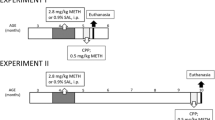
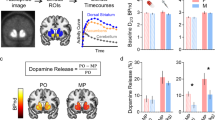
Abstract
Sex differences have been reported in methamphetamine (METH) use disorder in humans and in animal models of METH exposure. Specifically, animals that self-administer METH show sex-related dissimilarities in dopamine (DA) metabolism. To better understand the molecular bases for the differences in DA metabolism, we measured the levels of mRNAs of enzymes that catalyze DA synthesis and breakdown in the prefrontal cortex (PFC), nucleus accumbens (NAc), dorsal striatum (dSTR), and hippocampus (HIP) of rats that had self-administered METH. There were significant sex differences in control rats, with males having higher basal levels of Th in the PFC and dSTR, Ddc in the NAc, and MaoB in the HIP. In contrast, female controls showed higher basal levels of Comt in the HIP. Male and female METH SA rats also showed some distinct responses to the drug. Specifically, female METH rats exhibited increased expression of Ddc and MaoB, whereas male METH animals showed higher levels of Comt mRNA in the PFC compared to their respective controls. In the NAc, male METH rats displayed decreased Th and Ddc mRNA levels. Together, our results identified sex-dependent and region-specific changes in the mRNA expression of several enzymes involved in DA synthesis and breakdown in response to METH SA, with the majority of differences being observed in the mesocorticolimbic dopaminergic system. These findings are of significant translational importance providing further support for the inclusion of sex as an important variable when planning and evaluating therapeutic interventions against METH use disorder in human clinical studies.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amalric M, Koob GF (1993) Functionally selective neurochemical afferents and efferents of the mesocorticolimbic and nigrostriatal dopamine system. Prog Brain Res 99(C):209–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(08)61348-5
Bortolato M, Chen K, Shih JC (2008) Monoamine oxidase inactivation: From pathophysiology to therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(13–14):1527–1533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2008.06.002
Bourque M, Dluzen DE, Di Paolo T (2012) Sex and temporally-dependent effects of methamphetamine toxicity on dopamine markers and signaling pathways. Neuropharmacology 62(7):2363–2372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.02.009
Bourque M, Liu B, Dluzen DE, Di Paolo T (2011) Sex differences in methamphetamine toxicity in mice: effect on brain dopamine signaling pathways. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36(7):955–969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.12.007
Brecht ML, Greenwell L, Mayrhauser CV, Anglin MD (2006) Two-year outcomes of treatment for methamphetamine use. J Psychoactive Drugs 38:415–426. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2006.10400605
Cadet JL, Brannock C (1997) Free radicals and the pathobiology of brain dopamine systems. Neurochem Int 32(2):117–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0197-0186(97)00031-4
Cadet JL, Krasnova IN, Ladenheim B, Cai NS, McCoy MT, Atianjoh FE (2009) Methamphetamine preconditioning: differential protective effects on monoaminergic systems in the rat brain. Neurotox Res 15(3):252–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9026-0
Cadet JL, Sheng P, All S, Rothman R, Carlson E, Epstein C (1994) Rapid communication: attenuation of methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in copper/zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. J Neurochem 62(1):380–383. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.62010380.x
Chen W, Nong Z, Li Y, Huang J, Chen C, Huang L (2017) Role of dopamine signaling in drug addiction. Curr Top Med Chem 17(21):2440–2455. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026617666170504100642
Cordie R, McFadden LM (2019) Optogenetic inhibition of the medial prefrontal cortex reduces methamphetamine-primed reinstatement in male and female rats. Behav Pharmacol 30(6):506–513. https://doi.org/10.1097/FBP.0000000000000485
Cossette M, Lévesque D, Parent A (2005) Neurochemical characterization of dopaminergic neurons in human striatum. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 11(5):277–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2005.02.008
Cox BM, Young AB, See RE, Reichel CM (2013) Sex differences in methamphetamine seeking in rats: impact of oxytocin. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38(10):2343–2353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.05.005
