by targeting ROS1. Cancer Cell Int. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01208-9
Funding
This work was supported by Science and Technology project of Henan Science and Technology department: 222102310419 and Henan Medical Science and Technology Research Project: LHGJ20210420.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jinjin Yuan designed and performed the research; Junqi Liu, Zongwen Liu, and Ruitai Fan analyzed the data; Jinjin Yuan wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Written informed consents were obtained from all participants and this study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 2 The representative picture for Fig. 4C (A), 4D (B), 4E (C) and 4F (D).
**P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. (TIF 2241 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3 The representative picture for Fig. 6C (A), 6D (B), 6E (C) and 6F (D).
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. (TIF 2316 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Liu, Z., Liu, J. et al. Circ_0060055 Promotes the Growth, Invasion, and Radioresistance of Glioblastoma by Targeting MiR-197-3p/API5 Axis. Neurotox Res 40, 1292–1303 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00548-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00548-w