Da-Rosa DD, Valvassori SS, Steckert AV, Arent CO, Ferreira CL, Lopes-Borges J, Varela RB, Mariot E, Dal-Pizzol F, Andersen ML, Quevedo J (2012) Differences between dextroamphetamine and methamphetamine: behavioral changes and oxidative damage in brain of Wistar rats. J Neural Transm 119(1):31–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-011-0691-9
Daiwile AP, Jayanthi S, Cadet JL (2021) Sex- and brain region-specific changes in gene expression in male and female rats as consequences of methamphetamine self-administration and abstinence. Neuroscience 452:265–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.11.025
Daiwile AP, Jayanthi S, Cadet JL (2022a) Sex differences in methamphetamine use disorder perused from pre-clinical and clinical studies: potential therapeutic impacts. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 137:104674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104674
Daiwile AP, Jayanthi S, Ladenheim B, McCoy MT, Brannock C, Schroeder J, Cadet JL (2019) Sex differences in escalated methamphetamine self-administration and altered gene expression associated with incubation of methamphetamine seeking. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 22(11):710–723. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyz050
Daiwile AP, Sullivan P, Jayanthi S, Goldstein DS, Cadet JL (2022b) Sex-specific alterations in dopamine metabolism in the brain after methamphetamine self-administration. Int J Mol Sci 23(x)
Darke S, Duflou J, Kaye S (2017) Prevalence and nature of cardiovascular disease in methamphetamine-related death: a national study. Drug Alcohol Depend 179:174–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.07.001
Darke S, Kaye S, Duflou J, Lappin J (2019) Completed suicide among methamphetamine users: a national study. Suicide and Life-Threatening Behavior 49(1):328–337. https://doi.org/10.1111/sltb.12442
Deng X, Ladenheim B, Jayanthi S, Cadet JL (2007) Methamphetamine administration causes death of dopaminergic neurons in the mouse olfactory bulb. Biol Psychiat 61(11):1235–1243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.09.010
Di Giovanni G, Pessia M, Di Maio R (2012) Redox sensitivity of tyrosine hydroxylase activity and expression in dopaminergic dysfunction. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 11(4):419–429. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152712800792938
Dluzen DE, McDermott JL, Bourque M, Di Paolo T, Darvesh AS, B Buletko A, J Laping N (2011) Markers associated with sex differences in methamphetamine-induced striatal dopamine neurotoxicity. Curr Neuropharmacol 9(1):40–44. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015911795017399
Dluzen DE, McDermott JL, Darvesh AS (2010) Relationships among gender, age, time, and temperature in methamphetamine-induced striatal dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Neuroscience 167(4):985–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.076
Fitzmaurice PS, Tong J, Yazdanpanah M, Liu PP, Kalasinsky KS, Kish SJ (2006) Levels of 4-hydroxynonenal and malondialdehyde are increased in brain of human chronic users of methamphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319(2):703–709. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.106.109173
Foltin RW (2018) Self-administration of methamphetamine aerosol by male and female baboons. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 168:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2018.03.005
Garrick NA, Murphy DL (1980) Species differences in the deamination of dopamine and other substrates for monoamine oxidase in brain. Psychopharmacology 72(1):27–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00433804
Glasner-Edwards S, Marinelli-Casey P, Hillhouse M, Ang A, Mooney LJ, Rawson R (2009) Depression among methamphetamine users: association with outcomes from the methamphetamine treatment project at 3-year follow-up. J Nerv Ment Dis 197(4):225–231. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMD.0b013e31819db6fe
Goldstein DS (2018) Linking Stress, Catecholamine autotoxicity, and allostatic load with neurodegenerative diseases : a focused review in memory of Richard Kvetnansky. Cell Mol Neurobiol 38(1):13–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-017-0497-x
Goldstein DS, Kopin IJ, Sharabi Y (2014) Catecholamine autotoxicity. Implications for pharmacology and therapeutics of Parkinson disease and related disorders ☆. Pharmacol Ther 144(3):268–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.06.006
Haltia LT, Rinne JO, Helin S, Parkkola R, Någren K, Kaasinen V (2008) Effects of intravenous placebo with glucose expectation on human basal ganglia dopaminergic function. Synapse 62(9):682–688. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20541
Haltia LT, Rinne JO, Merisaari H, Maguire RP, Savontaus E, Helin S, Någren K, Kaasinen V (2007) Effects of intravenous glucose on dopaminergic function in the human brain in vivo. Synapse 61(9):748–756. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20418
Han Y, Lin V, Wu F, Hser YI (2016) Gender comparisons among asian american and pacific islander patients in drug dependency treatment. Subst Use Misuse 51(6):752–762. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2016.1155604
Hartwell EE, Moallem NR, Courtney KE, Glasner-Edwards S, Ray LA (2016) Sex differences in the association between internalizing symptoms and craving in methamphetamine users. J Addict Med 10(6):395–401. https://doi.org/10.1097/ADM.0000000000000250
Hazin R, Cadet JL, Kahook MY, Saed D (2009) Ocular manifestations of crystal methamphetamine use. Neurotox Res 15(2):187–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9019-z
Hirata H, Asanuma M, Cadet JL (1998) Melatonin attenuates methamphetamine-induced toxic effects on dopamine and serotonin terminals in mouse brain. Synapse 30(2):150–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1098-2396(199810)30:2%3c150::AID-SYN4%3e3.0.CO;2-B
Jayanthi S, Daiwile AP, Cadet JL (2021) Neurotoxicity of methamphetamine: main effects and mechanisms. Exp Neurol 344:113795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2021.113795
Jayanthi S, Deng X, Bordelon M, Mccoy MT, Cadet JL (2001) Methamphetamine causes differential regulation of pro-death and anti-death Bcl-2 genes in the mouse neocortex. FASEB J 15(10):1745–1752. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.01-0025com
Job MO, Chojnacki MR, Daiwile AP, Cadet JL (2020) Chemogenetic inhibition of dopamine D1-expressing neurons in the dorsal striatum does not alter methamphetamine intake in either male or female long evans rats. Neurosci Lett 729:134987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134987
Jones R, Woods C, Usher K (2018) Rates and features of methamphetamine-related presentations to emergency departments: an integrative literature review. J Clin Nurs 27(13–14):2569–2582. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.14493
Karhunen T, Tilgmann C, Ulmanen I, Julkunen I, Panula P (1994) Distribution of catechol-O-methyltransferase enzyme in rat tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 42(8):1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1177/42.8.8027527
Klein MO, Battagello DS, Cardoso AR, Hauser DN, Bittencourt JC, Correa RG (2019) Dopamine: functions, signaling, and association with neurological diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39(1):31–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-018-0632-3
Krasnova IN, Chiflikyan M, Justinova Z, McCoy MT, Ladenheim B, Jayanthi S, Quintero C, Brannock C, Barnes C, Adair JE, Lehrmann E, Kobeissy FH, Gold MS, Becker KG, Goldberg SR, Cadet JL (2013) CREB phosphorylation regulates striatal transcriptional responses in the self-administration model of methamphetamine addiction in the rat. Neurobiol Dis 58:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2013.05.009
Krasnova IN, Justinova Z, Ladenheim B, Jayanthi S, McCoy MT, Barnes C, Warner JE, Goldberg SR, Cadet JL (2010) Methamphetamine self-administration is associated with persistent biochemical alterations in striatal and cortical dopaminergic terminals in the rat. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008790
Laćan G, Hadamitzky M, Kuczenski R, Melega WP (2013) Alterations in the striatal dopamine system during intravenous methamphetamine exposure: effects of contingent and noncontingent administration. Synapse (new York, N.y.) 67(8):476–488. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.21654
Lisa P, Felicia K, Laura H, Daniela K, Marlies R, Stefanie N, Maik SJ, Anne S, Maximilian S, Kirsi M, Michael S, Gabi K (2019) Associations between methamphetamine use, psychiatric comorbidities and treatment outcome in two inpatient rehabilitation centers. Psychiatry Res 280:112505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112505
Mahoney JJ, Hawkins RY, De La Garza R, Kalechstein AD, Newton TF (2010) Relationship between gender and psychotic symptoms in cocaine-dependent and methamphetamine-dependent participants. Gend Med 7(5):414–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genm.2010.09.003
Mahoney JJ, Kalechstein AD, De La Garza R, Newton TF (2008) Presence and persistence of psychotic symptoms in cocaine- versus methamphetamine-dependent participants. Am J Addict 17(2):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1080/10550490701861201
Mao M, Nair A, Augustine GJ (2019) A novel type of neuron within the Dorsal striatum. Front Neural Circuits 13:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2019.00032
Marchitti SA, Deitrich RA, Vasiliou V (2007) Neurotoxicity and metabolism of the catecholamine-derived 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycolaldehyde: the role of aldehyde dehydrogenase. Pharmacol Rev 59(2):125–150. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.59.2.1
Meiser J, Weindl D, Hiller K (2013) Complexity of dopamine metabolism. Cell Commun Signal 11(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-11-34
Mihan R, Shahrivar Z, Mahmoudi-Gharaei J, Shakiba A, Hosseini M (2018) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults using methamphetamine: does it affect comorbidity, quality of life, and global functioning? Iran J Psychiatry 13(2):112–119
Milesi-Hallé A, Hambuchen MD, McMillan DE, Michael Owens S (2015) The pharmacokinetics of methamphetamine self-administration in male and female rats. Drug Alcohol Depend 150:164–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2015.02.032
Milesi-Hallé A, Hendrickson HP, Laurenzana EM, Gentry WB, Owens SM (2005) Sex- and dose-dependency in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of (+)-methamphetamine and its metabolite (+)-amphetamine in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 209(3):203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2005.04.007
Miller DR, Bu M, Gopinath A, Martinez LR, Khoshbouei H (2021) Methamphetamine dysregulation of the central nervous system and peripheral immunity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 379(3):372–385. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.121.000767
Molinoff PB, Axelrod J (1971) Biochemistry of catecholamines. Annu Rev Biochem 40:465–500. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002341
Munro CA, McCaul ME, Wong DF, Oswald LM, Zhou Y, Brasic J, Kuwabara H, Kumar A, Alexander M, Ye W, Wand GS (2006) Sex differences in striatal dopamine release in healthy adults. Biol Psychiat 59(10):966–974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.01.008
Nagatsu T, Levitt M, Udenfriend S (1964) Tyrosine hydroxylase: the initial step in norepinephrine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 239(9):2910–2917. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)93832-9
Neumann S, Soyka M, Franke A (2018) Bio-psycho-soziale Charakteristika und therapeutische Aspekte bei Methamphetamin-abhängigen Frauen – Gendersensible Ergebnisse einer systematischen Literaturrecherche. Psychother Psychosom Med Psychol 68(07):281–289. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-115003
Nutt DJ, Lingford-Hughes A, Erritzoe D, Stokes PRA (2015) The dopamine theory of addiction: 40 years of highs and lows. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(5):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3939
Oades RD, Halliday GM (1987) Ventral tegmental (A10) system: neurobiology. 1. Anatomy and connectivity. Brain Res Rev 12(2):117–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0173(87)90011-7
Oswald LM, Wand GS, Wong DF, Brown CH, Kuwabara H, Brašić JR (2015) Risky decision-making and ventral striatal dopamine responses to amphetamine: a positron emission tomography [11C]raclopride study in healthy adults. Neuroimage 113:26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.03.022
Polcin DL, Buscemi R, Nayak M, Korcha R, Galloway GP (2012) Sex differences in psychiatric symptoms among methamphetamine-dependent residents in sober living houses. Addict Disord Treat 11(2):53–63. https://doi.org/10.1097/ADT.0b013e3182213ef1
Popescu A, Marian M, Drăgoi A, Costea R-V (2021) Understanding the genetics and neurobiological pathways behind addiction (review). Exp Ther Med 21(5):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.9976
Reichel CM, Chan CH, Ghee SM, See RE (2012) Sex differences in escalation of methamphetamine self-administration: cognitive and motivational consequences in rats. Psychopharmacology 223(4):371–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2727-8
Ruda-Kucerova J, Amchova P, Babinska Z, Dusek L, Micale V, Sulcova A (2015) Sex differences in the reinstatement of methamphetamine seeking after forced abstinence in Sprague-Dawley rats. Front Psych. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2015.00091
Rungnirundorn T, Verachai V, Gelernter J, Malison RT, Kalayasiri R (2017) Sex differences in methamphetamine use and dependence in a Thai treatment center. J Addict Med 11(1):19–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/ADM.0000000000000262
Schoepp DD, Azzaro AJ (1981) Specificity of endogenous substrates for types A and B monoamine oxidase in rat striatum. J Neurochem 36(6):2025–2031. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb10829.x
Schweppe CA, Burzynski C, Jayanthi S, Ladenheim B, Cadet JL, Gardner EL, Xi ZX, van Praag H, Newman AH, Keck TM (2020) Neurochemical and behavioral comparisons of contingent and non-contingent methamphetamine exposure following binge or yoked long-access self-administration paradigms. Psychopharmacology 237(7):1989–2005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05513-z
Shepard JD, Chuang DT, Shaham Y, Morales M (2006) Effect of methamphetamine self-administration on tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine transporter levels in mesolimbic and nigrostriatal dopamine pathways of the rat. Psychopharmacology 185(4):505–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0316-4
Smith CT, Dang LC, Burgess LL, Perkins SF, San Juan MD, Smith DK, Cowan RL, Le NT, Kessler RM, Samanez-Larkin GR, Zald DH (2019) Lack of consistent sex differences in d-amphetamine-induced dopamine release measured with [18F]fallypride PET. Psychopharmacology 236(2):581–590. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5083-5
Solinas M, Belujon P, Fernagut PO, Jaber M, Thiriet N (2019) Dopamine and addiction: what have we learned from 40 years of research. In J Neural Transm (Vol. 126, Issue 4). Springer Vienna. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1957-2
Su H, Zhang J, Ren W, Xie Y, Tao J, Zhang X, He J (2017) Anxiety level and correlates in methamphetamine-dependent patients during acute withdrawal. Medicine (united States). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000006434
Szczepanik JC, de Almeida GRL, Cunha MP, Dafre AL (2020) Repeated methylglyoxal treatment depletes dopamine in the prefrontal cortex, and causes memory impairment and depressive-like behavior in mice. Neurochem Res 45(2):354–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02921-2
Urban NBL, Kegeles LS, Slifstein M, Xu X, Martinez D, Sakr E, Castillo F, Moadel T, O’Malley SS, Krystal JH, Abi-Dargham A (2010) Sex differences in striatal dopamine release in young adults after oral alcohol challenge: a positron emission tomography imaging study with [11C]raclopride. Biol Psychiat 68(8):689–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.06.005
Volkow ND, Wise RA, Baler R (2017) The dopamine motive system: implications for drug and food addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(12):741–752. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.130
Westbrook SR, Dwyer MR, Cortes LR, Gulley JM (2020) Extended access self-administration of methamphetamine is associated with age- and sex-dependent differences in drug taking behavior and recognition memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 390:112659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112659
Wise RA, Jordan CJ (2021) Dopamine, behavior, and addiction. J Biomed Sci 28(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-021-00779-7
Woodcock EA, Zakiniaeiz Y, Morris ED, Cosgrove KP (2020) Sex and the dopaminergic system: insights from addiction studies. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology (1st ed., Vol. 175). Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-64123-6.00011-4
Xi ZX, Kleitz HK, Deng X, Ladenheim B, Peng XQ, Li X, Gardner EL, Stein EA, Cadet JL (2009) A single high dose of methamphetamine increases cocaine self-administration by depletion of striatal dopamine in rats. Neuroscience 161(2):392–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.060
Yimsaard P, Maes MM, Verachai V, Kalayasiri R (2018) Pattern of methamphetamine use and the time lag to methamphetamine dependence. J Addict Med 12(2):92–98. https://doi.org/10.1097/ADM.0000000000000371
Zhao SX, Deluna A, Kelsey K, Wang C, Swaminathan A, Staniec A, Crawford MH (2021) Socioeconomic burden of rising methamphetamine-associated heart failure hospitalizations in California from 2008 to 2018. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.120.007638
Zlebnik NE, Holtz NA, Lepak VC, Saykao AT, Zhang Y, Carroll ME (2021) Age-specific treatment effects of orexin/hypocretin-receptor antagonism on methamphetamine-seeking behavior. Drug Alcohol Depend 224:108719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.108719
Funding
This project was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), NIH and DHHS [grant #-DA000552 (2021)].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, JLC, APD and AEM; Formal analysis, AEM and APD; Investigation, AEM and APD; Methodology, AEM and APD; Project administration, JLC, APD and AEM; Supervision, JLC and APD; Validation, AEM and APD; Visualization, AEM and APD; Writing-original draft, AEM; Writing-review and editing, AEM, APD and JLC. All authors have read and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, A.E., Daiwile, A.P. & Cadet, J.L. Sex-Dependent Alterations in the mRNA Expression of Enzymes Involved in Dopamine Synthesis and Breakdown After Methamphetamine Self-Administration. Neurotox Res 40, 1464–1478 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00545-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-022-00545-z